|
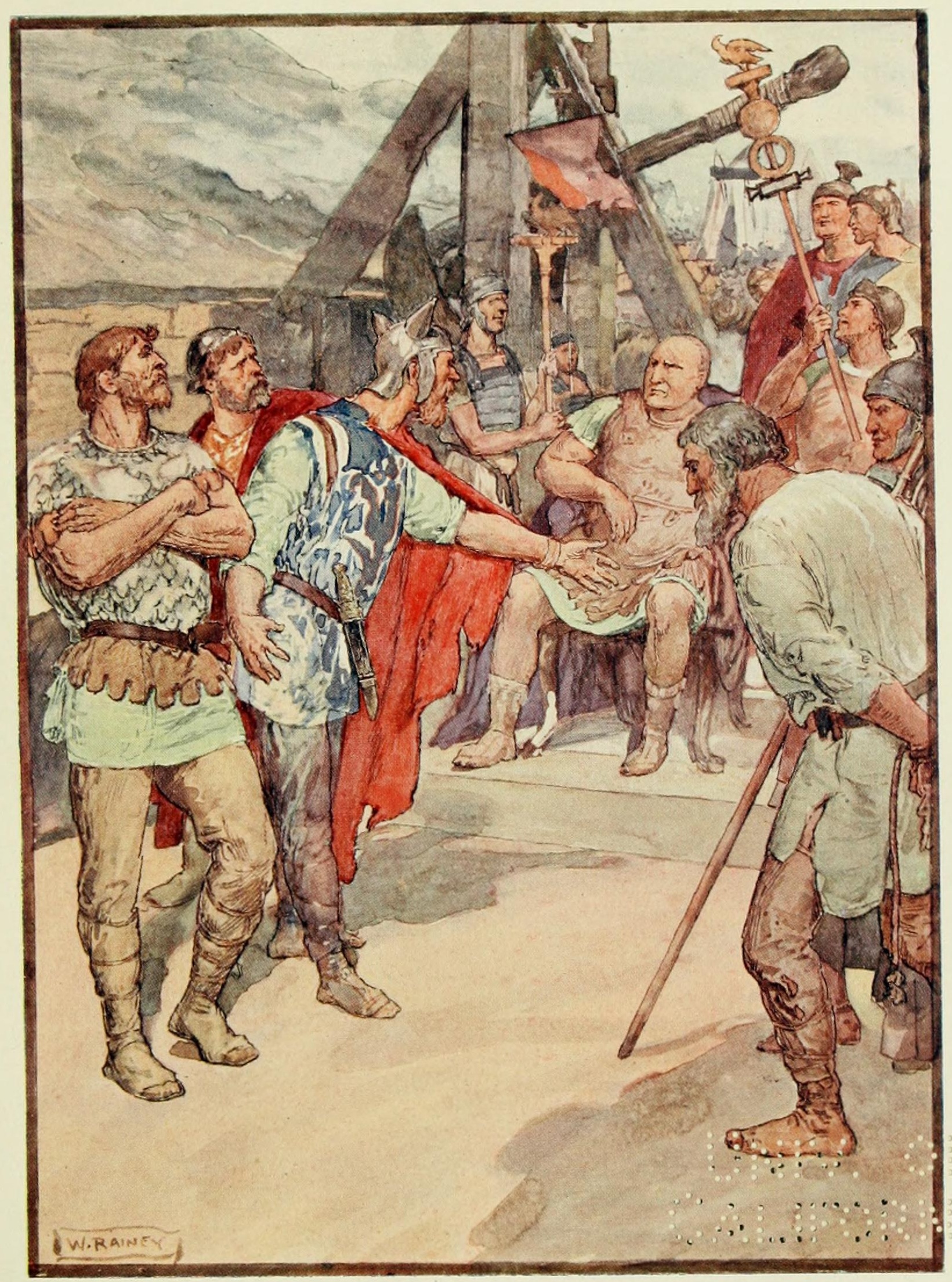
Siege Of Cirta
The siege of Cirta was fought between the rival Numidia, Numidian kings Adherbal (king of Numidia), Adherbal and Jugurtha in 113BC. They were contesting the throne of Numidia after the death of King Micipsa. Jugurtha invaded Adherbal's territory, defeated him and besieged him in his capital Cirta. Two Roman deputations attempted to negotiate a settlement, but Jugurtha ignored them. When the city surrendered he tortured Adherbal to death and executed all who had bourne arms against him, including numerous Romans. This last action was to spark the outbreak of the Jugurthine War between Rome and Numidia. Background Numidia was a kingdom located in North Africa (roughly corresponding to northern modern day Algeria) adjacent to what had been Roman Republic, Rome's arch enemy, Carthage. King Masinissa, who was a steadfast ally of Rome in the Third Punic War, died in 149, and was succeeded by his son Micipsa, who ruled from 149 to 118 BC. At the time of his death Micipsa had three poten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jugurthine War
The Jugurthine War ( la, Bellum Iugurthinum; 112–106 BC) was an armed conflict between the Roman Republic and king Jugurtha of Numidia, a kingdom on the north African coast approximating to modern Algeria. Jugurtha was the nephew and adopted son of Micipsa, King of Numidia, whom he succeeded on the throne, overcoming his rivals through assassination, war, and bribery. The war constituted an important phase in the Roman subjugation of Northern Africa, and the rise of the empire, but Numidia did not become a Roman province until 46 BC. Following Jugurtha's usurpation of the throne of Numidia, a loyal ally of Rome since the Punic Wars, Rome felt compelled to intervene. Jugurtha and Numidia Numidia was a kingdom located in North Africa (roughly corresponding to northern modern day Algeria) adjacent to what had been Rome's arch enemy, Carthage. King Masinissa, who was a steadfast ally of Rome in the Third Punic War, died in 149, and was succeeded by his son Micipsa, who ruled 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Senate
The Roman Senate ( la, Senātus Rōmānus) was a governing and advisory assembly in ancient Rome. It was one of the most enduring institutions in Roman history, being established in the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC). It survived the overthrow of the Roman monarchy in 509 BC; the fall of the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC; the division of the Roman Empire in AD 395; and the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476; Justinian's attempted reconquest of the west in the 6th century, and lasted well into the Eastern Roman Empire's history. During the days of the Roman Kingdom, most of the time the Senate was little more than an advisory council to the king, but it also elected new Roman kings. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Roman Republic. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the various executive magistr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
110s BC Conflicts
Eleven or 11 may refer to: *11 (number), the natural number following 10 and preceding 12 * one of the years 11 BC, AD 11, 1911, 2011, or any year ending in 11 Literature * ''Eleven'' (novel), a 2006 novel by British author David Llewellyn *''Eleven'', a 1970 collection of short stories by Patricia Highsmith *''Eleven'', a 2004 children's novel in The Winnie Years by Lauren Myracle *''Eleven'', a 2008 children's novel by Patricia Reilly Giff *''Eleven'', a short story by Sandra Cisneros Music *Eleven (band), an American rock band * Eleven: A Music Company, an Australian record label *Up to eleven, an idiom from popular culture, coined in the movie ''This Is Spinal Tap'' Albums * ''11'' (The Smithereens album), 1989 * ''11'' (Ua album), 1996 * ''11'' (Bryan Adams album), 2008 * ''11'' (Sault album), 2022 * ''Eleven'' (Harry Connick, Jr. album), 1992 * ''Eleven'' (22-Pistepirkko album), 1998 * ''Eleven'' (Sugarcult album), 1999 * ''Eleven'' (B'z album), 2000 * ''Eleven'' (Reamonn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Numidia
Numidia (Berber: ''Inumiden''; 202–40 BC) was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians located in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up modern-day Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia, Libya, and some parts of Morocco. The polity was originally divided between the Massylii in the east and the Masaesyli in the west. During the Second Punic War (218–201 BC), Masinissa, king of the Massylii, defeated Syphax of the Masaesyli to unify Numidia into one kingdom. The kingdom began as a sovereign state and later alternated between being a Roman province and a Roman client state. Numidia, at its largest extent, was bordered by Mauretania to the west, at the Moulouya River, Africa Proconsularis to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the north, and the Sahara to the south. It was one of the first major states in the history of Algeria and the Berbers. History Independence The Greek historians referred to these peoples as "Ν� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tullianum
The Mamertine Prison ( it, Carcere Mamertino), in antiquity the Tullianum, was a prison (''carcer'') with a dungeon (''oubliette'') located in the Comitium in ancient Rome. It is said to have been built in the 7th century BC and was situated on the northeastern slope of the Capitoline Hill, facing the Curia and the imperial fora of Nerva, Vespasian, and Augustus. Located between it and the Tabularium (record house) was a flight of stairs leading to the Arx of the Capitoline known as the Gemonian stairs. The church of San Giuseppe dei Falegnami now stands above the Mamertine. Name and origin The origins of the prison's names are uncertain. The traditional derivation of "Tullianum" is from the name of one of the Roman kings Tullus Hostilius or Servius Tullius (the latter is found in Livy, Varro, and also Sallust); there is an alternative theory that it is from the archaic Latin ''tullius'' "a jet of water", in reference to the cistern. The name "Mamertine" is medieval in origin, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius (; – 13 January 86 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. Victor of the Cimbric and Jugurthine wars, he held the office of consul an unprecedented seven times during his career. He was also noted for his important reforms of Roman armies. He set the precedent for the shift from the militia levies of the middle Republic to the professional soldiery of the late Republic; he also improved the '' pilum'', a javelin, and made large-scale changes to the logistical structure of the Roman army. Rising from a well-off provincial Italian family in Arpinum, Marius acquired his initial military experience serving with Scipio Aemilianus at the Siege of Numantia in 134 BC. He won election as tribune of the plebs in 119 BC and passed a law limiting aristocratic interference in elections. Barely elected praetor in 115 BC, he next became the governor of Further Spain where he campaigned against bandits. On his return from Spain he married Julia, the aunt of J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quintus Metellus Numidicus
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Numidicus (c. 155 BC – 91 BC) was an ancient Roman statesman and general, he was a leader of the Optimates, the conservative faction of the Roman Senate. He was a bitter political opponent of Gaius Marius. He was consul in 109 BC, in that capacity he commanded the Roman forces in Africa during the Jugurthine War. In 107 BC, he was displaced from his command by Marius. On his return he was granted a triumph and the cognomen Numidicus. He later became a censor, entering into exile in opposition to Marius. Metellus Numidicus enjoyed a reputation for integrity in an era when Roman politics was increasingly corrupt. William Smith, ed. (1867)"Metellus Numidicus" ''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology''. Youth and ''cursus honorum'' The son of Lucius Caecilius Metellus Calvus, in his youth he was sent to Athens where he studied under Carneades, celebrated philosopher and great master of oratory. He returned ostensibly cultured and with bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribune
Tribune () was the title of various elected officials in ancient Rome. The two most important were the tribunes of the plebs and the military tribunes. For most of Roman history, a college of ten tribunes of the plebs acted as a check on the authority of the senate and the annual magistrates, holding the power of ''ius intercessionis'' to intervene on behalf of the plebeians, and veto unfavourable legislation. There were also military tribunes, who commanded portions of the Roman army, subordinate to higher magistrates, such as the consuls and praetors, promagistrates, and their legates. Various officers within the Roman army were also known as tribunes. The title was also used for several other positions and classes in the course of Roman history. Tribal tribunes The word ''tribune'' is derived from the Roman tribes. The three original tribes known as the ''Ramnes'' or ''Ramnenses'', ''Tities'' or ''Titienses,'' and the ''Luceres,'' were each headed by a tribune, who rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Memmius (proconsul Of Macedonia)
Gaius Memmius (c. 140s BC – December 100 BC) was a Roman politician. He was murdered by Gaius Servilius Glaucia during the disturbances that rocked Rome during the violent uprising and suppression of Lucius Appuleius Saturninus. Career Gaius Memmius was elected tribune of the plebs in 111 BC, and was instrumental in relaunching the Jugurthine War after Jugurtha’s surrender in 111 BC. During his tribunate, he accused the consul Lucius Calpurnius Bestia, the senator Marcus Aemilius Scaurus and other aristocrats of accepting bribes from King Jugurtha. He summoned Jugurtha to appear in Rome, and promised him safe conduct in order that he may be questioned, but when Jugurtha arrived, Memmius was prevented from questioning the king by his colleague Gaius Baebius, whom Jugurtha bribed to impose his veto. Memmius served as praetor sometime between in 107 and 102 BC, and this was followed by the proconsular governorship of Macedonia. Then, Marcus Aemilius Scaurus prosecuted Memmius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utica, Tunisia
Utica () was an ancient Phoenician and Carthaginian city located near the outflow of the Medjerda River into the Mediterranean, between Carthage in the south and Hippo Diarrhytus (present-day Bizerte) in the north. It is traditionally considered to be the first colony to have been founded by the Phoenicians in North Africa. After Carthage's loss to Rome in the Punic Wars, Utica was an important Roman colony for seven centuries. Today, Utica no longer exists, and its remains are located in Bizerte Governorate in Tunisia – not on the coast where it once lay, but further inland because deforestation and agriculture upriver led to massive erosion and the Medjerda River silted over its original mouth."Utica (Utique) Tunisia" ''The Princeton Encyclopedia of Classical Sites. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Aemilius Scaurus (consul 115 BC)
{{hndis, Scaurus, Marcus ...
Marcus Scaurus may refer to: * Marcus Aemilius Scaurus (consul 115 BC) * Marcus Aemilius Scaurus (praetor 56 BC) * Marcus Aemilius Scaurus (son of Mucia) * Marcus Aurelius Scaurus Marcus Aurelius Scaurus (died 105 BC) was a Roman politician and general during the Cimbrian War. After one of the consul designates was prosecuted and condemned, Scaurus was made consul suffectus in 108 BC. In 105 BC he went as a senior legate wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ampsaga
The Rhumel River (also Rhummel, Rummel, El-Kebîrl; Arabic: وادي الرمال) is the largest river in the Constantine region of Algeria. Geography The source of the Rhumel river is in the Ferdjioua (Mila) mountains. From there it meanders through the Constantine plateau, then narrows considerably north of Aïn Smara where it forms an almost complete oxbow before infiltrating, in a SW/NE orientation, the Djebel El Hadjar limestone tables and the Aïn El Bey plateau. From here, it flows into a narrow ravine near Boussouf, goes through several curves, and becomes very narrow again at a place called "the Roman arches". This leads to the entrance to the Kheneg gorges, whose huge eastern pillar, called "Tiddis mountain", is the site of Tiddis a significant Berber and Roman city that was explored by the archaeologist André Berthier. Not far away is the village of Messaoud Boudjriou (previously Aïn-Kerma) and its old antimony mine. The lower Rhumel (or Oued-el-Kebir) passes th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_-_Facciata_(Mamertinum).jpg)