|
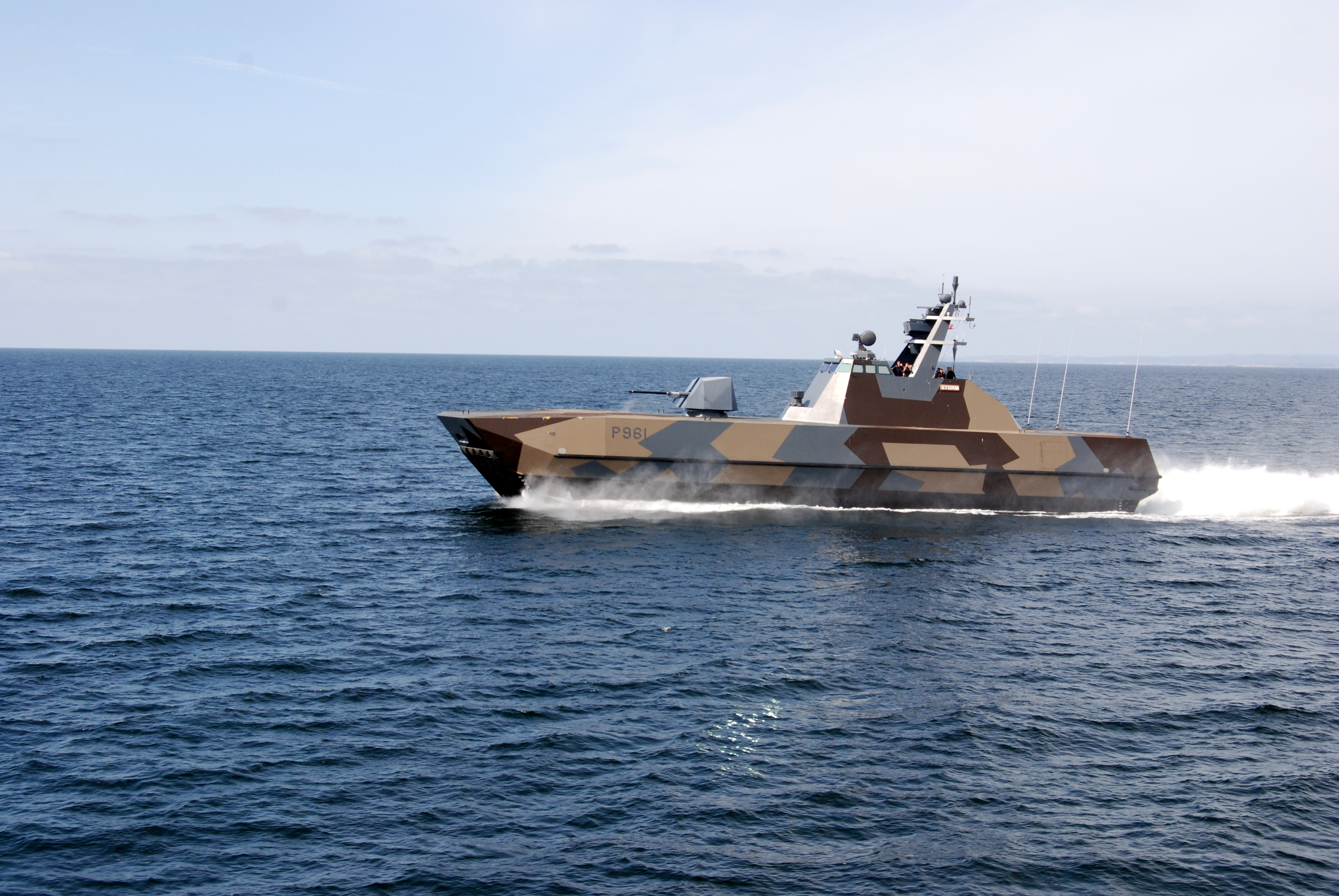
Skjold Class
''Skjold''-class corvettes (skjold means "shield" in Norwegian) are a class of six light, superfast, stealth missile corvettes in service with the Royal Norwegian Navy. The boats were formerly classed as MTBs ( motor torpedo boats) but, from 2009, the Royal Norwegian Navy has described them as corvettes (''korvett'') because their seaworthiness is seen as comparable to corvettes, and because they do not carry torpedoes. They were built at the Umoe Mandal yard. With a maximum speed of , the ''Skjold''-class corvettes were the fastest combat ships afloat at the time of their introduction. Development and production The ''Skjold''-class vessels began with the development of the Royal Norwegian Navy's "Project SMP 6081", and the first preproduction version was ordered on 30 August 1996. The first ship of its class, P960, was launched on 22 September 1998 and commissioned 17 April 1999. A Norwegian Parliamentary White Paper of 2001 recommended building five additional boats, and this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umoe Mandal
Umoe Mandal AS is a shipbuilding company in the Ulltveit-Moe Group. Their shipyards are based at Mandal in Norway. Founded in 1989 as Kværner Båtservice, later Kværner Mandal, and known as Umoe Mandal since 2000, the company specialises in high-speed naval vessels, mine countermeasure vessels (MCMVs) and fast patrol boats (FPBs). They supply the Royal Norwegian Navy, for whom they are currently in production with the Fast Attack Craft series ''Skjold''. The company is especially known for its expertise in the use of fibre reinforced plastic (FRP) technology in naval applications and undertakes the design of naval and commercial vessels in FRP and other advanced composites structures for military applications, as well as shock design, stealth design, and EMI/EMC measures and weight/strength optimisation. The company also produces a range of special products in its market area, such radar stealth air intakes, carbon fibre composite centrifugal fans and, through its subsidiary U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface-to-air Missile
A surface-to-air missile (SAM), also known as a ground-to-air missile (GTAM) or surface-to-air guided weapon (SAGW), is a missile designed to be launched from the ground to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-aircraft system; in modern armed forces, missiles have replaced most other forms of dedicated anti-aircraft weapons, with anti-aircraft guns pushed into specialized roles. The first attempt at SAM development took place during World War II, but no operational systems were introduced. Further development in the 1940s and 1950s led to operational systems being introduced by most major forces during the second half of the 1950s. Smaller systems, suitable for close-range work, evolved through the 1960s and 1970s, to modern systems that are man-portable. Shipborne systems followed the evolution of land-based models, starting with long-range weapons and steadily evolving toward smaller designs to provide a layered defence. This evolution of design increasin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coaming
Coaming is any vertical surface on a ship designed to deflect or prevent entry of water. It usually consists of a raised section of deck plating around an opening, such as a cargo hatch. Coamings also provide a frame onto which to fit a hatch cover. The protective metal sheeting or plating protecting against water entry into ventilation shafts in large ships is called a coaming as it suits this purpose. The term was borrowed by the aviation industry to refer to a low rim around the opening for an unenclosed cockpit. The origin of the term is unknown. ''Coaming'' also refers to the raised structure around the cockpit of a kayak A kayak is a small, narrow watercraft which is typically propelled by means of a double-bladed paddle. The word kayak originates from the Greenlandic word ''qajaq'' (). The traditional kayak has a covered deck and one or more cockpits, each se .... References External links Code of Federal Regulations, Title 46 Watercraft components {{na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
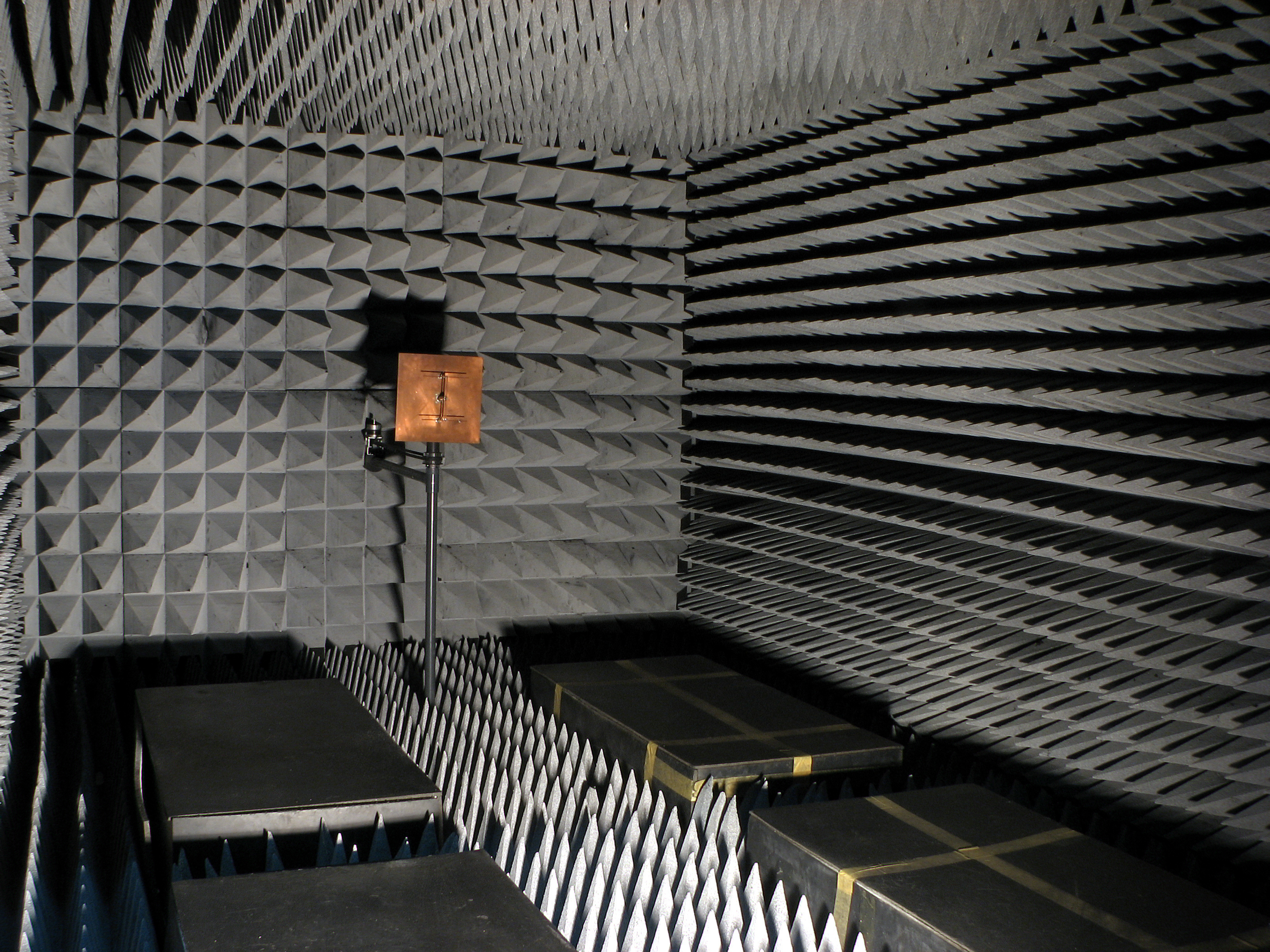
Radar Absorbent Material
In materials science, radiation-absorbent material, usually known as RAM, is a material which has been specially designed and shaped to absorb incident RF radiation (also known as non-ionising radiation), as effectively as possible, from as many incident directions as possible. The more effective the RAM, the lower the resulting level of reflected RF radiation. Many measurements in electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and antenna radiation patterns require that spurious signals arising from the test setup, including reflections, are negligible to avoid the risk of causing measurement errors and ambiguities. Introduction One of the most effective types of RAM comprises arrays of pyramid shaped pieces, each of which is constructed from a suitably lossy material. To work effectively, all internal surfaces of the anechoic chamber must be entirely covered with RAM. Sections of RAM may be temporarily removed to install equipment but they must be replaced before performing any tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
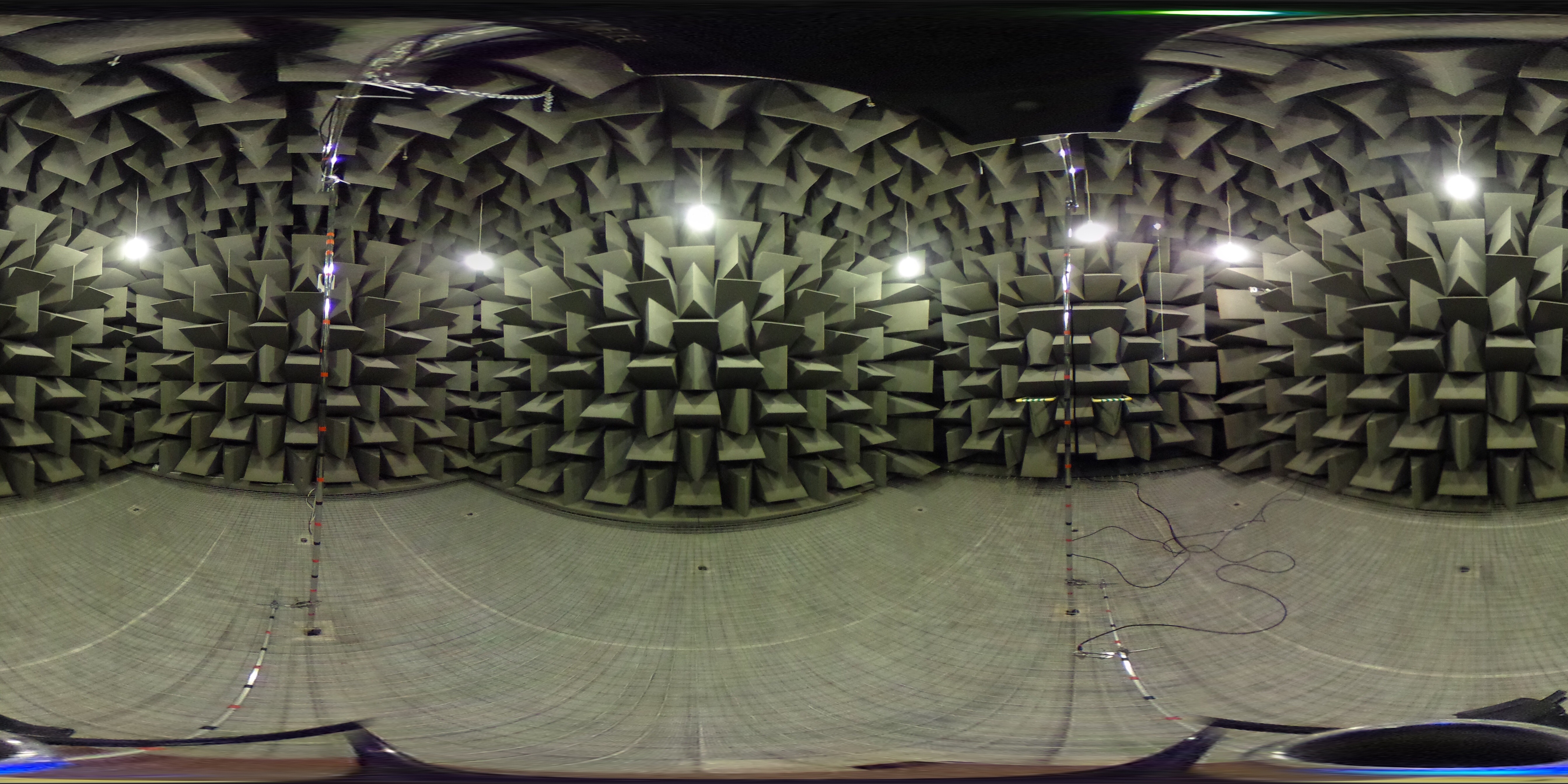
Anechoic Chamber
An anechoic chamber (''an-echoic'' meaning "non-reflective") is a room designed to stop reflections of either sound or electromagnetic waves. They are also often isolated from energy entering from their surroundings. This combination means that a person or detector exclusively hears direct sounds (no reflected sounds), in effect simulating being outside in a free field. Anechoic chambers, a term coined by American acoustics expert Leo Beranek, were initially exclusively used to refer to acoustic anechoic chambers. Recently, the term has been extended to other RF and Sonar anechoic chambers, which eliminate reflection and external noise caused by electromagnetic waves. Anechoic chambers range from small compartments the size of household microwave ovens to ones as large as aircraft hangars. The size of the chamber depends on the size of the objects and frequency ranges being tested. Acoustic anechoic chambers The requirement for what was subsequently called an anechoic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
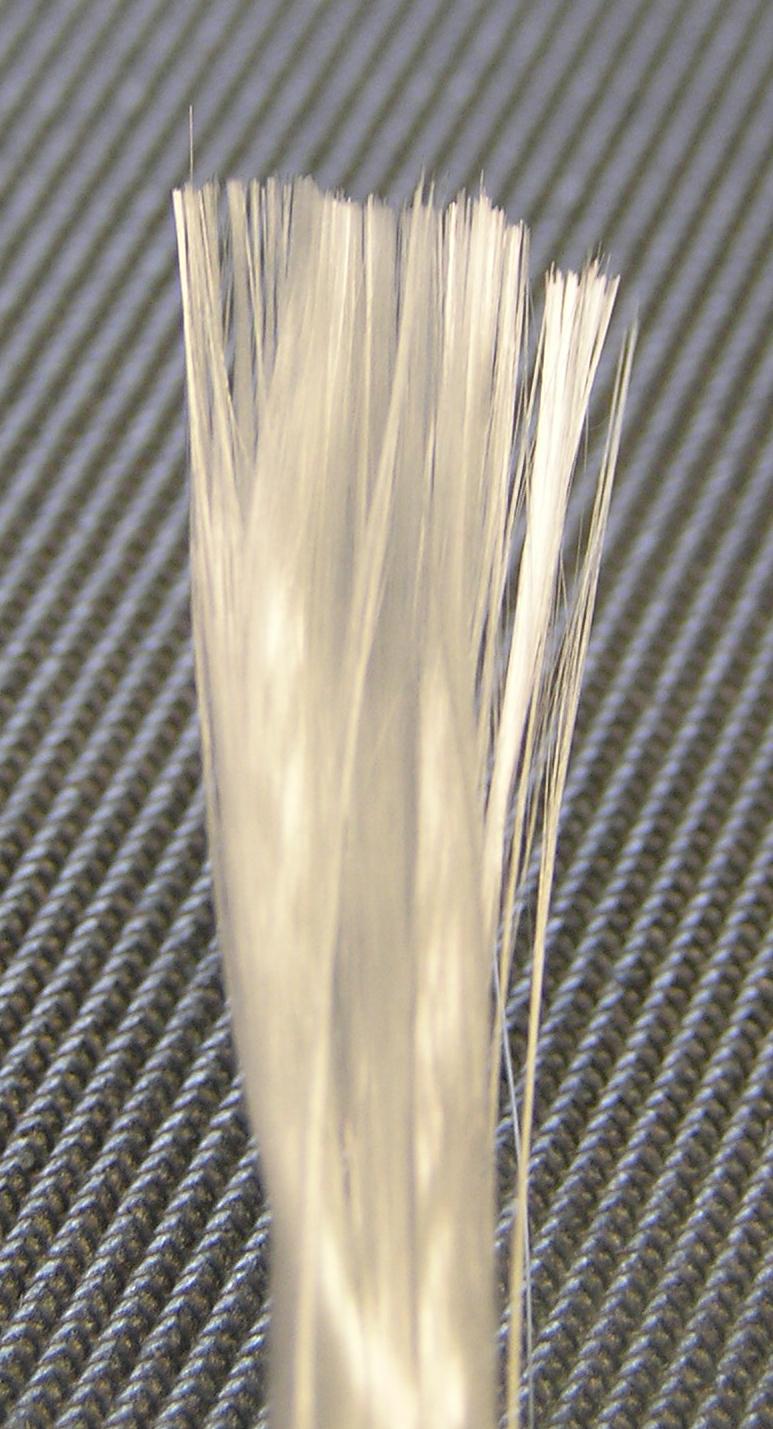
Glass Fibre
Glass fiber ( or glass fibre) is a material consisting of numerous extremely fine fibers of glass. Glassmakers throughout history have experimented with glass fibers, but mass manufacture of glass fiber was only made possible with the invention of finer machine tooling. In 1893, Edward Drummond Libbey exhibited a dress at the World's Columbian Exposition incorporating glass fibers with the diameter and texture of silk fibers. Glass fibers can also occur naturally, as Pele's hair. Glass wool, which is one product called "fiberglass" today, was invented some time between 1932 to 1933 by Games Slayter of Owens-Illinois, as a material to be used as thermal building insulation. It is marketed under the trade name Fiberglas, which has become a genericized trademark. Glass fiber when used as a thermal insulating material is specially manufactured with a bonding agent to trap many small air cells, resulting in the characteristically air-filled low-density "glass wool" family of prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Effect Ship
A Surface Effect Ship (SES) or Sidewall Hovercraft is a watercraft that has both an air cushion, like a hovercraft, and twin hulls, like a catamaran. When the air cushion is in use, a small portion of the twin hulls remains in the water. When the air cushion is turned off ("off-cushion" or "hull borne"), the full weight of the vessel is supported by the buoyancy of the twin hulls. The SES has two advantages over a hovercraft for open sea operation: it is more resistant to slipping sideways when acted on by air or sea, and it can use water jets for propulsion since the inlet nozzles are always covered by water. History United States Navy The United States Navy initiated the SES model test program in 1960. By 1963, a 10-ton test craft called the XR-1 was designed and built to test the surface effect concept. The first version of the XR-1 used fixed plywood seals at the fore and aft ends of the captured air bubble section. A jet engine providing 1700 pounds of thrust was used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seakeeping
Seakeeping ability or seaworthiness is a measure of how well-suited a watercraft is to conditions when underway. A ship or boat which has good seakeeping ability is said to be very seaworthy and is able to operate effectively even in high sea states. Measure In 1976, St. Denis suggested four principal terms needed to describe a seakeeping performance. These are: *Mission: what the ship is intended to accomplish. The role of the ship while at sea. *Environment: the conditions under which the ship is operating. This can be described as sea state, wind speed, geographic region or some combination thereof. *Ship responses: the response of the ship to the environmental conditions. The responses are a function of the environment and the vessel characteristics. *Seakeeping performance criteria: the established limits for the ship's responses. These are based on the ship motions and the accelerations experienced, and include comfort criteria such as noise, vibration and sea sickness, perfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Norwegian Navy
The Royal Norwegian Navy ( no, Sjøforsvaret, , Sea defence) is the branch of the Norwegian Armed Forces responsible for naval operations of Norway. , the Royal Norwegian Navy consists of approximately 3,700 personnel (9,450 in mobilized state, 32,000 when fully mobilized) and 70 vessels, including 4 heavy frigates, 6 submarines, 14 patrol boats, 4 minesweepers, 4 minehunters, 1 mine detection vessel, 4 support vessels and 2 training vessels. It also includes the Coast Guard. This navy has a history dating back to 955. From 1509 to 1814, it formed part of the navy of Denmark-Norway, also referred to as the "Common Fleet". Since 1814, the Royal Norwegian Navy has again existed as a separate navy. In Norwegian, all its naval vessels since 1946 bear ship prefix "KNM", Kongelig Norske Marine (which accurately translates to Royal Norwegian Navy/Naval vessel). In English, they are permitted still to be ascribed prefix "HNoMS", meaning "His/Her Norwegian Majesty's Ship" ("HNMS" could b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Language
Norwegian ( no, norsk, links=no ) is a North Germanic language spoken mainly in Norway, where it is an official language. Along with Swedish and Danish, Norwegian forms a dialect continuum of more or less mutually intelligible local and regional varieties; some Norwegian and Swedish dialects, in particular, are very close. These Scandinavian languages, together with Faroese and Icelandic as well as some extinct languages, constitute the North Germanic languages. Faroese and Icelandic are not mutually intelligible with Norwegian in their spoken form because continental Scandinavian has diverged from them. While the two Germanic languages with the greatest numbers of speakers, English and German, have close similarities with Norwegian, neither is mutually intelligible with it. Norwegian is a descendant of Old Norse, the common language of the Germanic peoples living in Scandinavia during the Viking Age. Today there are two official forms of ''written'' Norwegian, (literally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Link 16
Link 16 is a military tactical data link network used by NATO and nations allowed by the MIDS International Program Office (IPO). Its specification is part of the family of Tactical Data Links. With Link 16, military aircraft as well as ships and ground forces may exchange their tactical picture in near-real time. Link 16 also supports the exchange of text messages, imagery data and provides two channels of digital voice (2.4 kbit/s or 16 kbit/s in any combination). Link 16 is defined as one of the digital services of the JTIDS / MIDS in NATO's '' Standardization Agreement'' STANAG 5516. MIL-STD-6016 is the related United States Department of Defense Link 16 MIL-STD. Technical characteristics Link 16 is a TDMA-based secure, jam-resistant, high-speed digital data link which operates in the radio frequency band 960–1,215 MHz, allocated in line with the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) Radio regulations to the ''aeronautical radionavigation'' servi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_during_Typhoon_Cobra%2C_December_1944.jpg)