|
Sitakunda Upazila
Sitakunda ( bn, সীতাকুণ্ড ''Shitakunḍo,'' ) is an upazila in the Chattogram District of Chattogram Division, Bangladesh. It includes one urban settlement, the Sitakunda Town, and 10 unions. Sitakunda is the home of the country's first eco-park, as well as alternative energy projects, specifically wind energy and geothermal power. Sitakunda is one of the oldest sites of human habitation in Bangladesh. During much of its history, it was ruled alternatively by various Buddhist rulers of Myanmar in the east and Muslims rulers of Bengal in the west. For a brief period in the 8th century, it was ruled by the Buddhist Pala Empire of India. The eastern rulers originated from the Kingdom of Arakan, the Mrauk U dynasty, Arakanese pirates and the Pagan Kingdom. The western rulers came from the Sultanate of Bengal and the Mughal province ( Suba) of Bangala. European rule of Sitakunda was heralded by Portuguese privateers in 16th and 17th centuries, who ruled togeth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sitakunda
Sitakunda or Sitakunda Town ( bn, সীতাকুণ্ড শহর) is an administrative centre and the sole municipality (''Paurashava'') of Sitakunda Upazila in Chattogram District, located in Chattogram Division, Bangladesh. Sitakunda is famous for the Chandranath Temple and Hindus temple. There is a hot water spring 5 km to the north of the town. Administration The Sitakunda town has 9 wards divided into 22 mahallas, and a population of 36,650 distributed to 6,914 units of households (average household size 5.3), including 18,662 men and 17,988 women (the male:female ratio is 104:100). The most notable mahallas of the town are Yakubnagar, Nunachara, Mohadebpur, Sobanbagh, Bhuiyan Para, Chowdhury Para (also known as Premtala), Moulvi Para, Amirabad, Edilpur and Shibpur. Shafiul Alam is the mayor of the town, gaining a landslide win over his nearest contender M Abul Kalam Azad in the 2008 mayoral election.News Desk,AL beats BNP in 8 of 9, ''The Independent'' (Dha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upazilas Of Bangladesh
An ''upazila'' ( bn, উপজেলা, upôzela, lit=sub-district pronounced: ), formerly called ''thana'', is an administrative region in Bangladesh, functioning as a sub-unit of a district. It can be seen as an analogous to a county or a borough of Western countries. Rural upazilas are further administratively divided into union council areas (union parishads). Bangladesh ha495 upazilas(as of 20 Oct 2022). The upazilas are the second lowest tier of regional administration in Bangladesh. The administrative structure consists of divisions (8), districts (64), upazilas (495) and union parishads (UPs). This system of devolution was introduced by the former military ruler and president of Bangladesh, Lieutenant General Hossain Mohammad Ershad, in an attempt to strengthen local government. Below UPs, villages (''gram'') and ''para'' exist, but these have no administrative power and elected members. The Local Government Ordinance of 1982 was amended a year later, redesignatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
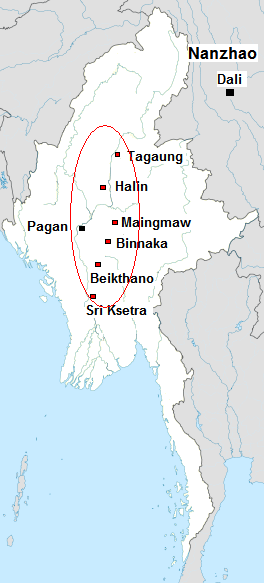
Myanmar
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John C. Wells, John Wells explains, the English spellings of both Myanmar and Burma assume a non-rhotic variety of English, in which the letter r before a consonant or finally serves merely to indicate a long vowel: [ˈmjænmɑː, ˈbɜːmə]. So the pronunciation of the last syllable of Myanmar as [mɑːr] or of Burma as [bɜːrmə] by some speakers in the UK and most speakers in North America is in fact a spelling pronunciation based on a misunderstanding of non-rhotic spelling conventions. The final ''r'' in ''Myanmar'' was not intended for pronunciation and is there to ensure that the final a is pronounced with the broad a, broad ''ah'' () in "father". If the Burmese name my, မြန်မာ, label=none were spelled "Myanma" in English, this would b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhaka-Chittagong Highway
The N1 or Dhaka–Chittagong Highway is a main transportation artery in Bangladesh, between Dhaka and Chittagong. Approximately in length, the road links the country's two largest cities, Dhaka and Chittagong. The highway is known along various stretches as the Chittagong–Cox's Bazar Highway and the Cox's Bazar–Teknaf Highway. Currently four lanes with a eight-lane expansion underway, the N1 is the busiest road in the country and a top development priority. Construction of a larger Dhaka-Chittagong expressway has been proposed to decrease traffic on the highway. Background When constructed, the highway was limited to two lanes of traffic for most of its length. Traffic jams or tailbacks of have been reported. In 2009, it was estimated that daily usage of the highway was 20,000–25,000 motorised vehicles, up 40% of which were trucks. The Roads and Highways Department (RHD) of the Ministry of Communication is expanding the Dhaka–Chittagong stretch to four lanes. The tar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diderul Alam
Didarul Alam ( bn, দিদারুল আলম) is a Bangladesh Awami League politician and the incumbent Member of Parliament from Chittagong-4 Chittagong-4 is a constituency represented in the Jatiya Sangsad (National Parliament) of Bangladesh since 2014 by Didarul Alam of the Awami League. Boundaries The constituency encompasses Sitakunda Upazila and Chittagong City Corporation wards .... Early life Alam was born on 6 April 1968. He has a B.A. degree. Career Alam was elected to Parliament on 5 January 2014 from Chittagong-4 as a Bangladesh Awami League candidate. His supporter and Jubo League leader, Ramzan Ali, was assassinated in August 2018 in Chittagong. Ramzan was accused in a number of criminal cases. References Awami League politicians Living people 1968 births 10th Jatiya Sangsad members 11th Jatiya Sangsad members People from Sandwip Upazila {{AwamiLeague-politician-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * and lasted from 1858 to 1947. * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of the League of Nations, a participating nation in the Summer Olympics in 1900, 1920, 1928, 1932, and 1936, and a founding member of the United Nations in San F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subah (province)
A Subah was the term for a province (State) in the Mughal Empire. The word is derived from Arabic and Persian. The governor/ruler of a ''Subah'' was known as a '' subahdar'' (sometimes also referred to as a "''Subeh''"), which later became '' subedar'' to refer to an officer in the Indian Army and Pakistan Army. The ''subahs'' were established by badshah (emperor) Akbar during his administrative reforms of years 1572–1580; initially they numbered to 12, but his conquests expanded the number of ''subahs'' to 15 by the end of his reign. ''Subahs'' were divided into '' Sarkars'', or districts. ''Sarkars'' were further divided into '' Parganas'' or '' Mahals''. His successors, most notably Aurangzeb, expanded the number of ''subahs'' further through their conquests. As the empire began to dissolve in the early 18th century, many ''subahs'' became effectively independent, or were conquered by the Marathas or the British. In modern context subah ( ur, ) is a word used for provinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the dynasty and the empire itself became indisputably Indian. The interests and futures of all concerned were in India, not in ancestral homelands in the Middle East or Central Asia. Furthermore, the Mughal empire emerged from the Indian historical experience. It was the end product of a millennium of Muslim conquest, colonization, and state-building in the Indian subcontinent." For some two hundred years, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus river basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of present-day Assam and Bangladesh in the east, and the uplands of the Deccan Plateau in South India. Quote: "The realm so defined and governed was a vast territory of some , rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultanate Of Bengal
The Sultanate of Bengal ( Middle Bengali: শাহী বাঙ্গালা ''Shahī Baṅgala'', Classical Persian: ''Saltanat-e-Bangālah'') was an empire based in Bengal for much of the 14th, 15th and 16th centuries. It was the dominant power of the Ganges–Brahmaputra Delta, with a network of mint towns spread across the region. The Bengal Sultanate had a circle of vassal states, including Odisha in the southwest, Arakan in the southeast, and Tripura in the east. Its raids and conquests reached Nepal in the north, Assam in the east, and Jaunpur and Varanasi in the west. The Bengal Sultanate controlled large parts of the north, east and northeast Indian subcontinent during its five dynastic periods, reaching its peak under Hussain Shahi dynasty. It was reputed as a thriving trading nation and one of Asia's strongest states. Its decline began with an interregnum by the Suri Empire, followed by Mughal conquest and disintegration into petty kingdoms. The Bengal Sultan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pagan Kingdom
The Kingdom of Pagan ( my, ပုဂံခေတ်, , ; also known as the Pagan Dynasty and the Pagan Empire; also the Bagan Dynasty or Bagan Empire) was the first Burmese kingdom to unify the regions that would later constitute modern-day Myanmar. Pagan's 250-year rule over the Irrawaddy River, Irrawaddy valley and its periphery laid the foundation for the ascent of Burmese language and Burmese culture, culture, the spread of Bamar people, Bamar ethnicity in Upper Myanmar, and the growth of Theravada Buddhism in Myanmar and in mainland Southeast Asia.Lieberman 2003: 88–123 The kingdom grew out of a small 9th-century settlement at Bagan, Pagan (present-day Bagan) by the Bamar, Mranma/Burmans, who had recently entered the Irrawaddy valley from the Kingdom of Nanzhao. Over the next two hundred years, the small principality gradually grew to absorb its surrounding regions until the 1050s and 1060s when King Anawrahta founded the Pagan Empire, for the first time unifying und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magh People
The Magh ( Mog ) is the term used in history of Bengali and others people of South Asia for the Marma and Arakanese/Rakhine of Arakan. During the 16th and 17th centuries, the meaning of Magh represent the people belongs to magadha (bihar) part of the indian state of Bihar. During the rise of Shunga dynasty & the fall of buddhism in the country of Moghs/Maghs or Magadha many of Local Buddhist people migrated towards east of Bengal, they established a Kingdom between chittagong & Arakan Yoma Mountain in Burma. the Mrauk U Kingdom of Arakan expanded its territories to the Chittagong area of Bengal. The navy of the kingdom of Arakan or rather Magh sailors along with the Portuguese had plundered along the coast of Chittagong; as well as in the rivers of Bengal; and captured many Bengalis and sold them in the slave markets that were run by the Dutch East India Company, VOC in Batavia. For those notorious activities in the past, the Arakanese were called Magh pirates by the people of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mrauk U
Mrauk U ( ) is a town in northern Rakhine State, Myanmar. It is the capital of Mrauk-U Township, a subregion of the Mrauk-U District. Mrauk U is of great cultural importance to the local Rakhine (Arakanese) people, and is the location of many important archeological sites. From 1430 until 1785, it was the capital of the Mrauk U Kingdom, the largest and most powerful Rakhine kingdom in history. Geography Mrauk U lies roughly east of the Kaladan River on the banks of its minor tributaries. The town is located on a small outcrop of the Rakhine Yoma on the eastern side of the Kaladan's alluvial plain. Thus, the surrounding countryside is hilly yet also contains a great deal of marshes, mangroves and lakes. Climate Mrauk U, like all of Rakhine State, is situated in a coastal tropical monsoon rainforest climate (Köppen ''Am'') region. The town receives over of rain a year from the Southwestern Monsoon, making it one of the wettest regions in Myanmar. The Monsoon season usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |