|
Simpson Planetary Gearset
The Simpson planetary gearset is a compound planetary gear train consisting of two planetary gearsets sharing a common sun gear. A Simpson gearset delivers three forward gears and one reverse, plus neutral, and is commonly employed in three and four ratio automatic transmissions. It is one of the several designs invented by American engineer Howard Simpson. Overview The two planetaries are interdependent via two permanent connections, that commonly but not necessarily have the same gears and gear ratios, both gearsets share a common sun gear. The planet carrier of the first gearset ("first" means closer to the input shaft) is in synchrony with the second gearset's ring. Owing to these linkages, only two bands and two clutches are needed to command the gearsets. In the first gear, the first gearset actuates on the second gearset and output shaft; the second gearset reacts and makes the sun turn in reverse, causing the first gearset to increase the reduction ratio. In first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sprag Clutch
A sprag clutch is a one-way freewheel clutch. It resembles a roller bearing but, instead of cylindrical rollers, non-revolving asymmetric figure-eight shaped sprags, or other elements allowing single direction rotation, are used. When the unit rotates in one direction the rollers slip or free-wheel, but when a torque is applied in the opposite direction, the sprags tilt slightly, producing a wedging action and binding because of friction. Applications Automatic transmissions A sprag clutch is used in some automatic transmissions as a method of allowing the transmission to change gears smoothly under load. Various models of General Motors' Turbo-Hydramatic transmission have used this system as well as many transmissions from Ford, such as the Ford C6 transmission. A sprag clutch is used in most older automatic transmissions and some newer ones for shifts which require the synchronized engagement of one clutch with the disengagement of another. Using an overrunning clutch instea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepelletier Gear Mechanism , home of the Paris Opera, 1821-1873
{{disambiguation, surname ...
The name le Peletier (also spelled Lepeletier or Lepelletier) may refer to: People *Amédée Louis Michel le Peletier, comte de Saint-Fargeau (1770–1845), French entomologist *Edmond Lepelletier (1846–1913), French journalist, poet and politician *Louis-Michel le Peletier, marquis de Saint-Fargeau (1760–1793), French politician Other *Le Peletier (Paris Métro), stop on the Paris Métro *Lepelletier gear mechanism, three degrees of freedom epicyclic gear mechanism *Salle Le Peletier The Salle Le Peletier or Lepeletier (sometimes referred to as the Salle de la rue Le Peletier or the Opéra Le Peletier) was the home of the Paris Opera from 1821 until the building was destroyed by fire in 1873. The theatre was designed and con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicyclic Gearing
An epicyclic gear train (also known as a planetary gearset) consists of two gears mounted so that the center of one gear revolves around the center of the other. A carrier connects the centers of the two gears and rotates the planet and sun gears mesh so that their pitch circles roll without slip. A point on the pitch circle of the planet gear traces an epicycloid curve. In this simplified case, the sun gear is fixed and the planetary gear(s) roll around the sun gear. An epicyclic gear train can be assembled so the planet gear rolls on the inside of the pitch circle of a fixed, outer gear ring, or ring gear, sometimes called an ''annular gear''. In this case, the curve traced by a point on the pitch circle of the planet is a hypocycloid. The combination of epicycle gear trains with a planet engaging both a sun gear and a ring gear is called a ''planetary gear train''.J. J. Uicker, G. R. Pennock and J. E. Shigley, 2003, ''Theory of Machines and Mechanisms,'' Oxford University Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
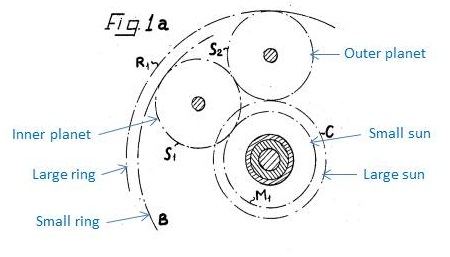
Ravigneaux Planetary Gearset
The Ravigneaux gearset is a double planetary gear set, invented by Pol Ravigneaux, who filed a patent application on July 28, 1949, in Neuilly-sur-Seine France. This planetary gear set, commonly used in automatic transmissions, is constructed from two gear pairs, ring–planet and planet–planet. The Ravigneaux set has two sun gears, a large sun and a small sun, and a single planet carrier, holding two sets of planetary gears, inner planets and outer planets. The carrier is one sub-assembly but has two radii to couple with the inner and outer planets, respectively. The two sets of planet gears rotate independently of the carrier but co-rotate with a fixed gear ratio with respect to each other. The inner planets couple with the small sun gear and co-rotate at a fixed gear ratio with respect to it. The outer planets couple with the large sun gear and co-rotates with a fixed gear ratio with respect to it. Finally, the ring gear also couples and co-rotates with the outer planets in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wide Open Throttle
Wide open throttle or wide-open throttle (WOT), also called full throttle, is the fully opened state of a throttle on an engine (internal combustion engine or steam engine). The term also, by extension, usually refers to the maximum-speed state of running the engine, as the normal result of a fully opened throttle plate/butterfly valve. In an internal combustion engine, this state entails the maximum intake of air and fuel that occurs when the throttle plates inside the carburetor or throttle body are "wide open" (fully opened up), providing the least resistance to the incoming air. In the case of an automobile, WOT is when the accelerator is depressed fully, sometimes referred to as "flooring it" (because automotive throttle controls are usually a pedal, so full throttle is selected by pressing the pedal to the floor, or as near as it will go). A throttle on a steam engine controls how much steam is sent to the cylinders from the boiler. In the case of a diesel engine, which d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overrunning Clutch
Freewheel mechanism In mechanical or automotive engineering, a freewheel or overrunning clutch is a device in a transmission that disengages the driveshaft from the driven shaft when the driven shaft rotates faster than the driveshaft. An overdrive is sometimes mistakenly called a freewheel, but is otherwise unrelated. The condition of a driven shaft spinning faster than its driveshaft exists in most bicycles when the rider stops pedaling. In a fixed-gear bicycle, without a freewheel, the rear wheel drives the pedals around. An analogous condition exists in an automobile with a manual transmission going downhill, or any situation where the driver takes their foot off the gas pedal, closing the throttle: the wheels drive the engine, possibly at a higher RPM. In a two-stroke engine, this can be catastrophic—as many two stroke engines depend on a fuel/oil mixture for lubrication, a shortage of fuel to the engine starves oil from the cylinders, and the pistons can soon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbo-Hydramatic
Turbo-Hydramatic or Turbo Hydra-Matic is the registered tradename for a family of automatic transmissions developed and produced by General Motors. These transmissions mate a three-element turbine torque converter to a Simpson planetary geartrain, providing three forward speeds plus reverse. The Turbo-Hydramatic or Turbo Hydra-Matic (THM) series was developed to replace both the original Hydra-Matic models and the Buick Dynaflow. In its original incarnation as the Turbo-Hydramatic 400, it was first used in the 1964 model year in Cadillacs. The Buick version, which followed shortly thereafter, was known as the Super-Turbine 400. By 1973, THM units had replaced all of GM's other automatic transmissions including Chevrolet's Powerglide, Buick's Super Turbine 300, and Oldsmobile's Jetaway. Starting in the early 1980s, the Turbo-Hydramatic was gradually supplanted by four-speed automatics, some of which continue to use the "Hydramatic" trade name. Although the Turbo Hydra-Matic n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retrograde And Prograde Motion
Retrograde motion in astronomy is, in general, orbital or rotational motion of an object in the direction opposite the rotation of its primary, that is, the central object (right figure). It may also describe other motions such as precession or nutation of an object's rotational axis. Prograde or direct motion is more normal motion in the same direction as the primary rotates. However, "retrograde" and "prograde" can also refer to an object other than the primary if so described. The direction of rotation is determined by an inertial frame of reference, such as distant fixed stars. In the Solar System, the orbits around the Sun of all planets and most other objects, except many comets, are prograde. They orbit around the Sun in the same direction as the sun rotates about its axis, which is counterclockwise when observed from above the Sun's north pole. Except for Venus and Uranus, planetary rotations around their axes are also prograde. Most natural satellites have prograde or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicyclic Gearing
An epicyclic gear train (also known as a planetary gearset) consists of two gears mounted so that the center of one gear revolves around the center of the other. A carrier connects the centers of the two gears and rotates the planet and sun gears mesh so that their pitch circles roll without slip. A point on the pitch circle of the planet gear traces an epicycloid curve. In this simplified case, the sun gear is fixed and the planetary gear(s) roll around the sun gear. An epicyclic gear train can be assembled so the planet gear rolls on the inside of the pitch circle of a fixed, outer gear ring, or ring gear, sometimes called an ''annular gear''. In this case, the curve traced by a point on the pitch circle of the planet is a hypocycloid. The combination of epicycle gear trains with a planet engaging both a sun gear and a ring gear is called a ''planetary gear train''.J. J. Uicker, G. R. Pennock and J. E. Shigley, 2003, ''Theory of Machines and Mechanisms,'' Oxford University Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that engages and disengages power transmission, especially from a drive shaft to a driven shaft. In the simplest application, clutches connect and disconnect two rotating shafts (drive shafts or line shafts). In these devices, one shaft is typically attached to an engine or other power unit (the driving member), while the other shaft (the driven member) provides output power for work. Typically the motions involved are rotary, but linear clutches also exist. In a motor vehicle, the clutch acts as a mechanical linkage between the engine and transmission, and briefly disconnects, or separates the engine from the transmission system. This disconnects the drive wheels whenever the clutch pedal is depressed, allowing the driver to smoothly change gears. In a torque-controlled drill, for instance, one shaft is driven by a motor, and the other drives a drill chuck. The clutch connects the two shafts so they may be locked together and spin at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |