|
Slingsby Kite 2
The Slingsby Type 26 Kite 2 was a post World War II development of the Slingsby Kite, a single seat medium performance sailplane. It sold in small numbers. Development At the end of World War II Slingsby Sailplanes built a revised and updated version of their earlier and quite successful Type 6 Kite, designated the Type 23 Kite 1A. This did not perform well and only one was built. Instead, Slingsby developed the Type 26 Kite 2, a much more thoroughly redesigned Kite. It had a new wing and a stretched fuselage. The Kite 2 was a fabric covered wooden aircraft. The original Kite (and the Kite 1A) had gull wings of curved planform, but the Kite 2's wings had constant 2.5o dihedral over the whole span and a straight tapered planform. The old Göttingen aerofoil was replaced with a newer NACA pair. There were no flaps, but spoilers were fitted to the upper wing surface. The wing was pylon mounted and, as on the earlier Kite, a single lift strut on each side linked wing and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft/page Content
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slingsby Aviation
Slingsby Aviation was a British aircraft manufacturer based in Kirkbymoorside, North Yorkshire, England. The company was founded to design and build gliders and sailplanes. From the early 1930s to around 1970 it built over 50% of all British club gliders and had success at national and international level competitions. It then produced some powered aircraft, notably the composite built Firefly trainer, before becoming a producer of specialised composite materials and components. The business is now known as Marshall Advanced Composites and produces composite parts for ships, submarines and aircraft. It is a subsidiary of Marshall of Cambridge. History The business was founded in Scarborough by Frederick Nicholas Slingsby, an RAF pilot in World War I. In 1920 he bought a partnership in a woodworking and furniture factory in Queen Street, Scarborough. In 1930 Slingsby was one of the founders of the Scarborough Gliding Club. After repairing some of the club's gliders, Sling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slingsby Kite
The Slingsby T.6/T.23 Kirby Kite was a single-seat sport glider produced from 1935, by Fred Slingsby in Kirbymoorside, Yorkshire. Design and development During the early 1930s there was a dearth of high-performance gliders that could be flown by relatively inexperienced pilots. To remedy this shortcoming Fred Slingsby modified the Grunau Baby design with longer gulled wings and rounded fuselage formers skinned with plywood, resulting in the T.6 Kirby Kite. Later developments included spoilers to improve landing performance and an enlarged rudder which improved the harmony of the controls. Further re-design was carried out at the end of World War II, with a raised wing pylon, landing wheel and spoilers fitted as standard. The T.23 Kite 1A flew in December 1945 but did not enter production due to the limited improvement in performance, but further development was planned, as the Type 23A, with a new 1° dihedral straight wings, the production of which is uncertain. The final itera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sailplane
A glider or sailplane is a type of glider aircraft used in the leisure activity and sport of gliding (also called soaring). This unpowered aircraft can use naturally occurring currents of rising air in the atmosphere to gain altitude. Sailplanes are aerodynamically streamlined and so can fly a significant distance forward for a small decrease in altitude. In North America the term 'sailplane' is also used to describe this type of aircraft. In other parts of the English-speaking world, the word 'glider' is more common. Types Gliders benefit from producing the least drag for any given amount of lift, and this is best achieved with long, thin wings, a slender fuselage and smooth surfaces with an absence of protuberances. Aircraft with these features are able to soar – climb efficiently in rising air produced by thermals or hills. In still air, sailplanes can glide long distances at high speed with a minimum loss of height in between. Sailplanes have rigid wings and either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gull Wings
The gull wing is an aircraft wing configuration, known also as ''Pulaski wings'', with a prominent bend in the wing inner section towards the wing root. Its name is derived from the seabirds which it resembles. Numerous aircraft have incorporated such wings for a diverse range of purposes. The gull wing was commonly used to improve visibility in a high wing arrangement, because such wing could be thinnest by the fuselage, and in theory should limit pilot's view no more than Pillar (car), A-pillars of a windscreen in a car body. Glider (sailplane), Gliders were the first aircraft to feature the gull wing, starting with the Weltensegler in 1921; it was not until the record-breaking RRG Fafnir, Fafnir at the end of that decade did the configuration gain popularity. Beyond becoming popular for the next three decades amongst high-performance gliders, various ground-based aircraft and flying boats also adopted various forms of gull wings. It rose to particular prominence in Poland, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
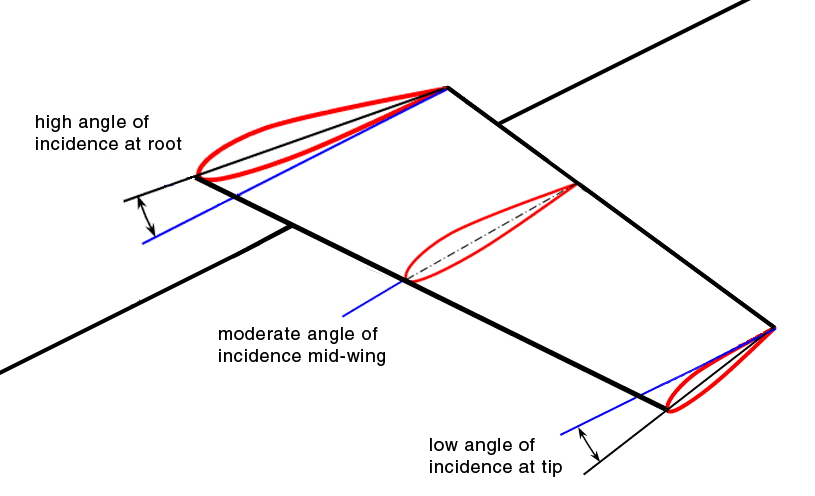
Washout (aviation)
Washout is a characteristic of aircraft wing design which deliberately reduces the lift distribution across the span of an aircraft’s wing. The wing is designed so that the angle of incidence is greater at the wing roots and decreases across the span, becoming lowest at the wing tip. This is usually to ensure that at stall speed the wing root stalls before the wing tips, providing the aircraft with continued aileron control and some resistance to spinning. Washout may also be used to modify the spanwise lift distribution to reduce lift-induced drag. Design considerations Washout is commonly achieved by designing the wing with a slight twist, reducing the angle of incidence from root to tip, and therefore causing a lower angle of attack at the tips than at the roots. This feature is sometimes referred to as structural washout, to distinguish it from aerodynamic washout. Wingtip stall is unlikely to occur symmetrically, especially if the aircraft is maneuvering. As an air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Hearn Ltd
Martin Hearn Ltd. was a British aviation company which during World War II played a major role in the assembly of thousands of American and Canadian aircraft imported to Liverpool by shipping convoys. History Formation Martin Nieto Hearn (1st June 1906–June 1992) was a pilot and engineer. He gained his Royal Aero Club Aviator's Certificate (no. 8488) on 20 December 1928 and started his flying career in Avro 504Ks with Berkshire Aviation Tours. He then worked for Northern Air Transport, flying displays with Alan Cobham on his National Aviation Day tours starting in April 1932. Having once stood in for the resident Wing walking, wing-walker, he developed an expertise in aerial trapeze performance, soon becoming in Cobham's words “that most intrepid of wing-walkers”. Hearn then decided to adopt a less dangerous occupation, and became involved with Utility Airways at RAF Hooton Park, Hooton Aerodrome on the Wirral Peninsula, which had been known as Liverpool’s airport until L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slingsby Skylark 2
The Slingsby T.41 Skylark 2 was a sailplane produced from 1953 by Slingsby Sailplanes at Kirkbymoorside, Yorkshire. Design and development Following the technical success of the T.37 Skylark, the concept was expanded with the introduction of the T.41 Skylark 2. The use of laminar-flow sections was continued but the section at the tips was changed to NACA4415 to reduce the tendency to tip-stall. The Skylark 2 was very similar in shape to its predecessor but had a smooth-skinned rounded fuselage and a wing of greater span and area. Composite materials were introduced in the Skylark 2, with the nose cone, wingtips and various small fairings made from polyester resin glassfibre. The thickness of the aerofoils was increased to ensure that drag was reduced over a wider speed range allowing the Skylark 2 to climb faster in thermals at low speed and race between thermals at high speed. History The prototype was flown in November 1953 and tested by the British Gliding Association's Tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Air Force Gliding And Soaring Association
The Royal Air Force Gliding & Soaring Association is a British organisation which provides recreational flying in gliders to RAF personnel. Purpose The Royal Air Force Gliding & Soaring Association (RAFGSA) is a voluntary organisation which exists to provide recreational flying to all RAF servicemen and women, in particular those normally employed in ground duties. The RAFGSA Centre is at RAF Halton, employing a full-time staff to provide central organisational, training and workshop facilities. The Joint Services Gliding Centre (JSGC), located at the RAFGSA Chilterns Centre, RAF Halton, is part of the Joint Service Adventurous Training (JSAT) Air Sports organisation and provides training courses for military personnel. History In 1945, the British Air Forces of Occupation (BAFO) in Germany began using captured German gliders to provide recreational flying for RAF personnel. This resulted in a demand for similar facilities in the United Kingdom, and the Royal Air Force Gliding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)