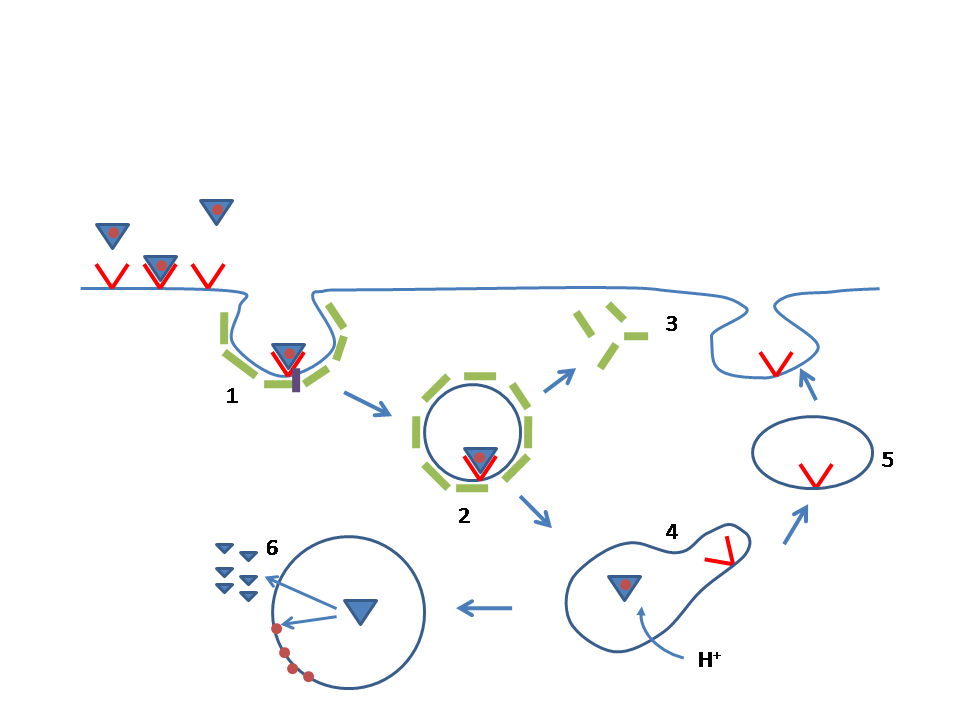
|
Sitosterolemia
Sitosterolemia is a rare autosomal recessively inherited lipid metabolic disorder. It is characterized by hyperabsorption and decreased biliary excretion of dietary sterols (including the plant phytosterol beta-sitosterol). Healthy persons absorb only about 5% of dietary plant sterols, but sitosterolemia patients absorb 15% to 60% of ingested sitosterol without excreting much into the bile. The phytosterol campesterol is more readily absorbed than sitosterol. Sitosterolemia patients develop hypercholesterolemia, tendon and tuberous xanthomas, premature development of atherosclerosis, and abnormal hematologic and liver function test results. Signs and symptoms Sitosterolemia may share several clinical characteristics with the well-characterized familial hypercholesterolemia (FH), such as the development of tendon xanthomas in the first 10 years of life and the development of premature atherosclerosis. However, in contrast to FH patients, sitosterolemia patients usually have nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABCG5 And ABCG8 Genes
ABCG5 and ABCG8 genes encode for two proteins sterolin-1 and -2, respectively. Sterolin-1 and –2 are two ‘half’ adenosine triphosphate binding (adenosine triphosphate, ATP) cassette (ABC) transporters which found to be indispensable for the regulation of sterol absorption and excretion. Mutations in either genes result in a lipid disorder, sitosterolemia. Locus of the genes The molecular mechanisms regulating the absorption of dietary sterols in the body are poorly understood, and as sitosterolemia is a rare autosomal recessively inherited lipid metabolic disorder characterized by hyperabsorption and decreased biliary excretion of dietary sterols, studies have focused on the molecular basis of sitosterolemia to shed light on important principles concerning intestinal sterol absorption as well as cholesterol secretion into bile. In 1998, sitosterolemia (STSL) locus has been mapped to the short arm of human chromosome 2 (2p21) after studying 10 well-characterized families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrotendinous Xanthomatosis
Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis, also called cerebral cholesterosis, is an autosomal recessive form of xanthomatosis. It falls within a group of genetic disorders called the leukodystrophies. Presentation An inherited disorder associated with the deposition of a steroid known as cholestanol in the brain and other tissues and with elevated levels of cholesterol in plasma but with normal total cholesterol level; it is characterized by progressive cerebellar ataxia beginning after puberty and by juvenile cataracts, juvenile or infantile onset chronic diarrhea, childhood neurological deficit, and tendineous or tuberous xanthomas. Genetics CTX is associated with mutations in the CYP27A1 gene, located on chromosome 2q33-qter. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome (chromosome 2 is an autosome), and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campesterol
Campesterol is a phytosterol whose chemical structure is similar to that of cholesterol, and is one of the ingredients for E number E499. Natural occurrences Many vegetables, fruits, nuts, and seeds contain campesterol, but in low concentrations. Banana, pomegranate, pepper, coffee, grapefruit, cucumber, onion, oat, potato, and lemon grass (citronella) are few examples of common sources containing campesterol at roughly 1–7 mg/100 g of the edible portion. In contrast, canola and corn oils contain as much as 16–100 mg/100 g. Levels are variable and are influenced by geography and growing environment. In addition, different strains have different levels of plant sterols. A number of new genetic strains are currently being engineered with the goal of producing varieties high in campesterol and other plant sterols. It is also found in dandelion coffee. It is so named because it was first isolated from the rapeseed (''Brassica campestris''). It is thought to have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetic disorder characterized by high cholesterol levels, specifically very high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL cholesterol), in the blood and early cardiovascular disease. The most common mutations diminish the number of functional LDL receptors in the liver. Since the underlying body biochemistry is slightly different in individuals with FH, their high cholesterol levels are less responsive to the kinds of cholesterol control methods which are usually more effective in people without FH (such as dietary modification and statin tablets). Nevertheless, treatment (including higher statin doses) is usually effective. FH is classified as a type 2 familial dyslipidemia. There are five types of familial dyslipidemia (not including subtypes), and each are classified from both the altered lipid profile and by the genetic abnormality. For example, high LDL (often due to LDL receptor defect) is type 2. Others include defects in chylomicron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosome, allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes is collectively known as atDNA or auDNA. For example, humans have a diploid human genome, genome that usually contains 22 pairs of autosomes and one allosome pair (46 chromosomes total). The autosome pairs are labeled with numbers (1–22 in humans) roughly in order of their sizes in base pairs, while allosomes are labelled with their letters. By contrast, the allosome pair consists of two X chromosomes in females or one X and one Y chromosome in males. Unusual combinations of XYY syndrome, XYY, Klinefelter syndrome, XXY, Triple X syndrome, XXX, XXXX syndrome, XXXX, XXXXX syndrome, XXXXX or XXYY syndrome, XXYY, among Aneuploidy, other Salome combinations, are known to occur and usually cause developmental abnormalities. Autosomes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemolysis
Hemolysis or haemolysis (), also known by several other names, is the rupturing (lysis) of red blood cells (erythrocytes) and the release of their contents (cytoplasm) into surrounding fluid (e.g. blood plasma). Hemolysis may occur in vivo or in vitro. One cause of hemolysis is the action of hemolysins, toxins that are produced by certain pathogenic bacteria or fungi. Another cause is intense physical exercise. Hemolysins damage the red blood cell's cytoplasmic membrane, causing lysis and eventually cell death. Etymology From hemo- + -lysis, from , "blood") + , "loosening"). Inside the body Hemolysis inside the body can be caused by a large number of medical conditions, including some parasites (''e.g.'', ''Plasmodium''), some autoimmune disorders (''e.g.'', autoimmune haemolytic anaemia, drug-induced hemolytic anemia, atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS)), some genetic disorders (''e.g.'', Sickle-cell disease or G6PD deficiency), or blood with too low a solute conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia is abnormally elevated levels of any or all lipids (fats, cholesterol, or triglycerides) or lipoproteins in the blood. citing: and The term ''hyperlipidemia'' refers to the laboratory finding itself and is also used as an umbrella term covering any of various acquired or genetic disorders that result in that finding. Hyperlipidemia represents a subset of dyslipidemia and a superset of hypercholesterolemia. Hyperlipidemia is usually chronic and requires ongoing medication to control blood lipid levels. Lipids (water-insoluble molecules) are transported in a protein capsule. The size of that capsule, or lipoprotein, determines its density. The lipoprotein density and type of apolipoproteins it contains determines the fate of the particle and its influence on metabolism. Hyperlipidemias are divided into primary and secondary subtypes. Primary hyperlipidemia is usually due to genetic causes (such as a mutation in a receptor protein), while secondary hyperlipidemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ezetimibe
Ezetimibe is a medication used to treat high blood cholesterol and certain other lipid abnormalities. Generally it is used together with dietary changes and a statin. Alone, it is less preferred than a statin. It is taken by mouth. It is also available in the fixed combinations ezetimibe/simvastatin, ezetimibe/atorvastatin, ezetimibe/rosuvastatin, and ezetimibe/bempedoic acid. The most commonly reported adverse events include upper respiratory tract infections, joint pain, diarrhea, and tiredness. Serious side effects may include anaphylaxis, liver problems, depression, and muscle breakdown. Use in pregnancy and breastfeeding is of unclear safety. Ezetimibe works by decreasing cholesterol absorption in the intestines. Ezetimibe was approved for medical use in the United States in 2002. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 100th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 7million prescriptions. Medical uses A 2015 review ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colestipol
Colestipol (trade names Colestid, Cholestabyl) is a bile acid sequestrant used to lower blood cholesterol, specifically low-density lipoprotein (LDL).Drugs.comColestipol Hydrochloride/ref> It is also used to reduce stool volume and frequency, and in the treatment of chronic diarrhea. Like cholestyramine, colestipol works in the gut by trapping bile acids and preventing them from being reabsorbed. This leads to decreased enterohepatic recirculation of bile acids, increased synthesis of new bile acids by the liver from cholesterol, decreased liver cholesterol, increased LDL receptor expression, and decreasing LDL in blood. Side effects The following notable side effects may occur: * gastrointestinal tract disturbances, especially (mild, occasionally severe) constipation * sometimes increase in VLDL and triglyceride synthesis Interactions Colestipol can bind to a number of drugs and nutrients in the gut and inhibit or delay their absorption. Such substances include: * thiazide di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholestyramine
Colestyramine ( INN) or cholestyramine ( USAN) (trade names Questran, Questran Light, Cholybar, Olestyr) is a bile acid sequestrant, which binds bile in the gastrointestinal tract to prevent its reabsorption. It is a strong ion exchange resin, which means it can exchange its chloride anions with anionic bile acids in the gastrointestinal tract and bind them strongly in the resin matrix. The functional group of the anion exchange resin is a quaternary ammonium group attached to an inert styrene- divinylbenzene copolymer. Colestyramine removes bile acids from the body by forming insoluble complexes with bile acids in the intestine, which are then excreted in the feces. As a result of this loss of bile acids, more plasma cholesterol is converted to bile acids in the liver to normalise levels.http://livertox.nih.gov/Cholestyramine.htm, United States National Institutes of Health (page visited on 22 June 2016). This conversion of cholesterol into bile acids lowers plasma cholesterol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statins
Statins, also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are a class of lipid-lowering medications that reduce illness and mortality in those who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. They are the most common cholesterol-lowering drugs. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play a key role in the development of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease via the mechanisms described by the lipid hypothesis. Statins are effective in lowering LDL cholesterol and so are widely used for primary prevention in people at high risk of cardiovascular disease, as well as in secondary prevention for those who have developed cardiovascular disease. Side effects of statins include muscle pain, increased risk of diabetes mellitus, and abnormal blood levels of liver enzymes. Additionally, they have rare but severe adverse effects, particularly muscle damage. They inhibit the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase which plays a central role in the production of cholesterol. High cholester ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serum (blood)
Serum () is the fluid and solute component of blood which does not play a role in Coagulation, clotting. It may be defined as blood plasma without the clotting factors, or as blood with all cells and clotting factors removed. Serum includes all proteins not used in Coagulation, blood clotting; all electrolytes, antibodies, antigens, hormones; and any exogenous substances (e.g., drugs or microorganisms). Serum does not contain white blood cells (leukocytes), red blood cells (erythrocytes), platelets, or clotting factors. The study of serum is serology. Serum is used in numerous diagnostic tests as well as blood typing. Measuring the concentration of various molecules can be useful for many applications, such as determining the therapeutic index of a drug candidate in a clinical trial. To obtain serum, a blood sample is allowed to clot (coagulation). The sample is then centrifuged to remove the clot and blood cells, and the resulting liquid wikt:supernatant, supernatant is serum. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |