|
Siegfried Czapski
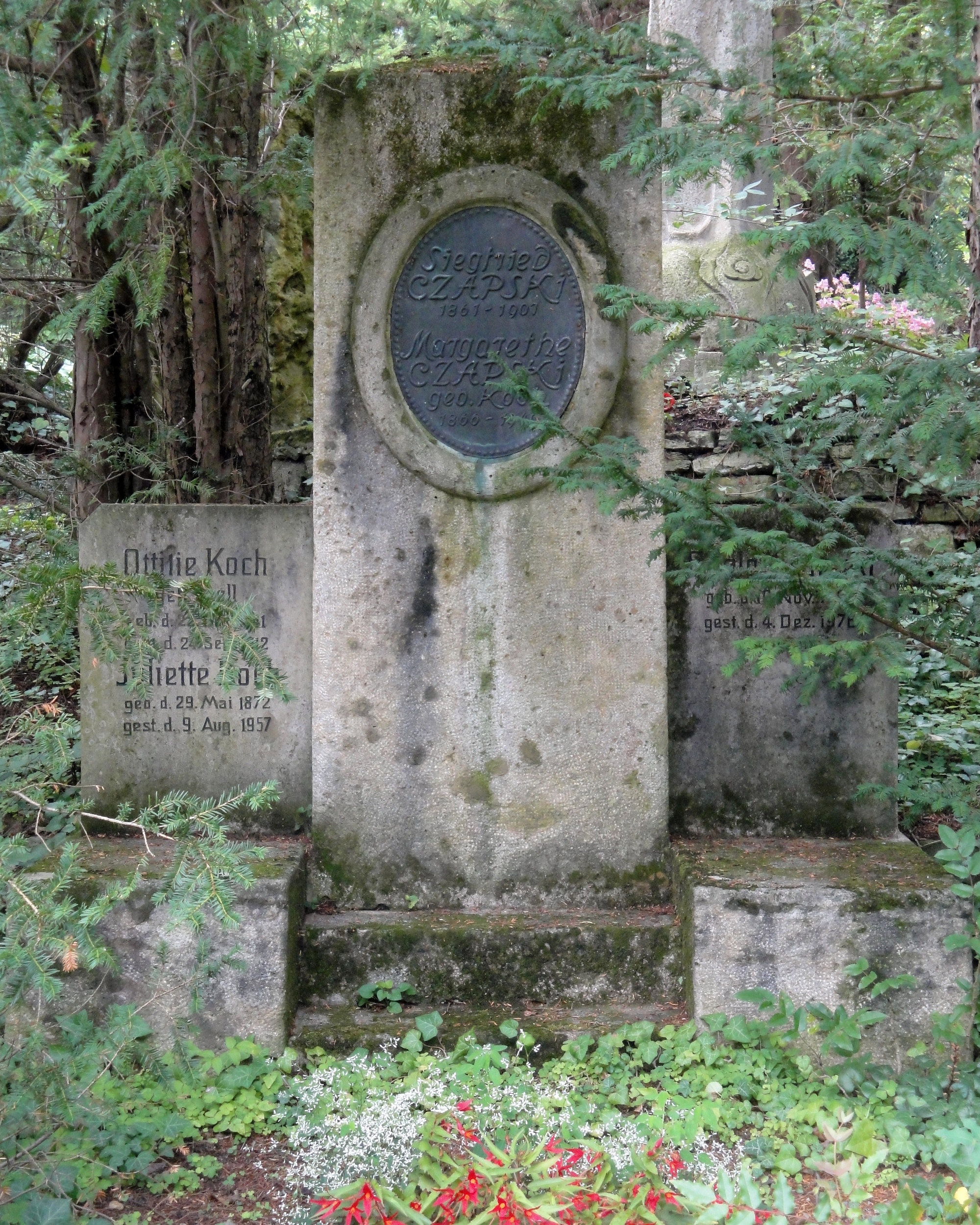
Siegfried Czapski (28 May 1861 – 29 June 1907) was a German physicist and optician. Childhood, school and university in Breslau (1870–1881) Czapski was the son of Simon Czapski (1826–1908) and his wife Rosalie Goldenring (1830-1916) on the Obra estate near Koschmin in the Province of Posen. His family was Jewish, and he was related to the physician Albert Neisser. In 1870 Czapski's father suffered a serious accident which left him unable to work. The family sold their estate and moved to Breslau (Wrocław) where, in 1872, eleven-year-old Czapski began attending school at the Maria Magdalenen Gymnasium. In 1879 he completed his university entrance examination (together with Wilhelm Prausnitz, Richard Reitzenstein and Felix Skutsch) and spent a semester studying at the University of Göttingen, attending lectures by Eduard Riecke (physics), Moritz Abraham Stern (mathematics) and Rudolf Hermann Lotze (philosophy). At the start of his second semester he switched to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siegfried Czapski
Siegfried Czapski (28 May 1861 – 29 June 1907) was a German physicist and optician. Childhood, school and university in Breslau (1870–1881) Czapski was the son of Simon Czapski (1826–1908) and his wife Rosalie Goldenring (1830-1916) on the Obra estate near Koschmin in the Province of Posen. His family was Jewish, and he was related to the physician Albert Neisser. In 1870 Czapski's father suffered a serious accident which left him unable to work. The family sold their estate and moved to Breslau (Wrocław) where, in 1872, eleven-year-old Czapski began attending school at the Maria Magdalenen Gymnasium. In 1879 he completed his university entrance examination (together with Wilhelm Prausnitz, Richard Reitzenstein and Felix Skutsch) and spent a semester studying at the University of Göttingen, attending lectures by Eduard Riecke (physics), Moritz Abraham Stern (mathematics) and Rudolf Hermann Lotze (philosophy). At the start of his second semester he switched to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oskar Emil Meyer
Oskar Emil Meyer (15 October 1834, Varel – 21 April 1909, Breslau) was a German physicist best known for his studies on the viscosity of gases. He was a younger brother to chemist Lothar von Meyer. Biography From 1854 he studied sciences at the universities of Heidelberg, Zurich and Königsberg, where he was a student of Franz Ernst Neumann. In 1860 he received his doctorate with a dissertation on the friction between two liquids, titled ''De mutua duorum fluidorum frictione''. In 1864 he succeeded Rudolf Lipschitz as an associate professor at the University of Breslau — teaching classes in mathematics and mathematical physics. During the following year he became a full professor at Breslau, and in 1867 succeeded Moritz Ludwig Frankenheim as director of the Physics Cabinet. Published works In 1899 his influential ''Die kinetische Theorie der Gase. In elementarer Darstellung mit mathematischen Zusätzen'' was translated into English and published with the title "Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eduard Zeller
Eduard Gottlob Zeller (; 22 January 1814, Kleinbottwar19 March 1908, Stuttgart) was a German philosopher and Protestant theologian of the Tübingen School of theology. He was well known for his writings on Ancient Greek philosophy, especially Pre-Socratic Philosophy, and most of all for his celebrated, multi-volume historical treatise ''The Philosophy of Greeks in their Historical Development'' (1844–52). Zeller was also a central figure in the revival of neo-Kantianism. Life Eduard Zeller was born at Kleinbottwar in Württemberg, the son of a government official. He was educated first at the Evangelical Seminaries of Maulbronn and Blaubeuren starting in 1831, and later at the University of Tübingen (the Tübinger Stift), then much under the influence of Hegel. He received his doctorate in 1836 with a thesis on Plato's Laws. In 1840 he was ''Privatdozent'' of theology at Tübingen, in 1847 professor of theology at Berne, and in 1849 professor of theology at Marburg, where he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopold Kronecker
Leopold Kronecker (; 7 December 1823 – 29 December 1891) was a German mathematician who worked on number theory, algebra and logic. He criticized Georg Cantor's work on set theory, and was quoted by as having said, "'" ("God made the integers, all else is the work of man").The English translation is from Gray. In a footnote, Gray attributes the German quote to "Weber 1891/92, 19, quoting from a lecture of Kronecker's of 1886". Weber, Heinrich L. 1891–1892Kronecker 2:5-23. (The quote is on p. 19.) Kronecker was a student and lifelong friend of . Biography Leopold Kronecker was born ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Julius Foerster
Wilhelm Julius Foerster (16 December 1832 – 18 January 1921) was a German astronomer. His name can also be written Förster, but is usually written "Foerster" even in most German sources where 'ö' is otherwise used in the text. Biography A native of Zielona Góra, Grünberg, Silesia, he studied at the University of Berlin and Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn, and worked as Johann Franz Encke's assistant. In 1860, he co-discovered asteroid 62 Erato with Oskar Lesser, the first co-discovery on record. He became professor of astronomy at the Humboldt University of Berlin, University of Berlin in 1863. After Encke's death in 1865, he became director of the Berlin Observatory and served in this position until 1904. In 1868 he was appointed director of the commission established by the North German Confederation, and continued from 1871 by the German Empire, for the determination of standards of measurement. In this capacity, he superintended the reorganization of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Physics
Experimental physics is the category of disciplines and sub-disciplines in the field of physics that are concerned with the observation of physical phenomena and experiments. Methods vary from discipline to discipline, from simple experiments and observations, such as Galileo's experiments, to more complicated ones, such as the Large Hadron Collider. Overview Experimental physics encompasses all the disciplines of physics that are concerned with data acquisition, data-acquisition methods, and the detailed conceptualization (beyond simple thought experiments) and realization of laboratory experiments. It is often contrasted with theoretical physics, which is more concerned with predicting and explaining the physical behaviour of nature than the acquisition of empirical data. Although experimental and theoretical physics are concerned with different aspects of nature, they both share the same goal of understanding it and have a symbiotic relationship. The former provides data a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopold Loewenherz
Leopold may refer to: People * Leopold (given name) * Leopold (surname) Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional characters * Leopold (''The Simpsons''), Superintendent Chalmers' assistant on ''The Simpsons'' * Leopold Bloom, the protagonist of James Joyce's ''Ulysses'' * Leopold "Leo" Fitz, a character on the television series ''Agents of S.H.I.E.L.D.'' * Leopold "Butters" Stotch, a character on the television series ''South Park'' * General Leopold von Flockenstuffen, a character in the BBC sitcom Allo 'Allo!'' * Leopold the Cat, Russian cartoon character Other arts, entertainment, and media * Leopold (prize), a biennial German prize for music for children * ''Kate & Leopold'', 2001 romantic comedy film * ''King Leopold's Ghost'', popular history book by Adam Hochschild * "King Leopold's Soliloquy", 1905 pamphlet by Mark Twain. * ''Leopold the Cat'', television series * Léopold Nord & Vous, Belgian musical band Brands and enterprises *Leopold (publisher), a Netherlands-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustav Kirchhoff
Gustav Robert Kirchhoff (; 12 March 1824 – 17 October 1887) was a German physicist who contributed to the fundamental understanding of electrical circuits, spectroscopy, and the emission of black-body radiation by heated objects. He coined the term black-body radiation in 1862. Several different sets of concepts are named "Kirchhoff's laws" after him, concerning such diverse subjects as black-body radiation and spectroscopy, electrical circuits, and thermochemistry. The Bunsen–Kirchhoff Award for spectroscopy is named after him and his colleague, Robert Bunsen. Life and work Gustav Kirchhoff was born on 12 March 1824 in Königsberg, Prussia, the son of Friedrich Kirchhoff, a lawyer, and Johanna Henriette Wittke. His family were Lutherans in the Evangelical Church of Prussia. He graduated from the Albertus University of Königsberg in 1847 where he attended the mathematico-physical seminar directed by Carl Gustav Jacob Jacobi, Franz Ernst Neumann and Friedrich Julius Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The Helmholtz Association, the largest German association of research institutions, is named in his honor. In the fields of physiology and psychology, Helmholtz is known for his mathematics concerning the eye, theories of vision, ideas on the visual perception of space, color vision research, the sensation of tone, perceptions of sound, and empiricism in the physiology of perception. In physics, he is known for his theories on the conservation of energy, work in electrodynamics, chemical thermodynamics, and on a mechanical foundation of thermodynamics. As a philosopher, he is known for his philosophy of science, ideas on the relation between the laws of perception and the laws of nature, the science of aesthetics, and ideas on the civilizing power of science. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humboldt University Of Berlin
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (german: Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, abbreviated HU Berlin) is a German public research university in the central borough of Mitte in Berlin. It was established by Frederick William III on the initiative of Wilhelm von Humboldt, Johann Gottlieb Fichte and Friedrich Ernst Daniel Schleiermacher as the University of Berlin () in 1809, and opened in 1810, making it the oldest of Berlin's four universities. From 1828 until its closure in 1945, it was named Friedrich Wilhelm University (german: Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität). During the Cold War, the university found itself in East Berlin and was ''de facto'' split in two when the Free University of Berlin opened in West Berlin. The university received its current name in honour of Alexander and Wilhelm von Humboldt in 1949. The university is divided into nine faculties including its medical school shared with the Freie Universität Berlin. The university has a student enrollment of around 32 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Heidenhain
Arthur is a common male given name of Brythonic origin. Its popularity derives from it being the name of the legendary hero King Arthur. The etymology is disputed. It may derive from the Celtic ''Artos'' meaning “Bear”. Another theory, more widely believed, is that the name is derived from the Roman clan '' Artorius'' who lived in Roman Britain for centuries. A common spelling variant used in many Slavic, Romance, and Germanic languages is Artur. In Spanish and Italian it is Arturo. Etymology The earliest datable attestation of the name Arthur is in the early 9th century Welsh-Latin text ''Historia Brittonum'', where it refers to a circa 5th to 6th-century Briton general who fought against the invading Saxons, and who later gave rise to the famous King Arthur of medieval legend and literature. A possible earlier mention of the same man is to be found in the epic Welsh poem ''Y Gododdin'' by Aneirin, which some scholars assign to the late 6th century, though this is still a mat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Freudenthal
Jacob Freudenthal (20 June 1839 – 1 June 1907) was a German philosopher. He was born at Bodenfelde, Hanover and died at Schreiberhau. Freudenthal received his education at the universities of Breslau and Göttingen, and at the rabbinical seminary of Breslau. After graduating from the University of Göttingen (1863) he became teacher of the in Wolfenbüttel (1863–64), whence be removed to Breslau as teacher in the rabbinical seminary there, a position which he resigned in 1888. In 1875, he became lecturer in philosophy at the University of Breslau; in 1878 he was elected assistant professor, in 1888 professor, of philosophy. He was a member of the senate of the university in 1894–96, and dean of the philosophical faculty in 1898–99. The Prussian Academy of Science sent him to England in 1888 to study English philosophy, and in 1898 to the Netherlands to research the life of Spinoza. The results of these voyages were his "Beiträge zur Englischen Philosophie", in the "Arc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)