|
Sikh Culture
The Sikhs are adherents to Sikhism the fifth largest organized religion in the world, with around 25 million adherents. Sikh History is around 500 years and in that time the Sikhs have developed unique expressions of art and culture which are influenced by their faith and synthesize traditions from many other cultures depending on the locality of the adherents of the religion. Sikhism is the only religion that originated in the Punjab region with all other religions coming from outside Punjab (with the possible exception of Punjabi Hinduism since the oldest Hindu scripture – the Rig Veda – was composed in the Punjab region. Some other religions, like Jainism, may also claim to have originated in Punjab since Jain symbolism has been found among artifacts of the Indus Valley Civilization). All the Sikh gurus, many saints and many of the martyrs in Sikh history were from Punjab and from the Punjabi people (as well as other parts of the Indian Subcontinent). Punjabi culture and S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikhs
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism (Sikhi), a monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Sikh'' has its origin in the word ' (), meaning 'disciple' or 'student'. Male Sikhs generally have ''Singh'' ('lion'/'tiger') as their last name, though not all Singhs are necessarily Sikhs; likewise, female Sikhs have ''Kaur'' ('princess') as their last name. These unique last names were given by the Gurus to allow Sikhs to stand out and also as an act of defiance to India's caste system, which the Gurus were always against. Sikhs strongly believe in the idea of "Sarbat Da Bhala" - "Welfare of all" and are often seen on the frontline to provide humanitarian aid across the world. Sikhs who have undergone the ''Amrit Sanchar'' ('baptism by Khanda'), an initiation ceremony, are from the day of their initiation known as Khalsa, and they m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mul Mantar
The Mūl Mantar ( pa, ਮੂਲ ਮੰਤਰ, ) is the opening verse of the Sikh scripture, the ''Guru Granth Sahib''. It consists of thirteen words in the Punjabi language, written in Gurmukhi script, and are the most widely known among the Sikhs. They summarize the essential teaching of Guru Nanak,Eleanor Nesbitt, "Sikhism: a very short introduction", , Oxford University Press, pp. 22-24 thus constituting a succinct doctrinal statement of Sikhism. It has been variously translated, with the interpretation of the first two words particularly contested. These are rendered as "There is one god", "One reality is", "This being is one" and others. Sometimes the disagreements include capitalizing g in god, or r in reality, which affects the implied meaning in English. Some consider it monotheistic, others monist. The general view favors the monotheistic interpretation, but not the Semitic understanding of monotheism. It is rather "Guru Nanak's mystical awareness of the one that is exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guru Nanak
Gurū Nānak (15 April 1469 – 22 September 1539; Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਨਾਨਕ; pronunciation: , ), also referred to as ('father Nānak'), was the founder of Sikhism and is the first of the ten Sikh Gurus. His birth is celebrated worldwide as Guru Nanak Gurpurab on '' Katak Pooranmashi'' ('full-moon of Kattak'), i.e. October–November. Nanak is said to have travelled far and wide across Asia teaching people the message of ''ik onkar'' (), who dwells in every one of his creations and constitutes the eternal Truth. With this concept, he would set up a unique spiritual, social, and political platform based on equality, fraternal love, goodness, and virtue. Nanak's words are registered in the form of 974 poetic hymns, or ''shabda'', in the holy text of Sikhism, the Guru Granth Sahib, with some of the major prayers being the ''Japji Sahib'' (; ''ji'' and ''sahib'' are suffixes signifying respect); the ''Asa di Var'' ('ballad of hope'); and the '' Sidh Gosht'' ('discussi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
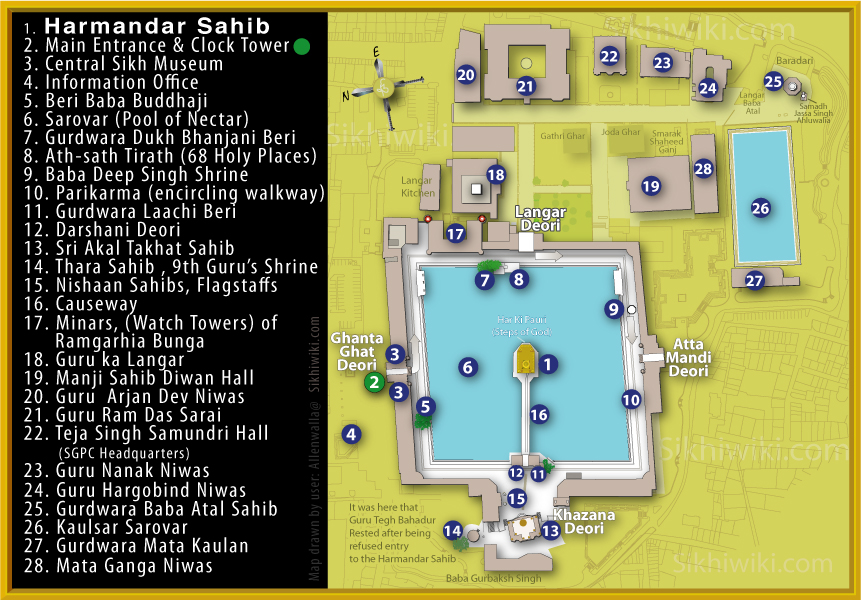
Sikh Architecture
Sikh architecture is a style of architecture that was developed under Sikh Empire during 18th and 19th century in the Punjab region. Due to its progressive style, it is constantly evolving into many newly developing branches with new contemporary styles. Although Sikh architecture was initially developed within Sikhism its style has been used in many non-religious buildings due to its beauty. 300 years ago, Sikh architecture was distinguished for its many curves and straight lines; Shri Keshgarh Sahib and the Sri Harmandir Sahib ( Golden Temple) are prime examples. Sikh Architecture is heavily influenced by Mughal and Islamic styles. The onion dome, frescoes, in-lay work, and multi-foil arches, are Mughal influences, more specially from Shah Jahan's period, whereas ''chattris'', oriel windows, bracket supported eaves at the string-course, and ornamented friezes are derived from elements of Rajput architecture. Apart from religious buildings, Sikh architecture includes secu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Language
Persian (), also known by its endonym Farsi (, ', ), is a Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and used officially within Iran, Afghanistan, and Tajikistan in three mutually intelligible standard varieties, namely Iranian Persian (officially known as ''Persian''), Dari Persian (officially known as ''Dari'' since 1964) and Tajiki Persian (officially known as ''Tajik'' since 1999).Siddikzoda, S. "Tajik Language: Farsi or not Farsi?" in ''Media Insight Central Asia #27'', August 2002. It is also spoken natively in the Tajik variety by a significant population within Uzbekistan, as well as within other regions with a Persianate history in the cultural sphere of Greater Iran. It is written officially within Iran and Afghanistan in the Persian alphabet, a derivation of the Arabic script, and within Tajikistan in the Tajik alphabet, a der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the List of largest empires, largest empire in history, spanning a total of from the Balkans and ancient Egypt, Egypt in the west to Central Asia and the Indus River, Indus Valley in the east. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Medes, Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the formal establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognized for its imposition of a successful model of centralized, bureaucratic administration; its multicultural policy; building comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the dynasty and the empire itself became indisputably Indian. The interests and futures of all concerned were in India, not in ancestral homelands in the Middle East or Central Asia. Furthermore, the Mughal empire emerged from the Indian historical experience. It was the end product of a millennium of Muslim conquest, colonization, and state-building in the Indian subcontinent." For some two hundred years, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus river basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of present-day Assam and Bangladesh in the east, and the uplands of the Deccan Plateau in South India. Quote: "The realm so defined and governed was a vast territory of some , rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
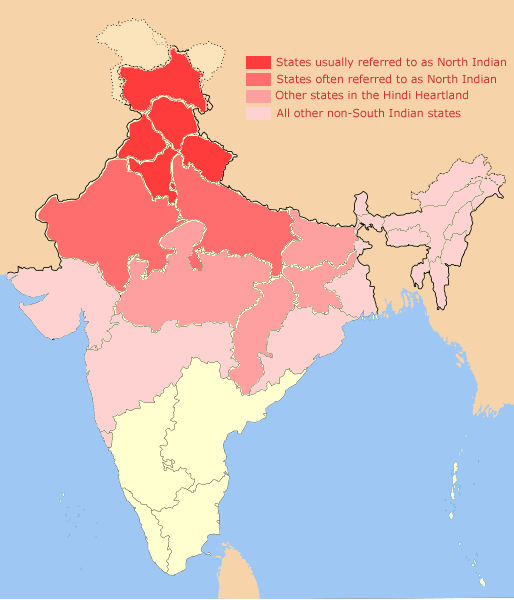
Northern India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia. The term North India has varying definitions. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Northern Zonal Council Administrative division included the states of Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab and Rajasthan and Union Territories of Chandigarh, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. The Ministry of Culture in its ''North Culture Zone'' includes the state of Uttarakhand but excludes Delhi whereas the Geological Survey of India includes Uttar Pradesh and Delhi but excludes Rajasthan and Chandigarh. Other states sometimes included are Bihar, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh and West Bengal. North India has been the historical centre of the Mughal Empire, the Delhi Sultanate and the British Indian Empire. It has a diverse culture, and includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baba Ram Rai
Baba Ram Rai (Gurmukhi: ਰਾਮ ਰਾਏ; ''rāma rā'ē''; 1645–1687) was the eldest son of the seventh Sikh Guru, Guru Har Rai, and the founder of the Ramraiyas, an unorthodox sect in Sikhism. He founded the Guru Ram Rai Darbar Sahib, a Darbar in Dehradun which was built in Indo-Islamic architecture style. Ram Rai's brother, Guru Har Krishan Guru Har Krishan (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰੂ ਹਰਿ ਕ੍ਰਿਸ਼ਨ, pronunciation: ; 7 July 1656 – 30 March 1664) was the eighth of the ten Sikh Gurus. At the age of five, he became the youngest Guru in Sikhism on 7 October 1661, ..., was the eighth of the ten Sikh Gurus. After his death, he was succeeded as head of the sect by mahant Aud Dass, who was helped by Ram Rai's widow, Panjab Kaur. References Bibliography * External links Guru Ram Rai Darbar Sahib - History Sikh warriors 1645 births 1687 deaths Punjabi people {{Sikhism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hukamnama
A Hukamnama ( Punjabi: ਹੁਕਮਨਾਮਾ, translit. ''Hukamanāmā''), in modern-times, refers to a hymn from the Guru Granth Sahib which is given as an injunction, order, or edict to Sikhs. It also refers to edicts issued by the contemporary Takhts. In the historical sense, it was used to refer to an issued injunction, order, or edict given by one of the Gurus of Sikhism or their officiated followers and associates during their lives. Nowadays, after the period of human gurus, The Hukumnama refers to a hymn from a randomly selected left hand side page from the Guru Granth Sahib on a daily basis in the morning. This is seen as the order of God for that particular day. The Hukamnama is distributed and then read aloud in Gurdwaras throughout the world. Etymology Hukamnama, is a compound of two words ''hukam'', meaning command or order, and ''namah'', meaning statement. Collections and research The tradition of issuing ''hukamnamas'' began in the period of the early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
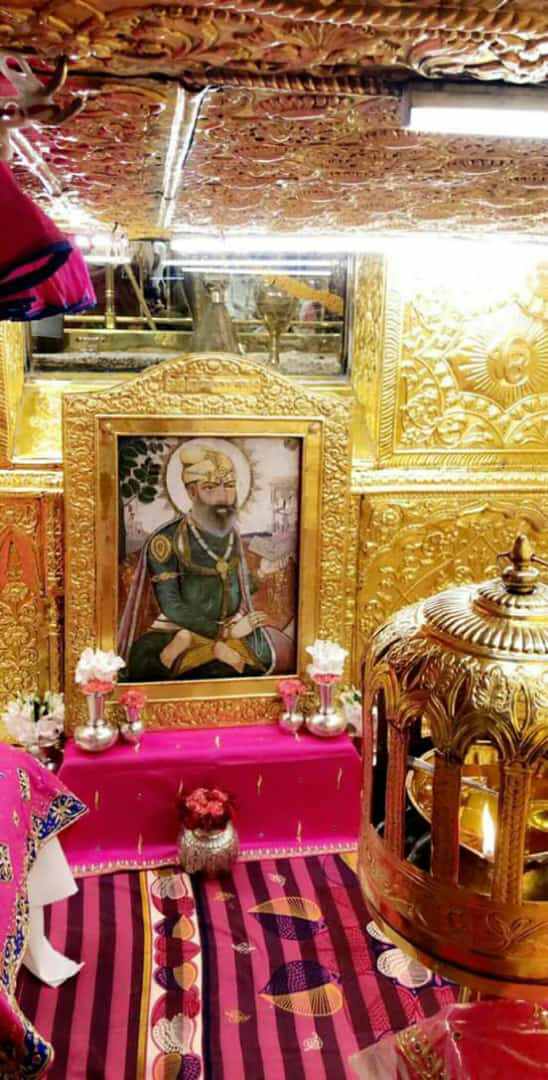
Guru Gobind Singh
Guru Gobind Singh (; 22 December 1666 – 7 October 1708), born Gobind Das or Gobind Rai the tenth Sikh Guru, a spiritual master, warrior, poet and philosopher. When his father, Guru Tegh Bahadur, was executed by Aurangzeb, Guru Gobind Singh was formally installed as the leader of the Sikhs at the age of nine, becoming the tenth and final human Sikh Guru. His four biological sons died during his lifetime – two in battle, two executed by the Mughal governor Wazir Khan.; Among his notable contributions to Sikhism are founding the '' Sikh'' warrior community called ''Khalsa'' in 1699 and introducing ''the Five Ks'', the five articles of faith that Khalsa Sikhs wear at all times. Guru Gobind Singh is credited with the ''Dasam Granth'' whose hymns are a sacred part of Sikh prayers and Khalsa rituals. He is also credited as the one who finalized and enshrined the ''Guru Granth Sahib'' as Sikhism's primary scripture and eternal Guru. Family and early life Gobind Singh was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guru Tegh Bahadur
Guru Tegh Bahadur ( Punjabi: ਗੁਰੂ ਤੇਗ਼ ਬਹਾਦਰ (Gurmukhi); ; 1 April 1621 – 11 November 1675) was the ninth of ten Gurus who founded the Sikh religion and the leader of Sikhs from 1665 until his beheading in 1675. He was born in Amritsar, Punjab, India in 1621 and was the youngest son of Guru Hargobind, the sixth Sikh guru. Considered a principled and fearless warrior, he was a learned spiritual scholar and a poet whose 115 hymns are included in ''Sri Guru Granth Sahib,'' the main text of Sikhism. Guru Tegh Bahadur was executed on the orders of Aurangzeb, the sixth Mughal emperor, in Delhi, India.;;; Sikh holy premises Gurudwara Sis Ganj Sahib and Gurdwara Rakab Ganj Sahib in Delhi mark the places of execution and cremation of Guru Tegh Bahadur. His martyrdom is remembered as the ''Shaheedi Divas of Guru Tegh Bahadur'' every year on 24 November. Biography Early life Guru Tegh Bahadur was the youngest son of Guru Hargobind, the sixth guru: Guru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







_02.jpg)

