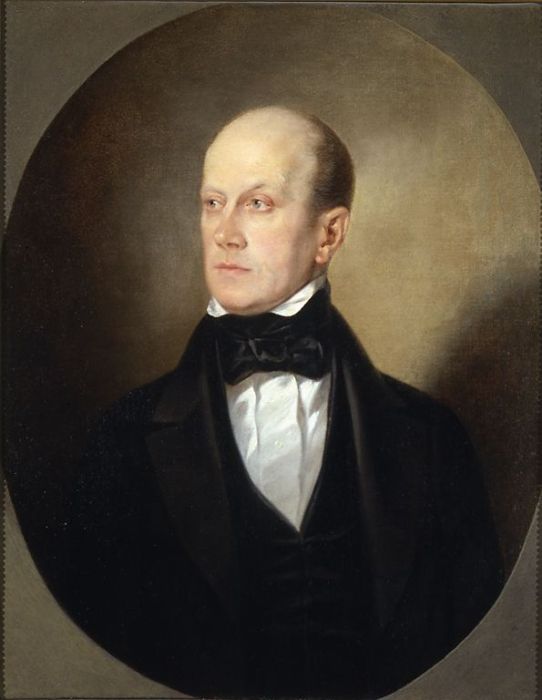|
Slavonic Library In Prague
The Slavonic Library in Prague is a publicly accessible specialised research library for the field of Slavic Studies. It is one of the largest and most important Slavic libraries in Europe. Since its foundation in 1924, it has been systematically complementing, processing and making accessible its collection of world research Slavic (mainly historical, philological and political-science) literature and selected original production of Slavic authors. Its depositories contain more than 850,000 volumes of library documents, a collection of maps, posters, visual and artistic materials, and numerous collections of special documents. The Slavonic Library provides library and information services concerning the political, economic and cultural life of the Slavic nations, their mutual relations and their relations to other nations in the past as well as the present. Documents can be studied in the library's public reading room, provided with free internet access, an extensive reference lib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milan Rešetar
Milan Rešetar (February 1, 1860 – January 14, 1942) was a linguist, historian and literary critic from Dubrovnik. Biography Rešetar was born in Dubrovnik. After the gymnasium in Dubrovnik, he studied classical philology and Slavic languages in Vienna and Graz. He worked as a high-school professor in Koper, Zadar and Split, and later a professor of Slavic studies on the universities of Vienna and Zagreb). He also edited the Croatian edition of "''List drevnih zakona''" magazine. Rešetar was a student of Vatroslav Jagić. He was a notable member of the Serb-Catholic movement in Dubrovnik. After retirement, he moved to Florence where he died 1942. The main areas of his works included dialectology and accentology of South Slavic languages, as well as philologically impeccable editions of 15th to 18th century writers for the Yugoslav Academy of Sciences and Arts. He was one of founders of South Slavic dialectology, investigating features of Štokavian dialects (''Der Štokawisch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halyna Mazepa
Halyna Mazepa also known as Halyna Mazepa de Koval (9 February 1910 – 30 June, 1995) was a Ukrainian and Venezuelan modern artist, illustrator, and ceramist. She was the Daughter of Isaak Mazepa, the Prime Minister of Ukrainian People’s Republic (1919). Early life and education Halyna Mazepa was born on 9 February 1910 in St. Petersburg. Her father was Isaak Mazepa, best known as the Prime Minister of Ukrainian People’s Republic. Her mother was Natalia Singalevych, a bacteriologist and teacher. In 1915, Mazepa’s family settled in Katerynoslav (now Dnipro, Ukraine). They stayed in Katerynoslav until 1920 when they had to immigrate to Lviv. In 1921, Mazepas moved to Kalisz, Poland, escaping from Bolshevism. In 1923, the family moved to Prague. In the 1920s and 1930s Prague was the intellectual capital of the Ukrainian emigrants. In Prague Mazepa studied at the Ukrainian Studio of Plastic Arts, the School of Applied Art (1929-1935), and the Academy of Arts. In the 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasyl Kasiyan
Vasyl Illich Kasiyan ( uk , Василь Ілліч Касіян; 1 January 1896 – 26 June 1976) was a Soviet and Ukrainian painter, graphic, parliamentary, People's Painter of the USSR, academician of the Academy of Arts of the Soviet Union. A native of Eastern Galicia, he was a World War I veteran. While studying in Academy of Fine Arts, Prague in 1920s, Kasiyan was a student of Czech painter Max Švabinský. External links Vasyl Kasiyanin the Ukrainian Soviet Encyclopedia The ''Ukrainian Soviet Encyclopedia'' ( uk, Українська радянська енциклопедія, ''Ukrayinska radyanska entsyklopediya'') was a multi-purpose encyclopedia of Ukraine, issued in the USSR. First attempt Following th ... * Yankovska, O.V. Kasiyan Vasyl Illich (КАСІЯН ВАСИЛЬ ІЛЛІЧ)'. Encyclopedia of History of Ukraine. {{DEFAULTSORT:Kasiyan, Vasyl 1896 births 1976 deaths 20th-century Ukrainian politicians People from Sniatyn People from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukrainian People's Republic
The Ukrainian People's Republic (UPR), or Ukrainian National Republic (UNR), was a country in Eastern Europe that existed between 1917 and 1920. It was declared following the February Revolution in Russia by the First Universal. In March 1917, the National Congress in Kyiv elected the Central Council composed of socialist parties on the same principles as throughout the rest of the Russian Republic. The republic's autonomy was recognized by the Russian Provisional Government. Following the October Revolution, it proclaimed its independence from the Russian Republic on 22 January 1918 by the Fourth Universal. During its short existence, the republic went through several political transformations – from the socialist-leaning republic headed by the Central Council of Ukraine with its general secretariat to the socialist republic led by the Directorate and by Symon Petliura. Between April and December 1918, the socialist authority of the Ukrainian People's Republic was sus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fyodor Dostoevsky
Fyodor Mikhailovich Dostoevsky (, ; rus, Фёдор Михайлович Достоевский, Fyódor Mikháylovich Dostoyévskiy, p=ˈfʲɵdər mʲɪˈxajləvʲɪdʑ dəstɐˈjefskʲɪj, a=ru-Dostoevsky.ogg, links=yes; 11 November 18219 February 1881), sometimes transliterated as Dostoyevsky, was a Russian novelist, short story writer, essayist and journalist. Dostoevsky's literary works explore the human condition in the troubled political, social, and spiritual atmospheres of 19th-century Russia, and engage with a variety of philosophical and religious themes. His most acclaimed novels include ''Crime and Punishment'' (1866), ''The Idiot'' (1869), ''Demons'' (1872), and ''The Brothers Karamazov'' (1880). His 1864 novella, ''Notes from Underground'', is considered to be one of the first works of existentialist literature. Numerous literary critics regard him as one of the greatest novelists in all of world literature, as many of his works are considered highly influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo Tolstoy
Count Lev Nikolayevich TolstoyTolstoy pronounced his first name as , which corresponds to the romanization ''Lyov''. () (; russian: link=no, Лев Николаевич Толстой,In Tolstoy's day, his name was written as in pre-reformed Russian. ; ), usually referred to in English as Leo Tolstoy, was a Russian writer who is regarded as one of the greatest authors of all time. He received nominations for the Nobel Prize in Literature every year from 1902 to 1906 and for the Nobel Peace Prize in 1901, 1902, and 1909; the fact that he never won is a major controversy. Born to an aristocratic Russian family in 1828, Tolstoy's notable works include the novels ''War and Peace'' (1869) and ''Anna Karenina'' (1878), often cited as pinnacles of realist fiction. He first achieved literary acclaim in his twenties with his semi-autobiographical trilogy, ''Childhood'', '' Boyhood'', and ''Youth'' (1852–1856), and '' Sevastopol Sketches'' (1855), based upon his experiences in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyotr Chaadayev
Pyotr or Petr Yakovlevich Chaadayev (russian: Пётр Я́ковлевич Чаада́ев; also spelled Chaadaev, or Čaadajev; 7 June 7 May Old Style">Old_Style.html" ;"title="7 May Old Style">7 May Old Style1794 – 26 April [14 April O.S.] 1856) was a Russian philosopher. He was one of the Russian Schellingians. Chaadayev wrote eight "Philosophical Letters" about Russia in French between 1826 and 1831, which circulated among intellectuals in Russia in manuscript form for many years. They comprise an indictment of Russian culture for its laggard role far behind the leaders of Western civilization. He cast doubt on the greatness of the Russian past, and ridiculed Orthodoxy for failing to provide a sound spiritual basis for the Russian mind. He extolled the achievements of Europe, especially in rational and logical thought, its progressive spirit, its leadership in science, and indeed its leadership on the path to freedom. The Russian government saw his ideas as dangerous and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija; sk, Juhoslávia; ro, Iugoslavia; cs, Jugoslávie; it, Iugoslavia; tr, Yugoslavya; bg, Югославия, Yugoslaviya ) was a country in Southeast Europe and Central Europe for most of the 20th century. It came into existence after World War I in 1918 under the name of the ''Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes'' by the merger of the provisional State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs (which was formed from territories of the former Austria-Hungary) with the Kingdom of Serbia, and constituted the first union of the South Slavic people as a sovereign state, following centuries in which the region had been part of the Ottoman Empire and Austria-Hungary. Peter I of Serbia was its first sovereign. The kingdom gained international recog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |