|
Skerton Bridge
Skerton Bridge is a road bridge carrying the southbound lanes of the A6 road (England), A6 road over the River Lune in Lancaster, Lancashire, Lancaster, Lancashire, England. The bridge is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade II* Listed building#England and Wales, listed building and Scheduled Monument. History The history of a bridge at Skerton is somewhat amusingly related in Cross Fleury's 1891 publication ''Time-Honoured Lancaster'', which notes that, with the looming arrival of the Jacobitism, Jacobites in the first Rising of 1715, the people attempted to forestall a rapid occupation of the town by damaging the only link to the northern bank of the Lune (the Old Loyne Bridge), knocking the battlements off the sides of the existing bridge to its northern end. The Governors of the town had, in fact, planned to blow up the bridge but, upon being informed that the river was shallow enough to ford easily at numerous points, opted not to cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancaster, Lancashire
Lancaster (, ) is a city and the county town of Lancashire, England, standing on the River Lune. Its population of 52,234 compares with one of 138,375 in the wider City of Lancaster local government district. The House of Lancaster was a branch of the English royal family. The Duchy of Lancaster still holds large estates on behalf of Charles III, who is also Duke of Lancaster. Its long history is marked by Lancaster Castle, Lancaster Priory Church, Lancaster Cathedral and the Ashton Memorial. It is the seat of Lancaster University and has a campus of the University of Cumbria. The Port of Lancaster played a big role in the city's growth, but for many years the outport of Glasson Dock has become the main shipping facility. History The name of the city first appeared in the Domesday Book of 1086, as ''Loncastre'', where "Lon" refers to the River Lune and "castre" (from the Old English ''cæster'' and Latin ''castrum'' for "fort") to the Roman fort that stood on the site. Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashlar
Ashlar () is finely dressed (cut, worked) stone, either an individual stone that has been worked until squared, or a structure built from such stones. Ashlar is the finest stone masonry unit, generally rectangular cuboid, mentioned by Vitruvius as opus isodomum, or less frequently trapezoidal. Precisely cut "on all faces adjacent to those of other stones", ashlar is capable of very thin joints between blocks, and the visible face of the stone may be quarry-faced or feature a variety of treatments: tooled, smoothly polished or rendered with another material for decorative effect. One such decorative treatment consists of small grooves achieved by the application of a metal comb. Generally used only on softer stone ashlar, this decoration is known as "mason's drag". Ashlar is in contrast to rubble masonry, which employs irregularly shaped stones, sometimes minimally worked or selected for similar size, or both. Ashlar is related but distinct from other stone masonry that is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Rennie The Elder
John Rennie FRSE FRS (7 June 1761 – 4 October 1821) was a Scottish civil engineer who designed many bridges, canals, docks and warehouses, and a pioneer in the use of structural cast-iron. Early years He was born the younger son of James Rennie, a farmer near Phantassie, near East Linton, East Lothian, Scotland. John showed a taste for mechanics at a very early age, and was allowed to spend much time in the workshop of Andrew Meikle, a millwright and the inventor of the threshing machine, who lived at Houston Mill on the Phantassie estate. After receiving a normal basic education at the parish school of Prestonkirk Parish Church, he was sent to the burgh school at Dunbar, and in November 1780 he matriculated at the University of Edinburgh, where he remained until 1783. His older brother George remained to assist in the family agricultural business. Rennie worked as a millwright to have established a business. His originality was exhibited by the introduction of cast iron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Rodolphe Perronet
Jean-Rodolphe Perronet (27 October 1708 – 27 February 1794) was a French architect and structural engineer, known for his many stone arch bridges. His best known work is the Pont de la Concorde (1787). Early life Perronet was born in Suresnes, a suburb of Paris, the son of a Swiss Guardsman. At age 17 he entered the architectural practice of Jean Beausire, "first architect" to the city of Paris, as an apprentice. He was put in charge of the design and construction of Paris's grand sewer, embankment works and the maintenance of the banlieue's roads. In 1735, he was named sous-ingénieur (under-engineer) to Alençon and in 1736 entered the Corps des ponts et chaussées. In 1737, he became sous-ingénieur, then engineer to the généralité of Alençon. Career In 1747, Perronet was named director of the Bureau des dessinateurs du Roi (Royal office of designers), which had also just put Daniel-Charles Trudaine in charge of producing maps and plans for the kingdom. This first É ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuilly-sur-Seine
Neuilly-sur-Seine (; literally 'Neuilly on Seine'), also known simply as Neuilly, is a commune in the department of Hauts-de-Seine in France, just west of Paris. Immediately adjacent to the city, the area is composed of mostly select residential neighbourhoods, as well as many corporate headquarters and a handful of foreign embassies. It is the wealthiest and most expensive suburb of Paris. Together with the 16th and 7th arrondissement of Paris, the town of Neuilly-sur-Seine forms the most affluent and prestigious residential area in the whole of France. It has the 2nd highest average household income in France, at €112,504 per year (in 2020). History Originally Pont de Neuilly was a small hamlet under the jurisdiction of Villiers, a larger settlement mentioned in medieval sources as early as 832 and now absorbed by the commune of Levallois-Perret. It was not until 1222 that the little settlement of Neuilly, established on the banks of the Seine, was mentioned for the first t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Smeaton
John Smeaton (8 June 1724 – 28 October 1792) was a British civil engineer responsible for the design of bridges, canals, harbours and lighthouses. He was also a capable mechanical engineer and an eminent physicist. Smeaton was the first self-proclaimed "civil engineer", and is often regarded as the "father of civil engineering".Mark Denny (2007). "Ingenium: Five Machines That Changed the World". p. 34. JHU Press. He pioneered the use of hydraulic lime in concrete, using pebbles and powdered brick as aggregate. Smeaton was associated with the Lunar Society. Law and physics Smeaton was born in Austhorpe, Leeds, England. After studying at Leeds Grammar School he joined his father's law firm, but left to become a mathematical instrument maker (working with Henry Hindley), developing, among other instruments, a pyrometer to study material expansion. In 1750, his premises were in the Great Turnstile in Holborn. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1753 and in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coldstream Bridge
Coldstream Bridge, linking Coldstream, Scottish Borders with Cornhill-on-Tweed, Northumberland, is an 18th-century Category A/Grade II* listed bridge between England and Scotland, across the River Tweed. The bridge carries the A697 road across the Tweed. The bridge is one of three bridges spanning the River Tweed section of the Anglo-Scottish border (the others being the Union Chain Bridge and the Ladykirk and Norham Bridge), and the oldest of the three. History The architect for the bridge was John Smeaton (responsible for the third Eddystone Lighthouse), working for the Tweed Bridges Trust. Construction lasted from July 1763 to 28 October 1766, when it opened to traffic. The cost of the bridge was £6,000, with government grants available for the project and the shortfall covered by a mixture of local subscription and loans from Edinburgh's banks, which were to be paid back by the tolling system. There was controversy when the project's resident engineer, Robert Reid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abutment
An abutment is the substructure at the ends of a bridge span or dam supporting its superstructure. Single-span bridges have abutments at each end which provide vertical and lateral support for the span, as well as acting as retaining walls to resist lateral movement of the earthen fill of the bridge approach. Multi-span bridges require piers to support ends of spans unsupported by abutments. Dam abutments are generally the sides of a valley or gorge, but may be artificial in order to support arch dams such as Kurobe Dam in Japan. The civil engineering term may also refer to the structure supporting one side of an arch, or masonry used to resist the lateral forces of a vault.Pevsner, N. (1970) ''Cornwall''; 2nd ed. Harmondsworth: Penguin; p. 245 The impost or abacus of a column in classical architecture may also serve as an abutment to an arch. The word derives from the verb "abut", meaning to "touch by means of a mutual border". Use in engineering An abutment may be us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
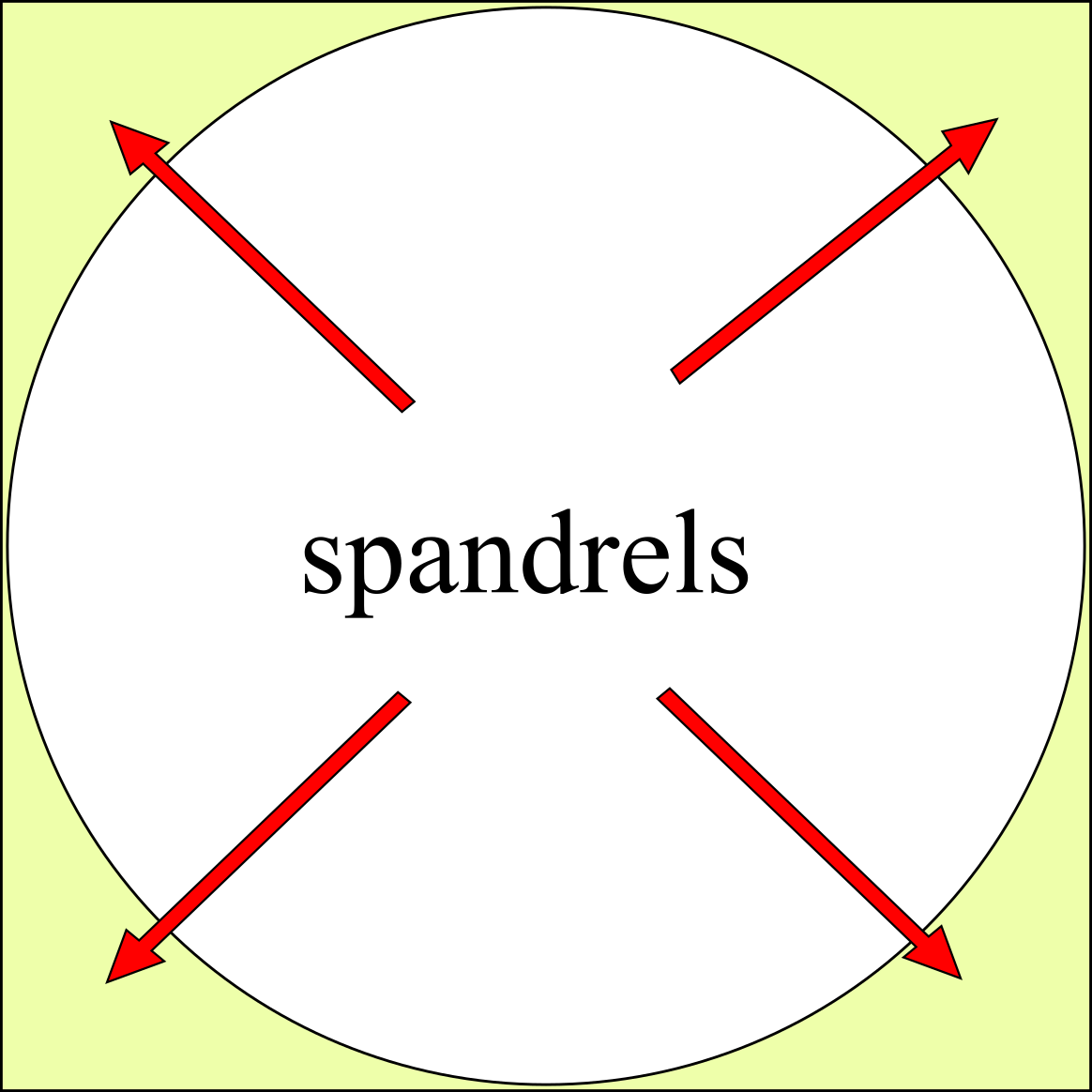
Spandrel
A spandrel is a roughly triangular space, usually found in pairs, between the top of an arch and a rectangular frame; between the tops of two adjacent arches or one of the four spaces between a circle within a square. They are frequently filled with decorative elements. Meaning There are four or five accepted and cognate meanings of the term ''spandrel'' in architectural and art history, mostly relating to the space between a curved figure and a rectangular boundary – such as the space between the curve of an arch and a rectilinear bounding moulding, or the wallspace bounded by adjacent arches in an arcade and the stringcourse or moulding above them, or the space between the central medallion of a carpet and its rectangular corners, or the space between the circular face of a clock and the corners of the square revealed by its hood. Also included is the space under a flight of stairs, if it is not occupied by another flight of stairs. In a building with more than one floor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford Dictionary Of National Biography
The ''Dictionary of National Biography'' (''DNB'') is a standard work of reference on notable figures from British history, published since 1885. The updated ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (''ODNB'') was published on 23 September 2004 in 60 volumes and online, with 50,113 biographical articles covering 54,922 lives. First series Hoping to emulate national biographical collections published elsewhere in Europe, such as the '' Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie'' (1875), in 1882 the publisher George Smith (1824–1901), of Smith, Elder & Co., planned a universal dictionary that would include biographical entries on individuals from world history. He approached Leslie Stephen, then editor of the ''Cornhill Magazine'', owned by Smith, to become the editor. Stephen persuaded Smith that the work should focus only on subjects from the United Kingdom and its present and former colonies. An early working title was the ''Biographia Britannica'', the name of an earlier eightee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parapet
A parapet is a barrier that is an extension of the wall at the edge of a roof, terrace, balcony, walkway or other structure. The word comes ultimately from the Italian ''parapetto'' (''parare'' 'to cover/defend' and ''petto'' 'chest/breast'). Where extending above a roof, a parapet may simply be the portion of an exterior wall that continues above the edge line of the roof surface, or may be a continuation of a vertical feature beneath the roof such as a fire wall or party wall. Parapets were originally used to defend buildings from military attack, but today they are primarily used as guard rails, to conceal rooftop equipment, reduce wind loads on the roof, and to prevent the spread of fires. In the Bible the Hebrews are obligated to build a parapet on the roof of their houses to prevent people falling (Deuteronomy 22:8). Parapet types Parapets may be plain, embattled, perforated or panelled, which are not mutually exclusive terms. *Plain parapets are upward extensions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)
