|
Siege Of Syracuse (213–212 BC)
The siege of Syracuse by the Roman Republic took place in 213–212 BC. The Romans successfully stormed the Hellenistic city of Syracuse after a protracted siege, giving them control of the entire island of Sicily. During the siege, the city was protected by weapons developed by Archimedes. Archimedes, the great inventor and polymath, was slain at the conclusion of the siege by a Roman soldier, in contravention of the Roman proconsul Marcellus' instructions to spare his life. Prelude Sicily, which was wrested from Carthaginian control during the First Punic War (264–241 BC), was the first province of the Roman Republic not directly part of Italy. The Kingdom of Syracuse was an allied independent region in the south east of the island and a close ally of Rome during the long reign of King Hiero II. In 215 BC, Hiero's grandson, Hieronymus, came to the throne on his grandfather's death and Syracuse fell under the influence of an anti-Roman faction, including two of his un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides the Carthaginians were defeated. Macedonia, Syracuse and several Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Iberian and Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal, a younger brother of Hannibal, defended the Carthaginian colonial cities with mixed success before moving into Italy; and Africa, where Rome finally won the war. The First Punic War had ended in a Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and greatest naval war of antiquity, the two powers struggled for supremacy. The war was fought primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. After immense losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were defeated. The war began in 264 BC with the Romans gaining a foothold on Sicily at Messana (modern Messina). The Romans then pressed Syracuse, the only significant independent power on the island, into allying with them and laid siege to Carthage's main base at Akragas. A large Carthaginian army attempted to lift the siege in 262 BC but was heavily defeated at the Battle of Akragas. The Romans then built a navy to challenge the Carthaginians', and using novel tactics inflicted severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stalemate
Stalemate is a situation in the game of chess where the player whose turn it is to move is not in check and has no legal move. Stalemate results in a draw. During the endgame, stalemate is a resource that can enable the player with the inferior position to draw the game rather than lose. In more complex positions, stalemate is much rarer, usually taking the form of a swindle that succeeds only if the superior side is inattentive. Stalemate is also a common theme in endgame studies and other chess problems. The outcome of a stalemate was standardized as a draw in the 19th century. Before this standardization, its treatment varied widely, including being deemed a win for the stalemating player, a half-win for that player, or a loss for that player; not being permitted; and resulting in the stalemated player missing a turn. Stalemate rules vary in other games of the chess family. Etymology and usage The first recorded use of stalemate is from 1765. It is a compounding of Middl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thesaurus Opticus Titelblatt
A thesaurus (plural ''thesauri'' or ''thesauruses'') or synonym dictionary is a reference work for finding synonyms and sometimes antonyms of words. They are often used by writers to help find the best word to express an idea: Synonym dictionaries have a long history. The word 'thesaurus' was used in 1852 by Peter Mark Roget for his ''Roget's Thesaurus''. While some thesauri, such as ''Roget's Thesaurus'', group words in a hierarchy, hierarchical hypernym, hypernymic taxonomy (general), taxonomy of concepts, others are organized alphabetically or in some other way. Most thesauri do not include definitions, but many dictionaries include listings of synonyms. Some thesauri and dictionary synonym notes characterize the distinctions between similar words, with notes on their "connotations and varying shades of meaning".''American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language'', 5th edition, Houghton Mifflin Harcourt 2011, , p. xxvii Some synonym dictionaries are primarily concerned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
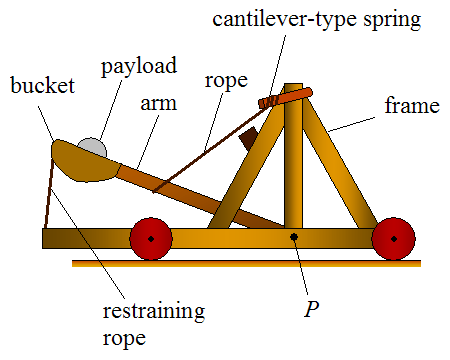
Onager (siege Weapon)
The onager (British , , U.S. /ˈɑnədʒər/) was a Roman torsion powered siege engine. It is commonly depicted as a catapult with a bowl, bucket, or sling at the end of its throwing arm. The onager was first mentioned in 353 AD by Ammianus Marcellinus, who described onagers as the same as a scorpion. The onager is often confused with the later mangonel, a "traction trebuchet" that replaced torsion powered siege engines in the 6th century CE. Etymology According to two authors of the later Roman Empire who wrote on military affairs, the onager derived its name from the kicking action of the machine that threw stones into the air, as did the hooves of the wild ass, the onager, which was native to the eastern part of the empire. Design The onager consisted of a large frame placed on the ground to whose front end a vertical frame of solid timber was rigidly fixed. A vertical spoke that passed through a rope bundle fastened to the frame had a cup, bucket, or sling attached which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballista
The ballista (Latin, from Greek βαλλίστρα ''ballistra'' and that from βάλλω ''ballō'', "throw"), plural ballistae, sometimes called bolt thrower, was an ancient missile weapon that launched either bolts or stones at a distant target. Developed from earlier Greek weapons, it relied upon different mechanics, using two levers with torsion springs instead of a tension prod (the bow part of a modern crossbow). The springs consisted of several loops of twisted skeins. Early versions projected heavy darts or spherical stone projectiles of various sizes for siege warfare. It developed into a smaller precision weapon, the '' scorpio'', and possibly the ''polybolos''. Greek weapon The early ballistae in Ancient Greece were developed from two weapons called oxybeles and gastraphetes. The gastraphetes ('belly-bow') was a handheld crossbow. It had a composite prod and was spanned by bracing the front end of the weapon against the ground while placing the end of a slider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archimedes' Heat Ray
Archimedes' heat ray is a device that Archimedes is purported to have used to burn attacking Roman ships during the Siege of Syracuse (213–212 BC), Siege of Syracuse (c. 214–212 BC). It does not appear in the surviving works of Archimedes and is described by historians writing many years after the siege. Historical accounts of the heat ray The 2nd century AD author Lucian wrote that during the Siege of Syracuse, Archimedes destroyed enemy ships with fire. Centuries later, Anthemius of Tralles mentions burning-glasses as Archimedes' weapon. The device was used to focus sunlight onto approaching ships, causing them to catch fire. Modern attempts to recreate the heat ray The heat ray has been the subject of ongoing debate about its credibility since the Renaissance. René Descartes rejected it as false, while modern researchers have attempted to recreate the effect using only the means that would have been available to Archimedes. It has been suggested that a large array ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirror
A mirror or looking glass is an object that Reflection (physics), reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror will show an image of whatever is in front of it, when focused through the lens of the eye or a camera. Mirrors reverse the direction of the image in an equal yet opposite angle from which the light shines upon it. This allows the viewer to see themselves or objects behind them, or even objects that are at an angle from them but out of their field of view, such as around a corner. Natural mirrors have existed since prehistoric times, such as the surface of water, but people have been manufacturing mirrors out of a variety of materials for thousands of years, like stone, metals, and glass. In modern mirrors, metals like silver or aluminium are often used due to their high reflectivity, applied as a thin coating on glass because of its naturally smooth and very Hardness (materials science), hard surface. A mirror is a Wave (physics), wave reflector. Light consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claw Of Archimedes
The Claw of Archimedes ( grc, Ἁρπάγη, translit=harpágē, lit=snatcher; also known as the iron hand) was an ancient weapon devised by Archimedes to defend the seaward portion of Syracuse's city wall against amphibious assault. Although its exact nature is unclear, the accounts of ancient historians seem to describe it as a sort of crane equipped with a grappling hook that was able to drop an attacking ship partly down in to the water, then either cause the ship to capsize or suddenly drop it. It was dropped onto enemy ships, which would then swing on to defensive forces and destroy them. These machines featured prominently during the Second Punic War in 214 BC, when the Roman Republic attacked Syracuse with a fleet of 60 quinqueremes under Marcus Claudius Marcellus. When the Roman fleet approached the city walls under cover of darkness, the machines were deployed, sinking many ships and throwing the attack into confusion. Historians such as Livy attributed heavy Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grappling Hook
A grappling hook or grapnel is a device that typically has multiple hooks (known as ''claws'' or ''flukes'') attached to a rope; it is thrown, dropped, sunk, projected, or fastened directly by hand to where at least one hook may catch and hold onto objects. Generally, grappling hooks are used to temporarily secure one end of a rope. They may also be used to dredge for submerged objects. The device was invented by the Romans in approximately 260 BC. The grappling hook was originally used in naval warfare to catch ship rigging so that it could be boarded. Design A common design has a central shaft with a hole ("eye") at the shaft base to attach the rope, and three or four equally spaced hooks at the end, arranged so that at least one is likely to catch on some protuberance of the target. Some modern designs feature folding hooks to resist unwanted attachment. Most grappling hooks are thrown by hand, but some used in rescue work are propelled by compressed air (e.g., the Plum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Tower
A Roman siege tower or breaching tower (or in the Middle Ages, a belfry''Castle: Stephen Biesty's Cross-Sections''. Dorling Kindersley Pub (T); 1st American edition (September 1994). Siege towers were invented in 300 BC. ) is a specialized siege engine, constructed to protect assailants and ladders while approaching the defensive walls of a fortification. The tower was often rectangular with four wheels with its height roughly equal to that of the wall or sometimes higher to allow archers to stand on top of the tower and shoot arrows into the fortification. Because the towers were wooden and thus flammable, they had to have some non-flammable covering of iron or fresh animal skins. Used since the 11th century BC by the Babylonians and Assyrians in the ancient Near East, the 4th century BC in Europe and also in antiquity in the Far East, siege towers were of unwieldy dimensions and, like trebuchets, were therefore mostly constructed on site of the siege. Taking considerable time t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
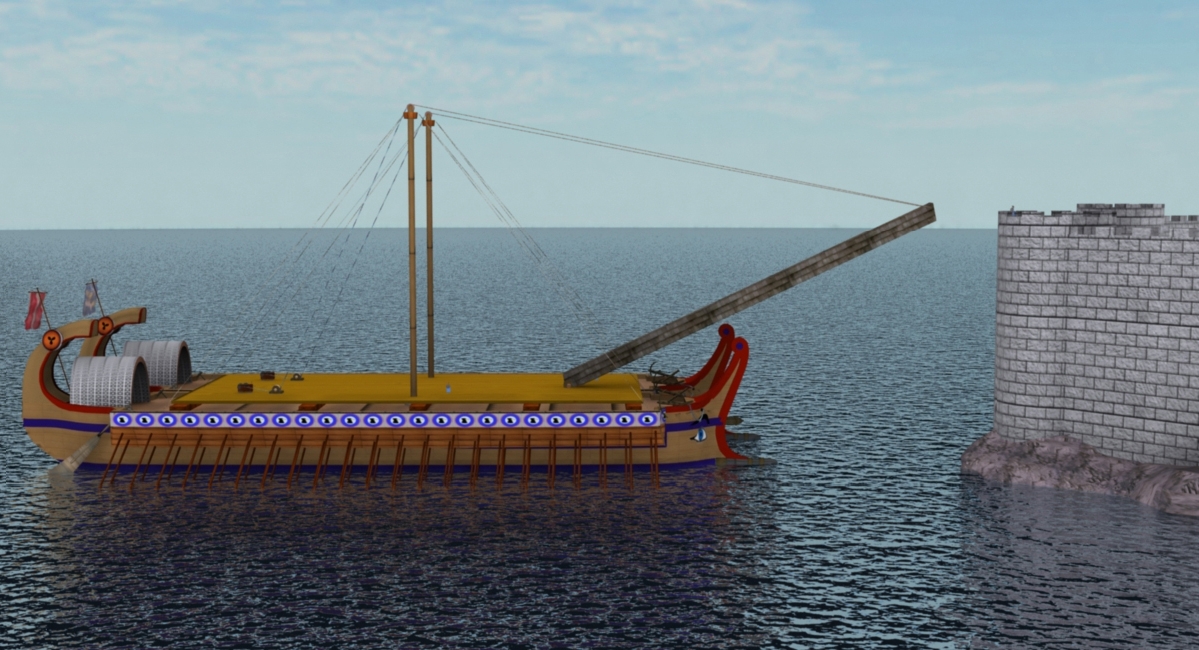
Sambuca (siege Engine)
The sambuca ( grc, σαμβύκη) was a ship-borne siege engine which was invented by Heracleides of Tarentum and was first used unsuccessfully by Marcus Claudius Marcellus during the Roman siege of Syracuse in 213 BC. Polybius describes usage of the machine: As well as these vessels he had eight quinqueremes in pairs. Each pair had had their oars removed, one on the port and the other on the starboard side, and then these had been lashed together on the sides thus left bare. On these double vessels, rowed by the outer oars of each of the pair, they brought up under the walls some engines called "Sambucae", the construction of which was as follows: A ladder was made four feet broad, and of a height to reach the top of the wall from the place where its foot had to rest; each side of the ladder was protected by a railing, and a covering or pent-house was added overhead. It was then placed so that its foot rested across the sides of the lashed-together vessels, which touched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |