|
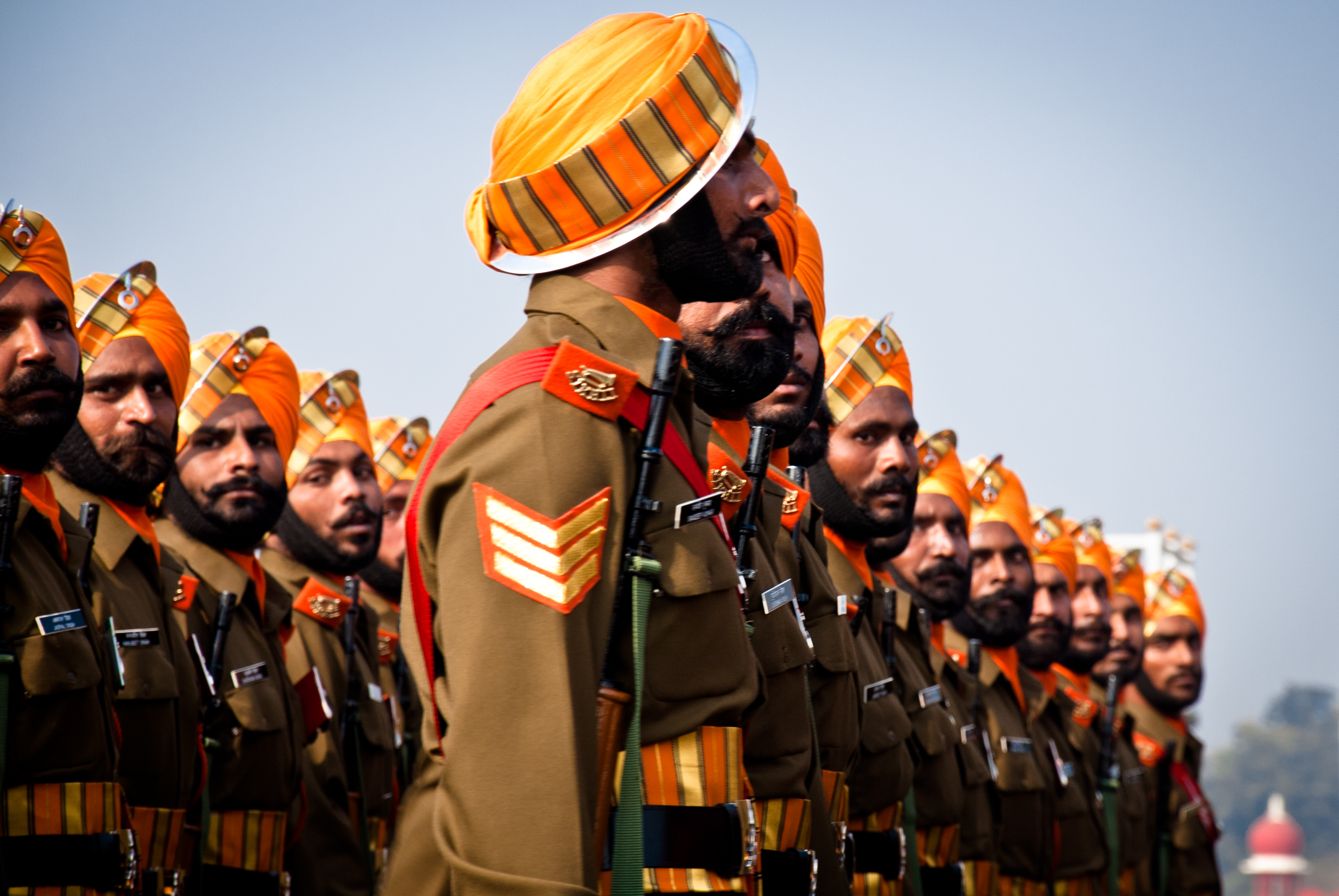
Sikh Light Infantry
The Sikh Light Infantry is a light infantry regiment of the Indian Army.Anniversary Celebrations of Sikh LI The regiment is the successor unit to the 23rd, 32nd and 34th Royal Sikh Pioneers of the . The regiment recruits from the Sikh community of |
Light Infantry
Light infantry refers to certain types of lightly equipped infantry throughout history. They have a more mobile or fluid function than other types of infantry, such as heavy infantry or line infantry. Historically, light infantry often fought as Reconnaissance, scouts, Raid (military), raiders, and skirmisher, skirmishers. These are loose formations that fight ahead of the main army to harass, delay, disrupt supply lines, engage the enemy’s own skirmishing forces, and generally "soften up" an enemy before the main battle. Light infantrymen were also often responsible for Screening (tactical), screening the main body of a military formation. Post-World War II, the term "light infantry" evolved to include rapid-deployment units (including commandos and Airborne forces, airborne units) that emphasize speed and mobility over armor and firepower. Some units or battalions that historically held a skirmishing role have kept their designation "light infantry" for the sake of traditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
32nd Sikh Pioneers
The 32nd Sikh Pioneers was a regiment of the Indian Army during British rule. The regiment was founded in 1857 as the ''Punjab Sappers (Pioneers)''. After a series of names changes, it became the ''32nd Punjab Pioneers'' in 1901 and the ''32nd Sikh Pioneers'' in 1903. To honour the visit of the Prince and Princess of Wales to Indian they took part in the Rawalpindi Parade 1905. In 1922, it united with 23rd Sikh Pioneers and 34th Sikh Pioneers, to form 2nd Bn, 3rd Sikh Pioneers. Their most celebrated feat of arms was the relief in 1895 of the besieged British garrison of Chitral, by a gruelling crossing of the snow-covered Shandur Pass. The regiment recruited the Mazhabi Sikhs and Ramdasia Sikhs Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism (Sikhi), a monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ... of Punjab province. Despite bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akali Nihang
The Nihang or Akali (lit. "the immortals") is an armed Sikh warrior order originating in the Indian subcontinent. Nihang are believed to have originated either from Fateh Singh and the attire he wore or from the "Akali" (lit. Army of the Immortal) started by Guru Hargobind. Early Sikh military history was dominated by the Nihang, known for their victories where they were heavily outnumbered. Traditionally known for their bravery and ruthlessness in the battlefield, the Nihang once formed the irregular guerrilla squads of the armed forces of the Sikh Empire, the Sikh Khalsa Army. Akali The ''word Akali/akaali'' means timeless or immortal. Literally, one who belongs to ''Akaal'' (beyond Time). In other words, an Akaali is that person who is subject of none but God only. Conceptually speaking, the terms Akaali, Khalsa and Sikh are synonymous. The term Akaali was first used during the time of Guru Gobind Singh Sahib. The term Akaali became popular in the last decades of the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirpan
The kirpan is a curved, single-edged dagger or knife carried by Sikhs. Traditionally, it was a full-sized sword but modern Sikhs have reduced the length to that of a dagger or knife due to modern considerations based on societal and legal changes since then. It is part of a religious commandment given by Guru Gobind Singh in 1699, in which he gave an option to the Sikhs, if they accepted they must wear the five articles of faith (the five Ks) at all times, the kirpan being one of five Ks. The Punjabi word ਕਿਰਪਾਨ, kirpān, has a folk etymology with two roots: ''kirpa'', meaning "mercy", "grace", "compassion" or "kindness"; and ''aanaa'', meaning "honor", "grace" or "dignity". It is derived from or related to Sanskrit कृपाण (kṛpaṇa, “sword, dagger, sacrificial knife”), ultimately from the Proto-Indo-European stem *kerp-, from *(s)ker, meaning "to cut". Sikhs are expected to embody the qualities of a ''Sant Sipahi'' or "saint-soldier", showing no fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chakram
Chakram ( sa, , script=latn; pa, , script=latn) is a throwing weapon from the Indian subcontinent. One of its major purposes is to protect the turban and the head from sword/melee attacks. It is circular with a sharpened outer edge and a diameter of . It is also known as chalikar meaning "circle", and was sometimes referred to in English writings as a "war- quoit". The Chakram is primarily a throwing weapon but can also be used hand-to-hand. A smaller variant called ''chakri'' is worn on the wrist. A related weapon is the ''chakri dong'', a bamboo staff with a chakri attached at one end. History The earliest references to the chakram come from the 5th century BCE Indian epics ''Mahabharata'' and ''Ramayana'' where the Sudarshana Chakra is the weapon of the god Vishnu. Contemporaneous Tamil poems from the 2nd century BCE record it as ''thikiri'' (திகிரி). Chakra-dhāri ("chakram-wielder" or "disc-bearer") is a name for Krishna. The chakram was later used extensively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh (; 22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708), born Gobind Das or Gobind Rai the tenth Sikh Guru, a spiritual master, warrior, poet and philosopher. When his father, Guru Tegh Bahadur, was executed by Aurangzeb, Guru Gobind Singh was formally installed as the leader of the Sikhs at the age of nine, becoming the tenth and final human Sikh Guru. His four biological sons died during his lifetime – two in battle, two executed by the Mughal governor Wazir Khan.; Among his notable contributions to Sikhism are founding the '' Sikh'' warrior community called ''Khalsa'' in 1699 and introducing ''the Five Ks'', the five articles of faith that Khalsa Sikhs wear at all times. Guru Gobind Singh is credited with the ''Dasam Granth'' whose hymns are a sacred part of Sikh prayers and Khalsa rituals. He is also credited as the one who finalized and enshrined the ''Guru Granth Sahib'' as Sikhism's primary scripture and eternal Guru. Family and early life Gobind Singh was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deg Tegh Fateh
Deg Teg Fateh ( pa, ਦੇਗ ਤੇਗ਼ ਫ਼ਤਿਹ, meaning Victory to Charity and Arms) is a Sikh slogan and the title of an anthem in the Punjabi language that signifies the dual obligations of the Khalsa: The responsibility to provide food, and to provide protection, for the needy and oppressed. Description ''Deg'' refers to the "cauldron" and ''Tegh'' to the "sword". The cauldron or kettle symbolizes charity and is a reference to the Sikh religious obligation to provide ''langar'', the free distribution of food, to all people, irrespective of an individual's religion, caste or ethnicity. The sword, or (''kirpan''), represents the warrior code of the ''Khalsa''. The ''Khanda'' icon conveys these two principles. A translation of the ''Degh Tegh Fateh'' into English: :"Victory in war and prosperity in peace have been obtained from Guru Nanak-Gobind Singh. God is one! Victory to the Presence! This is the order of ''Sri Sachcha Sahib'' to the entire ''Khalsa''. The ''Gur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Emergency Force
The United Nations Emergency Force (UNEF) was a military and peacekeeping operation established by the United Nations General Assembly to secure an end to the Suez Crisis of 1956 through the establishment of international peacekeepers on the border between Egypt and Israel. Approved by resolution 1001 (ES-I) of 7 November 1956, UNEF was developed in large measure as a result of efforts by UN Secretary-General Dag Hammarskjöld and a proposal from Canadian Minister of External Affairs Lester B. Pearson, who would later win the Nobel Peace Prize for it. The General Assembly had approved a plan submitted by the Secretary-General which envisaged the deployment of UNEF on both sides of the armistice line; Egypt accepted receiving the UN forces, but Israel refused it. In May 1967, Egypt asked that UNEF leave Egypt; as the troops started to evacuate over the next days, Israel invaded Egypt on 6 June 1967, initiating the Six-Day War and causing the death of one Brazilian Sergeant and 14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counter-terrorism
Counterterrorism (also spelled counter-terrorism), also known as anti-terrorism, incorporates the practices, military tactics, techniques, and strategies that governments, law enforcement, business, and intelligence agencies use to combat or eliminate terrorism. Counterterrorism strategies are a government's motivation to use the instruments of national power to defeat terrorists, the organizations they maintain, and the networks they contain. If definitions of terrorism are part of a broader insurgency, counterterrorism may employ counterinsurgency measures. The United States Armed Forces uses the term foreign internal defense for programs that support other countries' attempts to suppress insurgency, lawlessness, or subversion, or to reduce the conditions under which threats to national security may develop. History The first counter-terrorism body formed was the Special Irish Branch of the Metropolitan Police, later renamed the Special Branch after it expanded its scope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
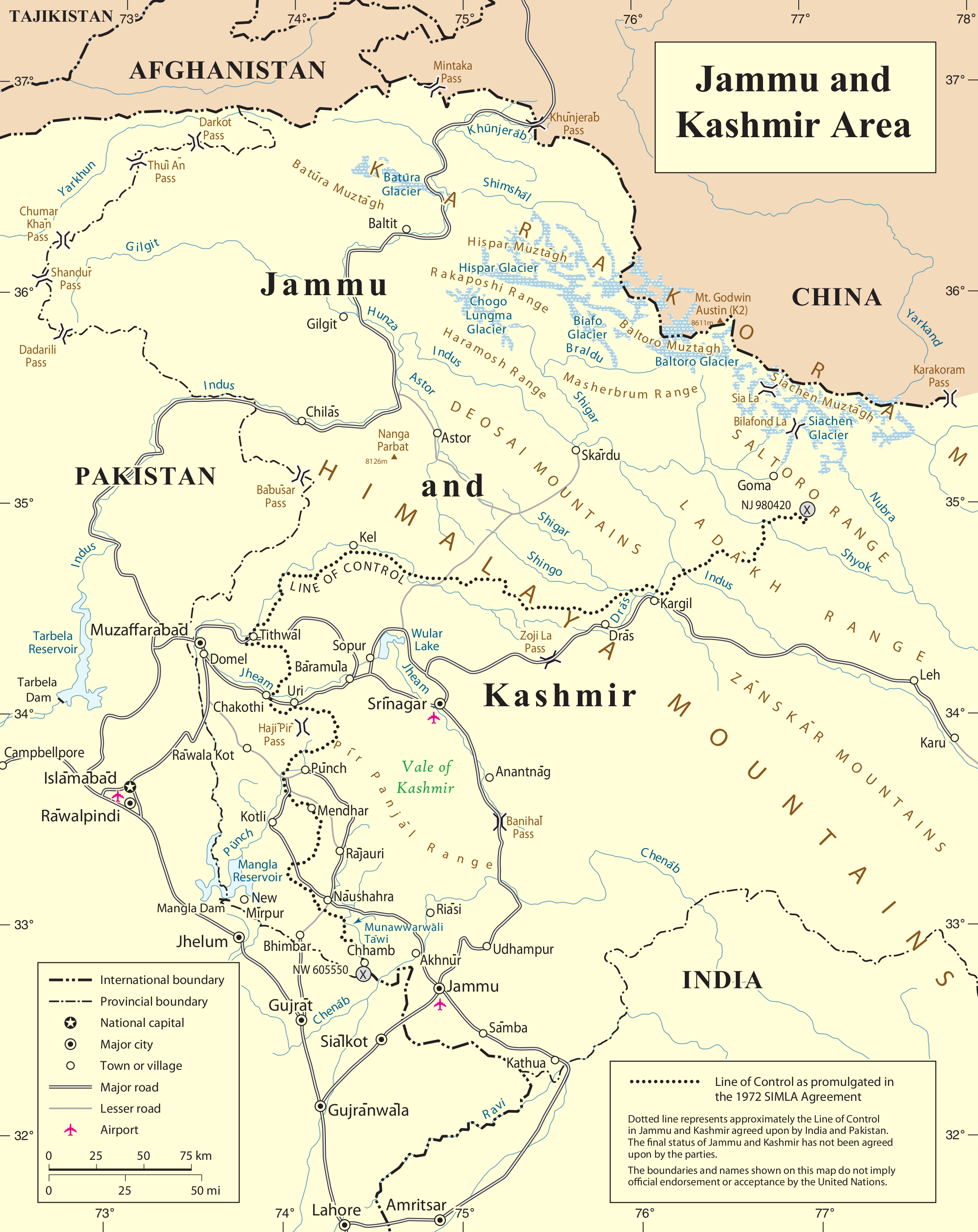
Siachen Conflict
The Siachen conflict, sometimes referred to as the Siachen Glacier conflict or the Siachen War, was a military conflict between India and Pakistan over the disputed Siachen Glacier region in Kashmir. The conflict was started in 1984 by India's successful capture of the Siachen Glacier as part of Operation Meghdoot, and continued with Operation Rajiv in 1987. India took control of the Siachen Glacier and its tributary glaciers, as well as all the main passes and heights of the Saltoro Ridge immediately west of the glacier, including Sia La, Bilafond La, and Gyong La. Pakistan controls the glacial valleys immediately west of the Saltoro Ridge. A cease-fire went into effect in 2003, but both sides maintain a heavy military presence in the area. The conflict has resulted in thousands of deaths, mostly due to natural hazards. External commentators of have characterized it as pointless, given the perceived uselessness of the territory, and indicative of bitter stubbornness on both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haryana, India
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land area. The state capital is Chandigarh, which it shares with the neighboring state of Punjab, and the most populous city is Faridabad, which is a part of the National Capital Region. The city of Gurugram is among India's largest financial and technology hubs. Haryana has 6 administrative divisions, 22 districts, 72 sub-divisions, 93 revenue tehsils, 50 sub-tehsils, 140 community development blocks, 154 cities and towns, 7,356 villages, and 6,222 villages panchayats. Haryana contains 32 special economic zones (SEZs), mainly located within the industrial corridor projects connecting the National Capital Region. Gurgaon is considered one of the major information technology and automobile hubs of India. Haryana ranks 11th among Indian states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punjab, India
Punjab (; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northern India. Forming part of the larger Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, the state is bordered by the States and union territories of India, Indian states of Himachal Pradesh to the north and northeast, Haryana to the south and southeast, and Rajasthan to the southwest; by the Indian union territory, union territories of Chandigarh to the east and Jammu and Kashmir (union territory), Jammu and Kashmir to the north. It shares an international border with Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab, a Pakistani province, province of Pakistan to the west. The state covers an area of 50,362 square kilometres (19,445 square miles), which is 1.53% of India's total geographical area, making it List of states and union territories of India by area, the 19th-largest Indian state by area out of 28 Indian states (20th largest, if UTs are considered). With over 27 million inhabitants, Punjab is List of states and union territories of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |