|
Sica Alexandrescu
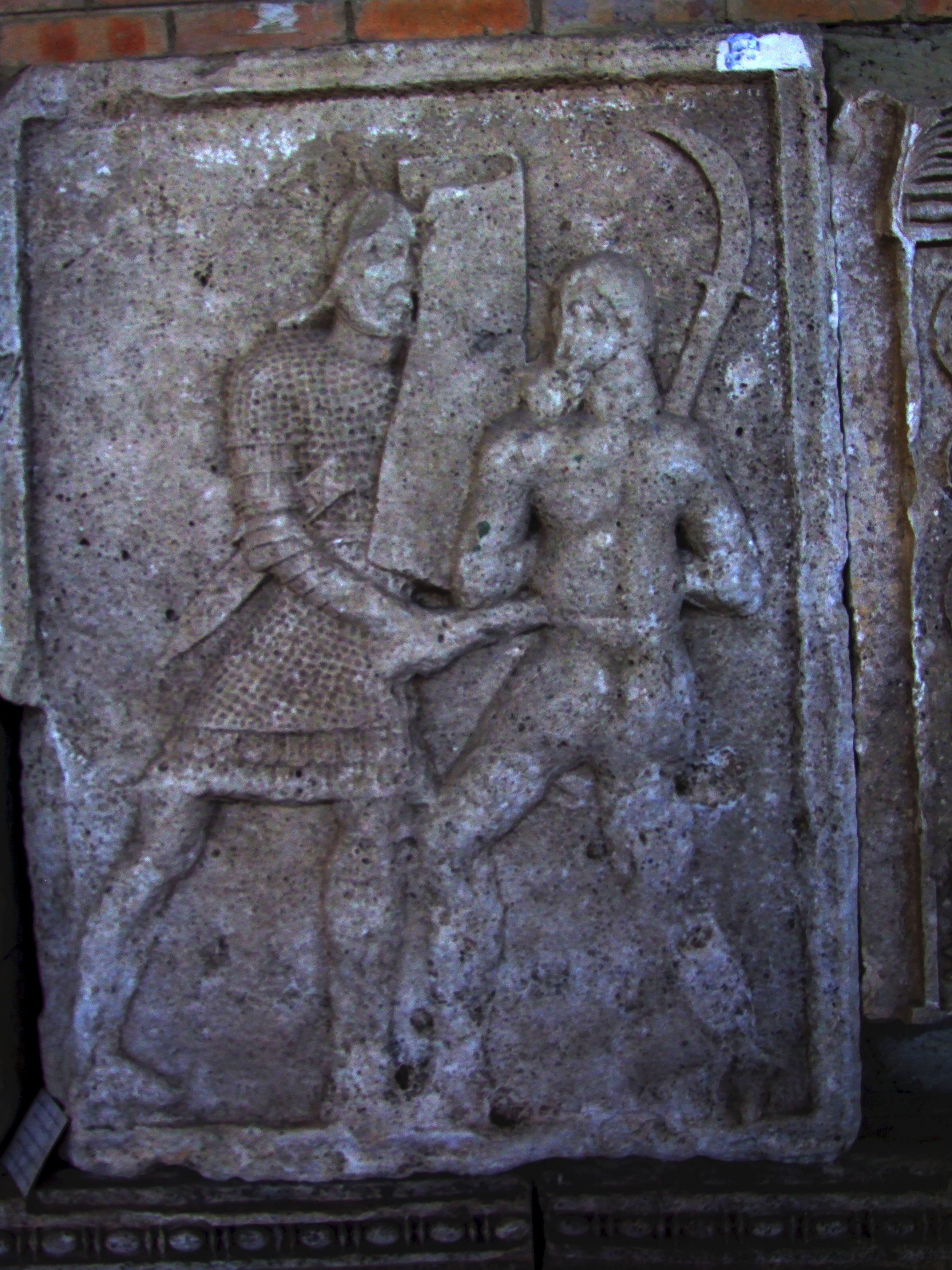
The sica was a short sword or large dagger of ancient Illyrians, Thracians and Dacians, used in Ancient Rome too, originating in the Halstatt culture. It was originally depicted as a curved sword (see the Zliten mosaic as well as numerous oil lamps) and many examples have been found in what are today Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Serbia and Romania. It is also depicted on Trajan's Column; notably the Dacian king Decebalus is depicted dying by suicide with one. Etymology Possibly from Proto-Albanian ''tsikā'' (whence Albanian ''thikë'', "knife"), from Proto-Indo-European ''ḱey''- ("to sharpen") possibly via Illyrian. According to ''Dictionnaire des Antiquités Grecques et Romaines'' the name ''Sica'' comes from Proto-Indo-European root ''sek-'', meaning "to cut", "to section", however De Vaan declares any connection to Proto-Indo-European ''sek''- to be formally impossible. Illyrian The Romans regarded the sica as a distinctive Illyrian weapon. The principa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
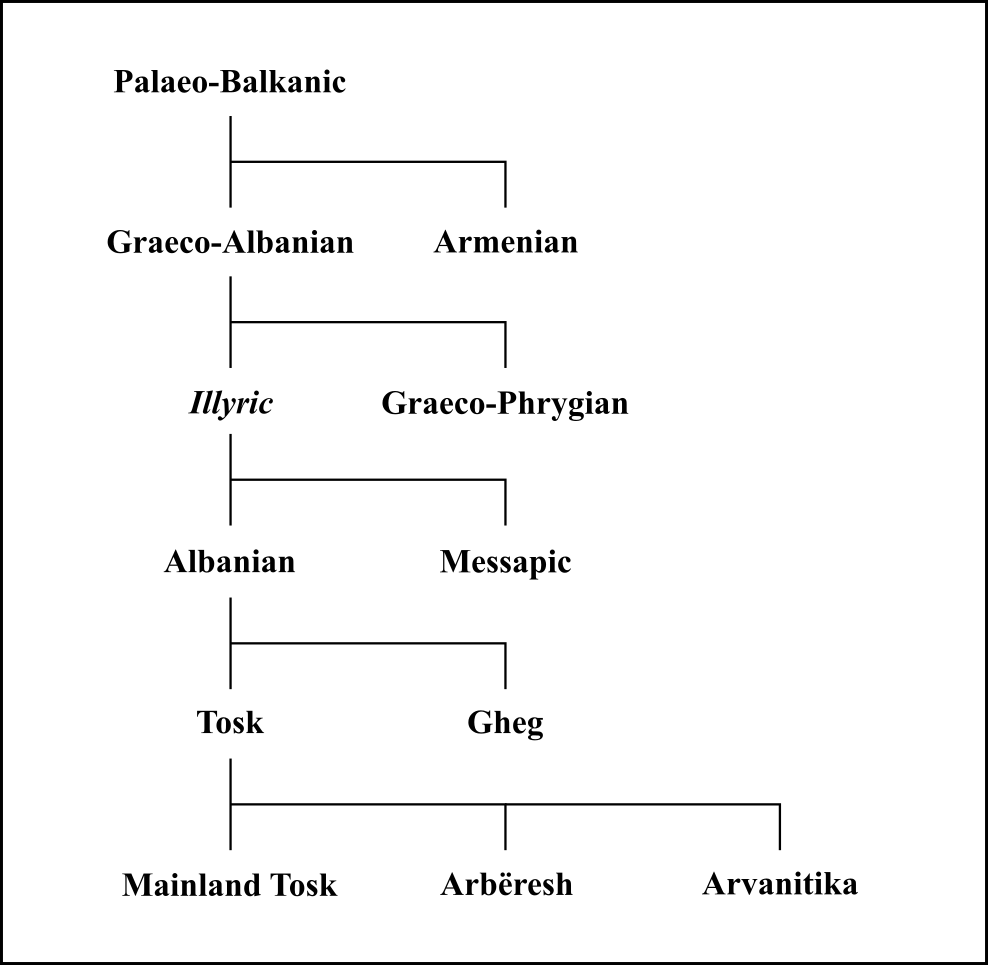
Proto-Albanian
The Proto-Albanian language is the unattested language from which Albanian later developed. Albanian evolved from an ancient Paleo-Balkan language, traditionally thought to be Illyrian, or otherwise a totally unattested Balkan Indo-European language that was closely related to Illyrian and Messapic,; which is sometimes also referred to as Albanoid. Proto-Albanian is reconstructed by way of the comparative method between the Tosk and Gheg dialects, as well as the treatment of loanwords, the most important of which are those from Latin (dated by De Vaan to the period 167 BCE to 400 CE) and from Slavic (dated from 600 CE onward). The evidence from loanwords allows linguists to construct in great detail the shape of native words at the points of major influxes of loans from well-attested languages. Proto-Albanian is broken up into different stages which are usually delimited by the onset of contact with different well-attested languages. Its earliest stages are dated to the ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falx
The ''falx'' was a weapon with a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge used by the Thracians and Dacians. The name was later applied to a siege hook used by the Romans. Etymology ''Falx'' is a Latin word originally meaning 'sickle' but was later used to mean any of a number of tools that had a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge like a sickle. ''Falx'' was thus also used to mean the weapon of the Thracians and Dacians, and the Roman siege hook. Dacian ''falx'' In Latin texts, the weapon was described as an ' (whence ''falcata'') by Ovid in ''Metamorphose'' and as a ' by Juvenal in ''Satiriae''. The Dacian ''falx'' came in two sizes: one-handed and two-handed. The shorter variant was called ''sica'' (sickle) in the Dacian language (Valerius Maximus, III, 2.12) with a blade length that varied but was usually around long with a handle 1/3 longer than the blade. The two-handed ''falx'' was a polearm. It consisted of a long wooden shaft with a long curved i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacian Warfare
The history of Dacian warfare spans from c. 10th century BC up to the 2nd century AD in the region defined by Ancient Greek and Latin historians as Dacia, populated by a collection of Thracian, Ionian, and Dorian tribes. It concerns the armed conflicts of the List of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia#Getic-Dacian, Dacian tribes and their kingdoms in the Balkans. Apart from conflicts between Dacians and neighboring nations and tribes, numerous wars were recorded among List of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia#Getic-Dacian, Dacians too. Mythological Tribal wars The Dacians fought amongst each other but were later united under Burebista. However, after his death in 44 BC, the empire again descended into conflict culminating in a full-scale civil war. This led to the division of Burebista's empire into five separate kingdoms, severely weakening the Dacian's defensive capabilities against enemies, particularly Rome. The Dacian tribes were again consolidated under Decebalus, who a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicarii
The Sicarii (Modern Hebrew: סיקריים ''siqariyim'') were a splinter group of the Jewish Zealots who, in the decades preceding Jerusalem's destruction in 70 CE, strongly opposed the Roman occupation of Judea and attempted to expel them and their sympathizers from the area. The Sicarii carried ''sicae'', or small daggers, concealed in their cloaks. At public gatherings, they pulled out these daggers to attack Romans and alleged Roman sympathizers alike, blending into the crowd after the deed to escape detection. The Sicarii are regarded as one of the earliest known organized assassination units of cloak and daggers, predating the Islamic Hashishin and Japanese ninja by centuries.Pichtel, John, ''Terrorism and WMDs: Awareness and Response'', CRC Press (April 25, 2011) p.3-4. Ross, Jeffrey Ian, ''Religion and Violence: An Encyclopedia of Faith and Conflict from Antiquity to the Present'', Routledge (January 15, 2011), Chapter: Sicarii. The derived Spanish Spanish might refer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murmillo
The murmillo (also sometimes spelled "mirmillo" or "myrmillo", pl. murmillones) was a type of gladiator during the Roman Imperial age. The murmillo-class gladiator was adopted in the early Imperial period to replace the earlier Gallus, named after the warriors of Gaul. As the Gauls inhabiting Italy had become well integrated with the Romans by the time of the reign of Augustus, it became undesirable to portray them as enemy outsiders; the Gallus-class gladiator thus had to be retired. Equipment and armaments The murmillo was armed with: *Gladius: Roman sword with a length of 64–81 cm and weight of 1.2-1.6 kg with a handle made of bone. *Scutum: Rectangular shield made of vertically connected wooden boards with a small bronze boss which protects the shield's handle. * Balteus: Leather belt with metal decorations and supplements. Similar to current boxing belts. * Manica: Segmented or scaled arm guard made of leather or some metal alloys. Manicae can also be mail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scutum (shield)
The ''scutum'' (; plural ''scuta'') was a type of shield used among Italic peoples in antiquity, most notably by the army of ancient Rome starting about the fourth century BC. The Romans adopted it when they switched from the military formation of the hoplite phalanx of the Greeks to the formation with maniples ( la, manipuli). In the former, the soldiers carried a round shield, which the Romans called a ''clipeus''. In the latter, they used the ''scutum'', which was larger. Originally it was oblong and convex, but by the first century BC it had developed into the rectangular, semi-cylindrical shield that is popularly associated with the ''scutum'' in modern times. This was not the only kind the Romans used; Roman shields were of varying types depending on the role of the soldier who carried it. Oval, circular and rectangular shapes were used throughout Roman history. History The first depictions of the scutum are by the Este culture in the 8th century bc, and subsequently sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thraex
The Thraex (pl. Thraeces), or Thracian, was a type of Roman gladiator, armed in the Thracian style with a small rectangular, square or circular shield called a '' parmula'' (about 60 x 65 cm) and a very short sword with a slightly curved blade called a ''sica'' (like a small version of the Dacian falx), intended to maim an opponent's unarmoured back. His other armour included armoured greaves, a protective belt above a loincloth, and a helmet with a side plume, visor and high crest. Ludia's female gladiators used the same weapons and armour. He and the hoplomachus, with his Greek equipment, were usually pitted against the murmillo, armed like a legionary, mimicking the opposition between Roman soldiers and their various slaves. In essence, these slaves were not trained well and died a gruesome death. See also * Ludus Dacicus * List of Roman gladiator types There were many different types of gladiators in ancient Rome. Some of the first gladiators had been prisoners-of- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
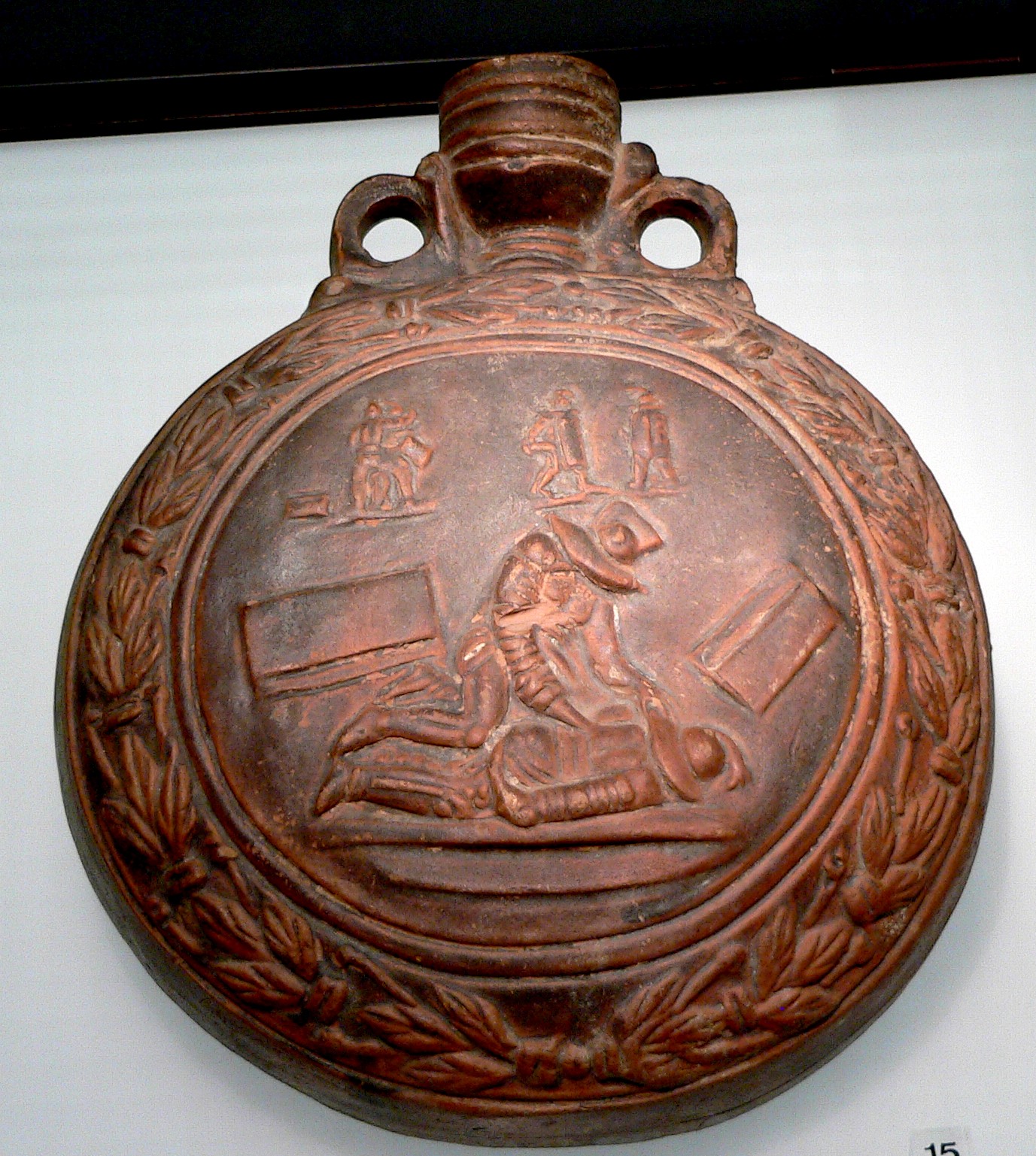
Decebal Suicide
Decebal may refer to: * Decebalus Decebalus (), sometimes referred to as Diurpaneus, was the last Dacians, Dacian king. He is famous for fighting three wars, with varying success, against the Roman Empire under two emperors. After raiding south across the Danube, he defeated a Rom ..., 1st-century king of Dacia * Decebal, a village in Tătărăuca Veche, Moldova * Decebal, a village in Vetiș, Romania * Decebal (name), a Romanian given name See also * * Decibel (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alba Iulia National Museum Of The Union 2011 - Inventory Pieces From Cugir Dacian Warrior Tomb-5
''Alba'' ( , ) is the Scottish Gaelic name for Scotland. It is also, in English language historiography, used to refer to the polity of Picts and Scots united in the ninth century as the Kingdom of Alba, until it developed into the Kingdom of Scotland of the late Middle Ages following the absorption of Strathclyde and English-speaking Lothian in the 12th century. It is cognate with the Irish term ' (gen. ', dat. ') and the Manx term ', the two other Goidelic Insular Celtic languages, as well as contemporary words used in Cornish (') and Welsh ('), both of which are Brythonic Insular Celtic languages. The third surviving Brythonic language, Breton, instead uses ', meaning 'country of the Scots'. In the past, these terms were names for Great Britain as a whole, related to the Brythonic name Albion. Etymology The term first appears in classical texts as ' or ' (in Ptolemy's writings in Greek), and later as ' in Latin documents. Historically, the term refers to Britain a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melee
A melee ( or , French: mêlée ) or pell-mell is disorganized hand-to-hand combat in battles fought at abnormally close range with little central control once it starts. In military aviation, a melee has been defined as " air battle in which several aircraft, both friend and foe, are confusingly intermingled". History of the term In the 1579 translation of Plutarch's '' Lives of the noble Grecians and Romanes'', Sir Thomas North uses the term '' to refer to a disorganized retreat. The phrase was later used in its current spelling in Shakespeare's ''Richard III'', 1594: The phrase comes from the French expression ''pêle-mêle'', a rhyme based on the old French ''mesler'', meaning to mix or mingle. The French term ''melee'' was first used in English in c. 1640 (also derived from the old French ''mesler'', but the Old French stem survives in '' medley'' and ''meddle''). Lord Nelson described his tactics for the Battle of Trafalgar as inducing a "pell mell battle" focused o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michiel De Vaan
Michiel Arnoud Cor de Vaan (; born 1973) is a Dutch linguist and Indo-Europeanist. He taught comparative Indo-European linguistics, historical linguistics and dialectology at the University of Leiden until 2014, when he moved to the University of Lausanne in Switzerland. De Vaan had been at the University of Leiden since 1991, first as a student and later as a teacher. He has published extensively on Limburgian, Dutch, Germanic, Albanian, Indo-Iranian and Indo-European linguistics and philology. He has published more than 100 papers, has written several books and has edited conference proceedings and a handbook of Indo-European. He wrote the etymological dictionary of Latin and other Italic languages as a contributor to the Leiden-based Indo-European Etymological Dictionary The ''Indo-European Etymological Dictionary'' (commonly abbreviated ''IEED'') is a research project of the Department of Comparative Indo-European Linguistics at Leiden University, initiated in 1991 by Pete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |