|
Simple Present
The simple present, present simple or present indefinite is one of the verb forms associated with the present tense in modern English. It is commonly referred to as a tense, although it also encodes certain information about aspect in addition to present time. The simple present is the most commonly used verb form in English, accounting for more than half of verbs in spoken English. It is called "simple" because its basic form consists of a single word (like ''write'' or ''writes''), in contrast with other present tense forms such as the present progressive (''is writing'') and present perfect (''has written''). For nearly all English verbs the simple present is identical to the base form (dictionary form) of the verb, except when the subject is third-person singular, in which case the ending ''-(e)s'' is added. There are a few verbs with irregular forms, the most notable being the copula ''be'', which has the simple present forms ''am'', ''is'', and ''are''.... Conjugation Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Present Tense
The present tense (abbreviated or ) is a grammatical tense whose principal function is to locate a situation or event in the present time. The present tense is used for actions which are happening now. In order to explain and understand present tense, it is useful to imagine time as a line on which the past tense, the present and the future tense are positioned. The term ''present tense'' is usually used in descriptions of specific languages to refer to a particular grammatical form or set of forms; these may have a variety of uses, not all of which will necessarily refer to present time. For example, in the English sentence "My train leaves tomorrow morning", the verb form ''leaves'' is said to be in the present tense, even though in this particular context it refers to an event in future time. Similarly, in the historical present, the present tense is used to narrate events that occurred in the past. There are two common types of present tense form in most Indo-European langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
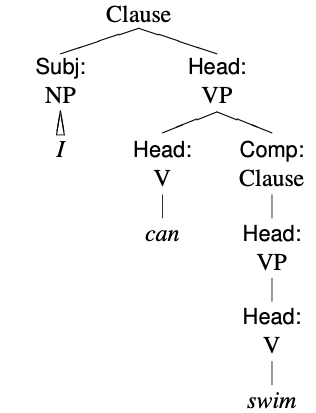
Auxiliary Verb
An auxiliary verb (abbreviated ) is a verb that adds functional or grammatical meaning to the clause in which it occurs, so as to express tense, aspect, modality, voice, emphasis, etc. Auxiliary verbs usually accompany an infinitive verb or a participle, which respectively provide the main semantic content of the clause. An example is the verb ''have'' in the sentence ''I have finished my lunch.'' Here, the auxiliary ''have'' helps to express the perfect aspect along with the participle, ''finished''. Some sentences contain a chain of two or more auxiliary verbs. Auxiliary verbs are also called helping verbs, helper verbs, or (verbal) auxiliaries. Research has been conducted into split inflection in auxiliary verbs. Basic examples Below are some sentences that contain representative auxiliary verbs from English, Spanish, German and French, with the auxiliary verb marked in bold: ::a. Do you want tea? – ''do'' is an auxiliary accompanying the infinitive, ''want'', used here t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Past
The simple past, past simple or past indefinite, sometimes called the preterite, is the basic form of the past tense in Modern English. It is used principally to describe events in the past, although it also has some other uses. Regular English verbs form the simple past in ''-ed''; however, there are a few hundred List of English irregular verbs, irregular verbs with different forms. The term "simple aspect, simple" is used to distinguish the syntax, syntactical construction whose basic form uses the plain past tense alone, from other past tense constructions which use auxiliaries in combination with participles, such as the past perfect and past progressive. Formation Regular verbs form the simple past end''-ed''; however there are a few hundred List of English irregular verbs, irregular verbs with different forms. The spelling rules for forming the past simple of regular verbs are as follows: verbs ending in -e add only –d to the end (e.g. live – lived, not *liveed), verbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Present Continuous
The present continuous, also called the present progressive or present imperfect, is a verb form used in modern English that combines the present tense with the continuous aspect. It is formed by the present tense form of be and the present participle of a verb. The present continuous is generally used to describe something that is taking place at the present moment and can be employed in both the indicative and subjunctive moods. It accounts for approximately 5% of verbs in spoken English. Formation The present continuous is formed by the present tense form of be and the present participle (-ing form) of the verb. For example, you would write the verb ''work'' in the present continuous form by adding the -ing suffix to the verb and placing a present tense form of be (am, are, is) in front of it: * I am working. * You are working. * She is working. * We are working. * They are working. Uses The present continuous is used in several instances. Its most common use is to des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Possession (linguistics)
In linguistics, possession is an asymmetric relationship between two constituents, the referent of one of which (the possessor) in some sense possesses (owns, has as a part, rules over, etc.) the referent of the other (the possessed). Possession may be marked in many ways, such as simple juxtaposition of nouns, possessive case, possessed case, construct state (as in Arabic, and Nêlêmwa), or adpositions (possessive suffixes, possessive adjectives). For example, English uses a possessive clitic, '' 's''; a preposition, ''of''; and adjectives, ''my'', ''your'', ''his'', ''her'', etc. Predicates denoting possession may be formed either by using a verb such as English ''have'' or by other means, such as existential clauses (as is usual in languages such as Russian). Some languages have more than two possessive classes. In Papua New Guinea, for example, Anêm has at least 20 and Amele has 32. Alienable and inalienable There are many types of possession, but a common distincti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conditional Sentence
Conditional sentences are natural language sentences that express that one thing is contingent on something else, e.g. "If it rains, the picnic will be cancelled." They are so called because the impact of the main clause of the sentence is ''conditional'' on the dependent clause. A full conditional thus contains two clauses: a dependent clause called the ''antecedent'' (or ''protasis'' or ''if-clause''), which expresses the condition, and a main clause called the ''consequent'' (or ''apodosis'' or ''then-clause'') expressing the result. Languages use a variety of grammatical forms and constructions in conditional sentences. The forms of verbs used in the antecedent and consequent are often subject to particular rules as regards their tense, aspect, and mood. Many languages have a specialized type of verb form called the conditional mood – broadly equivalent in meaning to the English "would (do something)" – for use in some types of conditional sentences. Types of conditiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dependent Clause
A subordinate clause, dependent clause, subclause, or embedded clause is a clause that is embedded within a complex sentence. For instance, in the English sentence "I know that Bette is a dolphin", the clause "that Bette is a dolphin" occurs as the complement of the verb "know" rather than as a freestanding sentence. Subtypes of dependent clauses include content clauses, relative clauses, and adverbial clauses. Content clause A content clause, also known as a "noun clause", provides content implied or commented upon by its main clause. It can be a subject, predicate nominative, direct object, appositive, indirect object, or object of the preposition. Some of the English words that introduce content clauses are ''that, who'' (and formal ''whom''), ''whoever'' (and formal ''whomever''), ''whether, why, what, how, when'', and ''where''. Notice that some of these words also introduce relative and adverbial clauses. A clause is a content clause if a pronoun (''he, she, it,'' or ''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headline
The headline or heading is the text indicating the content or nature of the article below it, typically by providing a form of brief summary of its contents. The large type ''front page headline'' did not come into use until the late 19th century when increased competition between newspapers led to the use of attention-getting headlines. It is sometimes termed a news ''hed'', a deliberate misspelling that dates from production flow during hot type days, to notify the composing room that a written note from an editor concerned a headline and should not be set in type. Headlines in English often use a set of grammatical rules known as '' headlinese'', designed to meet stringent space requirements by, for example, leaving out forms of the verb "to be" and choosing short verbs like "eye" over longer synonyms like "consider". Production A headline's purpose is to quickly and briefly draw attention to the story. It is generally written by a copy editor, but may also be written by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Present
In linguistics and rhetoric, the historical present or historic present, also called dramatic present or narrative present, is the employment of the present tense when narrating past events. It is widely used in writing about history in Latin (where it is sometimes referred to by its Latin name, ''praesens historicum'') and some modern European languages. In English, it is used above all in historical chronicles (listing a series of events). It is also used in fiction, for "hot news" (as in headlines), and in everyday conversation. In conversation, it is particularly common with quotative verbs such as ''say'' and ''go'', and especially the newer quotative ''like''. It is typically thought to heighten the dramatic force of the narrative by describing events as if they were still unfolding, and/or by foregrounding some events relative to others. Examples In an excerpt from Charles Dickens's ''David Copperfield'', the shift from the past tense to the historical present gives a se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stative Verb
According to some linguistics theories, a stative verb is a verb that describes a state of being, in contrast to a dynamic verb, which describes an action. The difference can be categorized by saying that stative verbs describe situations that are static or unchanging throughout their entire duration, whereas dynamic verbs describe processes that entail change over time. Many languages distinguish between these two types in terms of how they can be used grammatically. Contrast to dynamic Some languages use the same verbs for dynamic and stative situations, and others use different (but often related) verbs with some kind of qualifiers to distinguish between them. Some verbs may act as either stative or dynamic. A phrase like "he plays the piano" may be either stative or dynamic, according to the context. When, in a given context, the verb "play" relates to a state (an interest or a profession), he could be an amateur who enjoys music or a professional pianist. The dynamic interpr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Auxiliaries And Contractions
English auxiliary verbs are a small set of English verbs, which include the English modal verbs and a few others. Although definitions vary, as generally conceived an auxiliary lacks inherent semantic meaning but instead modifies the meaning of another verb it accompanies. In English, verb forms are often classed as auxiliary on the basis of certain grammatical properties, particularly as regards their syntax. They also participate in subject–auxiliary inversion and negation by the simple addition of ''not'' after them. History of the concept In English, the adjective ''auxiliary'' was "formerly applied to any formative or subordinate elements of language, e.g. prefixes, prepositions." As applied to verbs, its conception was originally rather vague and varied significantly. Some historical examples The first English grammar, ''Pamphlet for Grammar'' by William Bullokar, published in 1586, does not use the term "auxiliary", but says, All other verbs are called verbs-neuters-u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Do-support
''Do''-support (or ''do''-insertion), in English grammar, is the use of the auxiliary verb ''do'', including its inflected forms ''does'' and ''did'', to form negated clauses and questions as well as other constructions in which subject–auxiliary inversion is required. The verb "do" can be used as an auxiliary even in simple declarative sentences, and it usually serves to add emphasis, as in "I ''did'' shut the fridge." However, in the negated and inverted clauses referred to above, it is used because the conventions of Modern English syntax permit these constructions only when an auxiliary is present. It is not idiomatic in Modern English to add the negating word ''not'' to a lexical verb with finite form; ''not'' can be added only to an auxiliary or copular verb. For example, the sentence ''I am not'' with the copula ''be'' is fully idiomatic, but ''I know not'' with a finite lexical verb, while grammatical, is archaic. If there is no other auxiliary present when negation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |