|
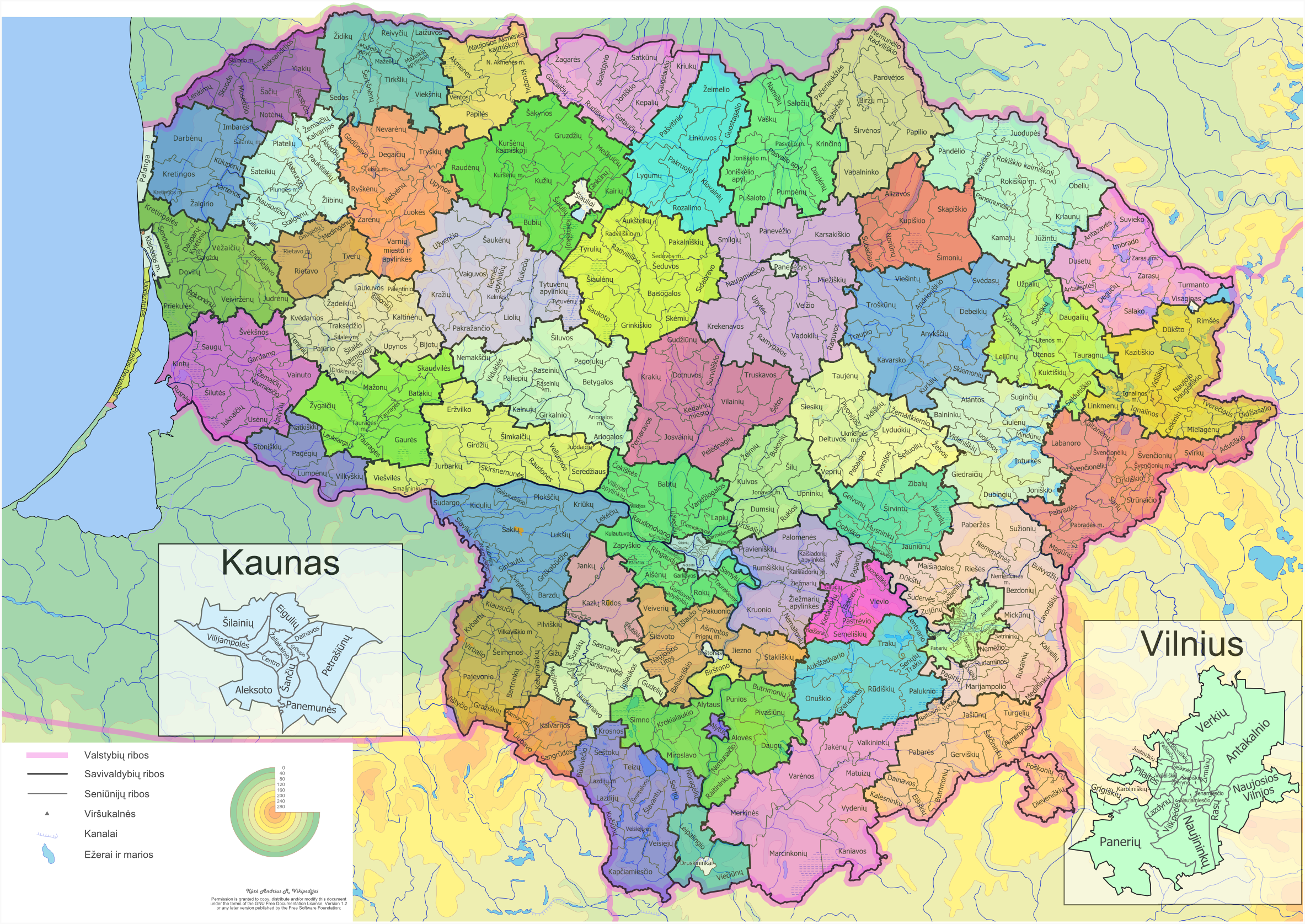
Skuodas District
Skuodas District Municipality is one of 60 municipalities in Lithuania. It is the only territory whose Council is using the Samogitian language Samogitian ( sgs, žemaitiu kalba, link=no or sometimes ', ''žemaitiu šnekta'' or '; lt, žemaičių tarmė, žemaičių kalba) is an Eastern Baltic language spoken mostly in Samogitia (in the western part of Lithuania). In Lithuania, it is .... References Municipalities of Klaipėda County Municipalities of Lithuania {{KlaipėdaCounty-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Municipalities Of Lithuania
__NOTOC__ Lithuania is divided into three layers of administrative divisions. The first-level division consists of 10 counties ( Lithuanian: singular – ''apskritis'', plural – ''apskritys''). These are sub-divided into 60 municipalities (Lithuanian: plural – ''savivaldybės'', singular – ''savivaldybė''), which in turn are further sub-divided into over 500 smaller groups, known as elderships (Lithuanian: plural – ''seniūnijos'', singular – ''seniūnija''). At the end of its tenure as a Soviet Socialist Republic, Lithuania's administrative divisions consisted of 44 regions, 12 cities, 80 towns, 19 settlements, and 426 rural districts. The reform of this system was an immediate concern for the new government. The Constitution of Lithuania, ratified in 1992, delegated the power of establishing future administrative units to the Lithuanian Parliament (Seimas). Accordingly, the Seimas passed two fundamental laws: a 1993 law on government representation and a 1994 law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skuodas
Skuodas (; Samogitian: ''Skouds'') is a city located in Klaipėda County, in northwestern Lithuania, on the border with Latvia. The Bartuva river flows through the town. History Skuodas was first mentioned in written sources in 1253. At that time it belonged to Ceklis land. In 1572 city rights were granted to Skuodas thanks to Jan Hieronimowicz Chodkiewicz who owned the city. The same year after the city rights were granted, a new part of the city started to settle on the right wing of Bartuva river. In the centre of this part there were built a new rectangular square, town hall, commercial buildings. After Chodkiewicz's era Sapieha family got the city as a trousseau and became the owners of Skuodas. Sapieha family owned the city until 1832. In 1776 Skuodas lost city rights and became just a border city with a customs. In 1821 present masonry Evangelical Lutheran Church was built. In 1847 the current Catholic Church was built using masonry of stone and bricks. It reflect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samogitian Language
Samogitian ( sgs, žemaitiu kalba, link=no or sometimes ', ''žemaitiu šnekta'' or '; lt, žemaičių tarmė, žemaičių kalba) is an Eastern Baltic language spoken mostly in Samogitia (in the western part of Lithuania). In Lithuania, it is mostly treated as a dialect of Lithuanian, but it is also considered as a separate language by some linguists inside and outside of Lithuania. Its recognition as a distinct language is increasing in recent years, and attempts have been made to standardize it. The Samogitian language should not be confused with the interdialect of the Lithuanian language as spoken in the Duchy of Samogitia before Lithuanian became a written language, which later developed into one of the two variants of written Lithuanian used in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania based on the so-called middle dialect of the Kėdainiai region. This was called the Samogitian (Žemaitian) language; the term "Lithuanian language" then referred to the other variant, which had bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania shares land borders with Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, Poland to the south, and Russia to the southwest. It has a Maritime boundary, maritime border with Sweden to the west on the Baltic Sea. Lithuania covers an area of , with a population of 2.8 million. Its capital and largest city is Vilnius; other major cities are Kaunas and Klaipėda. Lithuanians belong to the ethno-linguistic group of the Balts and speak Lithuanian language, Lithuanian, one of only a few living Baltic languages. For millennia the southeastern shores of the Baltic Sea were inhabited by various Balts, Baltic tribes. In the 1230s, Lithuanian lands were united by Mindaugas, Monarchy of Lithuania, becoming king and founding the Kingdom of Lithuania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ylakiai
Ylakiai ( pl, Iłoki) is a small town in Skuodas County, in northwestern Lithuania. According to the census of 2011, the town has a population of 950 people. History Ylakiai was first mentioned in 1568 in the inventory list of Grūstė parish made by Jokūbas Laskovskis. At that time Ylakiai village was in the dominion of Skuodas Skuodas (; Samogitian: ''Skouds'') is a city located in Klaipėda County, in northwestern Lithuania, on the border with Latvia. The Bartuva river flows through the town. History Skuodas was first mentioned in written sources in 1253. At t ... estate. In 1894 a church was built there, which stands to this day. In July 1941, 300 Jews were murdered in a mass execution perpetrated by Lithuanian nazis. A monument stone was erected in 1965 but a new monument was erected in 1988 at the location of the massacre. In 2002 President of the Republic of Lithuania approved the new coat of arms of Ylakiai. An urban monument stands in the central part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosėdis
Mosėdis is a small town in Samogitia, northwestern Lithuania in Klaipėda County, mostly known for its Museum of Rare Stones. The museum and impressive outdoor collection were initiated by Vaclovas Intas and have since expanded all over the town. The town also features a baroque The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ... catholic church of 18th century. Famous citizens * Svetlana Pauliukaitė, Olympic cyclist Geography The river of Bartuva runs through this town. The closest large city is Klaipėda, it is 58 km south of Mosėdis. It is approximately 34 km away from Baltic Sea, and roughly 12 km away from Latvia. External links Mosėdis gymnasiumMosėdis Stone Museum webpageMosedis Shtetl Project Towns in Lithuania Towns in Klaipėda County Telshevsky Uyezd [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern European Summer Time
Eastern European Summer Time (EEST) is one of the names of the UTC+03:00 time zone, which is 3 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used as a summer daylight saving time in some European and Middle Eastern countries, which makes it the same as Arabia Standard Time, East Africa Time, and Moscow Time. During the winter periods, Eastern European Time ( UTC+02:00) is used. Since 1996, European Summer Time has been applied from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October. Previously, the rules were not uniform across the European Union. Usage The following countries and territories use Eastern European Summer Time during the summer: * Belarus, Moscow Summer Time in years 1981–89, regular EEST from 1991-2011 * Bulgaria, regular EEST since 1979 * Cyprus, regular EEST since 1979 ( Northern Cyprus stopped using EEST in September 2016, but returned to EEST in March 2018) * Estonia, Moscow Summer Time in years 1981–88, regular EEST since 1989 * Finland, regu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern European Time
Eastern European Time (EET) is one of the names of UTC+02:00 time zone, 2 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. The zone uses daylight saving time, so that it uses UTC+03:00 during the summer. A number of African countries use UTC+02:00 all year long, where it is called Central Africa Time (CAT), although Egypt and Libya also use the term ''Eastern European Time''. The most populous city in the Eastern European Time zone is Cairo, with the most populous EET city in Europe being Athens. Usage The following countries, parts of countries, and territories use Eastern European Time all year round: * Egypt, since 21 April 2015; used EEST ( UTC+02:00; UTC+03:00 with daylight saving time) from 1988–2010 and 16 May–26 September 2014. See also Egypt Standard Time. * Kaliningrad Oblast (Russia), since 26 October 2014; also used EET in years 1945 and 1991–2011. See also Kaliningrad Time. * Libya, since 27 October 2013; switched from Central European Time, which was u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital (political)
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city that physically encompasses the government's offices and meeting places; the status as capital is often designated by its law or constitution. In some jurisdictions, including several countries, different branches of government are in different settlements. In some cases, a distinction is made between the official (constitutional) capital and the seat of government, which is in another place. English-language news media often use the name of the capital city as an alternative name for the government of the country of which it is the capital, as a form of metonymy. For example, "relations between Washington and London" refer to " relations between the United States and the United Kingdom". Terminology and etymology The word ''capital'' derives from the Latin word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations concerni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elderships Of Lithuania
A ''seniūnija'' (in English: eldership, elderate, ward, parish, or subdistrict) is the smallest administrative division of Lithuania. An eldership may comprise a very small region consisting of few villages, one single town, or a part of a big city. Elderships vary in size and population depending on their location and nature. A few elderships make up a municipality. Šilainiai (Kaunas) and Dainava (Kaunas) are the most populous elderates, with population counts over , exceeding the population of some entire municipalities. Elderships manage small-scale local matters, such as repairing pavements and dirt roads, and keep records on all families living in the eldership. The premise of the concept is that - unlike in higher administrative divisions - an elder (the leader of the eldership) could have time to talk to every person in the eldership who wants to. Modern Lithuania is divided into 10 counties, 60 municipalities, and 546 elderships. Elderships function as municip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klaipėda County
Klaipėda County ( lt, Klaipėdos apskritis) is one of ten counties in Lithuania, bordering Tauragė County to the southeast, Telšiai County to the northeast, Kurzeme in Latvia to the north, and Kaliningrad Oblast in Russia to the south. To the west is the Baltic Sea. It lies in the west of the country and is the only county to have a coastline and not landlocked. Its capital is Klaipėda. On 1 July 2010, the county administration was abolished, and since that date, Klaipėda County remains as the territorial and statistical unit. Geography The topography of Klaipėda County is divided into three regions, the highest in the east and lowest in the west: the Western Zemaičiai Plateau in the east, the Western Zemaičiai Plain in the center, and the Pajurys Lowland in the west and on the Baltic coast. Klaipėda County borders Kaliningrad Oblast, Russia, to the south via the Nemunas, which drains into the Curonian Lagoon. The Curonian Spit, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is split ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |