|
Simplified Airway Risk Index
The Simplified Airway Risk Index (SARI), or El-Ganzouri Risk Index (EGRI), is a multivariate risk score for predicting difficult tracheal intubation. The SARI score ranges from 0 to 12 points, where a higher number of points indicates a more difficult airway. A SARI score of 4 or above indicate a difficult intubation. Seven parameters is used to calculate the SARI score: Mouth opening, thyromental distance, Mallampati score, movement of the neck, the ability to create an underbite, body weight and previous intubation history. __TOC__ Calculation # Mouth opening: A mouth opening greater than 4 centimeters between the incisor Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, wher ...s results in 0 points whereas a distance below results in 1 point. # Thyromental distance:A thyromental d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallampati
In anesthesia, the Mallampati score or Mallampati classification, named after the Indian anaesthesiologist Seshagiri Mallampati, is used to predict the ease of endotracheal intubation. The test comprises a visual assessment of the distance from the tongue base to the roof of the mouth, and therefore the amount of space in which there is to work. It is an indirect way of assessing how difficult an intubation will be; this is more definitively scored using the Cormack-Lehane classification system, which describes what is actually seen using direct laryngoscopy during the intubation process itself. A high Mallampati score (class 3 or 4) is associated with more difficult intubation as well as a higher incidence of sleep apnea. Technique The score is assessed by asking the patient, in a sitting posture, to open their mouth and to protrude the tongue as much as possible. The anatomy of the oral cavity is visualized; specifically, the assessor notes whether the base of the uvula, fau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheal Intubation
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic catheter, tube into the vertebrate trachea, trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs. It is frequently performed in critically injured, ill, or anesthetized patients to facilitate Ventilation (physiology), ventilation of the lungs, including mechanical ventilation, and to prevent the possibility of asphyxiation or airway obstruction. The most widely used route is orotracheal, in which an tracheal tube, endotracheal tube is passed through the mouth and larynx, vocal apparatus into the trachea. In a nasotracheal procedure, an endotracheal tube is passed through the nose and vocal apparatus into the trachea. Other methods of intubation involve surgery and include the cricothyrotomy (used almost exclusively in emergency circumstances) and the tracheotomy, used primarily in situations where a prolonged need for airw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyromental Distance
Thyromental distance (TMD) measurement is a method commonly used to predict the difficulty of Tracheal intubation, intubation and is measured from the Superior thyroid notch, thyroid notch to the tip of the jaw with the head extended. If it is less than 7.0 cm with hard Scar, scarred tissues, it indicates possible difficult intubation. See also * Mallampati score * Simplified Airway Risk Index References {{Anesthesia Anesthesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallampati Score
In anesthesia, the Mallampati score or Mallampati classification, named after the Indian anaesthesiologist Seshagiri Mallampati, is used to predict the ease of endotracheal intubation. The test comprises a visual assessment of the distance from the tongue base to the roof of the mouth, and therefore the amount of space in which there is to work. It is an indirect way of assessing how difficult an intubation will be; this is more definitively scored using the Cormack-Lehane classification system, which describes what is actually seen using direct laryngoscopy during the intubation process itself. A high Mallampati score (class 3 or 4) is associated with more difficult intubation as well as a higher incidence of sleep apnea. Technique The score is assessed by asking the patient, in a sitting posture, to open their mouth and to protrude the tongue as much as possible. The anatomy of the oral cavity is visualized; specifically, the assessor notes whether the base of the uvula, fauci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neck
The neck is the part of the body on many vertebrates that connects the head with the torso. The neck supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that carry sensory and motor information from the brain down to the rest of the body. In addition, the neck is highly flexible and allows the head to turn and flex in all directions. The structures of the human neck are anatomically grouped into four compartments; vertebral, visceral and two vascular compartments. Within these compartments, the neck houses the cervical vertebrae and cervical part of the spinal cord, upper parts of the respiratory and digestive tracts, endocrine glands, nerves, arteries and veins. Muscles of the neck are described separately from the compartments. They bound the neck triangles. In anatomy, the neck is also called by its Latin names, or , although when used alone, in context, the word ''cervix'' more often refers to the uterine cervix, the neck of the uterus. Thus the adjective ''cervical'' ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
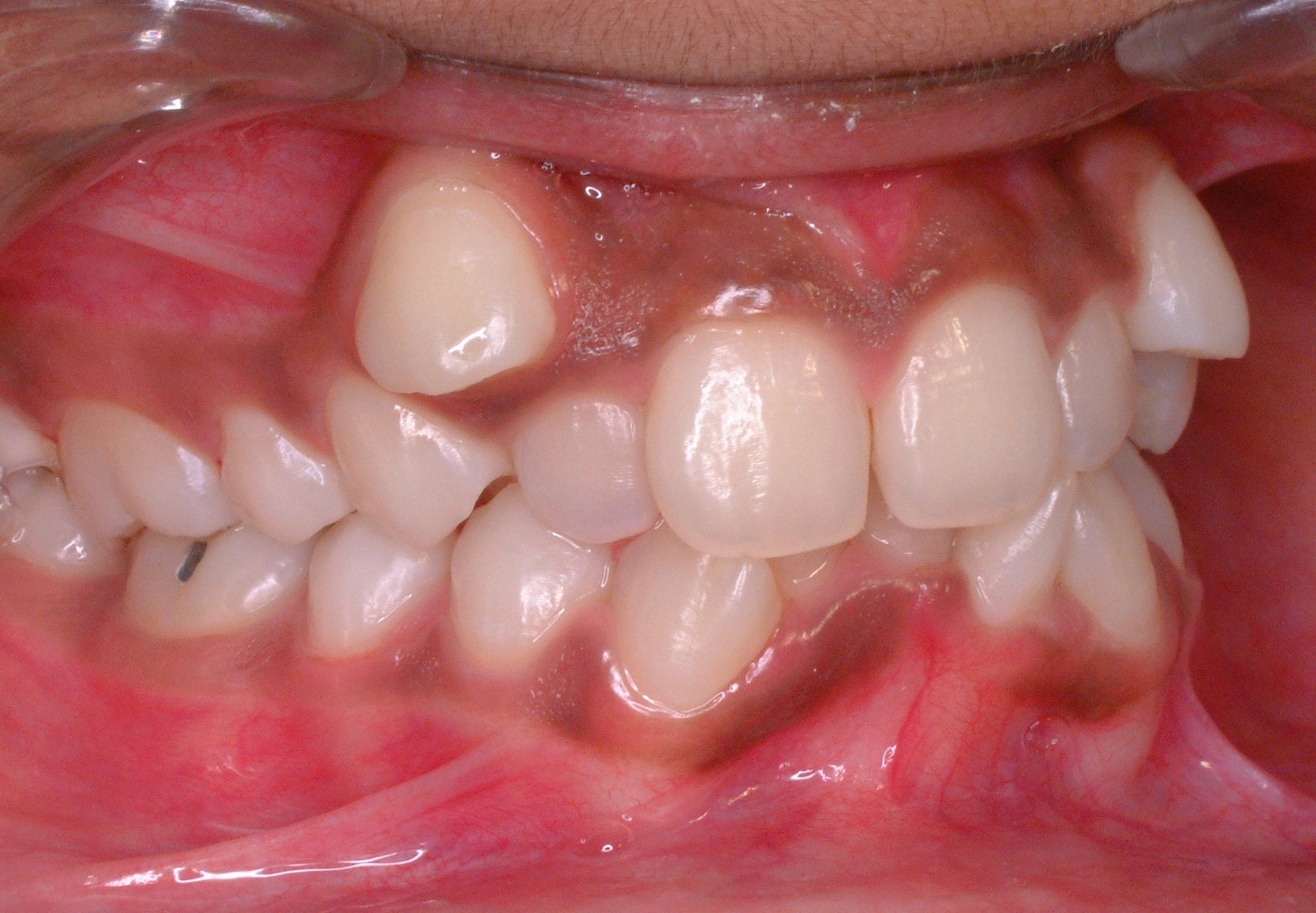
Underbite
In orthodontics, a malocclusion is a misalignment or incorrect relation between the teeth of the upper and lower dental arches when they approach each other as the jaws close. The English-language term dates from 1864; Edward Angle (1855-1930), the "father of modern orthodontics", popularised it. The word "malocclusion" derives from occlusion (dentistry), ''occlusion'', and refers to the manner in which opposing teeth meet (''wikt:mal-, mal-'' + ''occlusion'' = "incorrect closure"). The malocclusion classification is based on the relationship of the mesiobuccal cusp of the maxillary first molar and the buccal (other), buccal groove of the mandibular first molar. If this molar relationship exists, then the teeth can align into normal occlusion. According to Angle, malocclusion is any deviation of the occlusion from the ideal. However, assessment for malocclusion should also take into account aesthetics and the impact on functionality. If these aspects are acceptable t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Weight
Human body weight is a person's mass or weight. Strictly speaking, body weight is the measurement of weight without items located on the person. Practically though, body weight may be measured with clothes on, but without shoes or heavy accessories such as mobile phones and wallets, and using manual or digital weighing scales. Excess or reduced body weight is regarded as an indicator of determining a person's health, with body volume measurement providing an extra dimension by calculating the distribution of body weight. Average adult human weight varies by continent, from about in Asia and Africa to about in North America, with men on average weighing more than women. Estimation in children There are a number of methods to estimate weight in children for circumstances (such as emergencies) when actual weight cannot be measured. Most involve a parent or health care provider guessing the child's weight through weight-estimation formulas. These formulas base their findings o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incisor
Incisors (from Latin ''incidere'', "to cut") are the front teeth present in most mammals. They are located in the premaxilla above and on the mandible below. Humans have a total of eight (two on each side, top and bottom). Opossums have 18, whereas armadillos have none. Structure Adult humans normally have eight incisors, two of each type. The types of incisor are: * maxillary central incisor (upper jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * maxillary lateral incisor (upper jaw, beside the maxillary central incisor) * mandibular central incisor (lower jaw, closest to the center of the lips) * mandibular lateral incisor (lower jaw, beside the mandibular central incisor) Children with a full set of deciduous teeth (primary teeth) also have eight incisors, named the same way as in permanent teeth. Young children may have from zero to eight incisors depending on the stage of their tooth eruption and tooth development. Typically, the mandibular central incisors erupt first, followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cormack-Lehane Classification System
The Cormack-Lehane system classifies views obtained by direct laryngoscopy based on the structures seen. It was initially described by R.S. Cormack and J. Lehane in 1984 as a way of simulating potential scenarios that trainee anaesthetists might face. A modified version that subdivided Grade 2 was initially described in 1998. See also * Mallampati score * Simplified Airway Risk Index * Thyromental distance Thyromental distance (TMD) measurement is a method commonly used to predict the difficulty of Tracheal intubation, intubation and is measured from the Superior thyroid notch, thyroid notch to the tip of the jaw with the head extended. If it is less ... References {{reflist Anesthesia Medical scoring system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), amnesia (loss of memory), and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized. Anesthesia enables the painless performance of procedures that would otherwise cause severe or intolerable pain in a non-anesthetized individual, or would otherwise be technically unfeasible. Three broad categories of anesthesia exist: * General anesthesia suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of sensation, using either injected or inhaled drugs. * Sedation suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiety and creation of long-term memories without resulting in unconsciousness. * Regional and local anesthesia, which blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |