|
Sia (title)
Sia () was a hereditary title of Chinese origin, used mostly in colonial Indonesia. It was borne by the descendants of Chinese officers, who were high-ranking, Chinese civil bureaucrats in the Dutch colonial government, bearing the ranks of ''Majoor, Kapitein'' or ''Luitenant der Chinezen'' (see: ''Kapitan Cina''). History As with other Chinese honorifics, the title 'Sia' came at the end of the title holder's name: for example, as in Oey Tamba ''Sia'' (1827 - 1856). The title was used not with its holder's surname, but with his given name, so ''Tamba Sia'' instead of ''Oey Sia''. In everyday speech, use of the title was often combined with other honorifics, such as ''Ako Sia'' ('elder brother Sia') or '' Baba Sia'' ('sir Sia'). Originally, the honorific was used in Imperial China to address certain senior mandarins, the relatives of a mandarin or descendants of the House of Koxinga, formerly the ruling dynasty of the Kingdom of Tungning. In colonial Indonesia, the honorific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Javanese Language
Javanese (, , ; , Aksara Jawa: , Pegon: , IPA: ) is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken by the Javanese people from the central and eastern parts of the island of Java, Indonesia. There are also pockets of Javanese speakers on the northern coast of western Java. It is the native language of more than 98 million people. Javanese is the largest of the Austronesian languages in number of native speakers. It has several regional dialects and a number of clearly distinct status styles. Its closest relatives are the neighboring languages such as Sundanese, Madurese, and Balinese. Most speakers of Javanese also speak Indonesian for official and commercial purposes as well as a means to communicate with non-Javanese-speaking Indonesians. There are speakers of Javanese in Malaysia (concentrated in the West Coast part of the states of Selangor and Johor) and Singapore. Javanese is also spoken by traditional immigrant communities of Javanese descent in Suriname, Sri Lanka an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
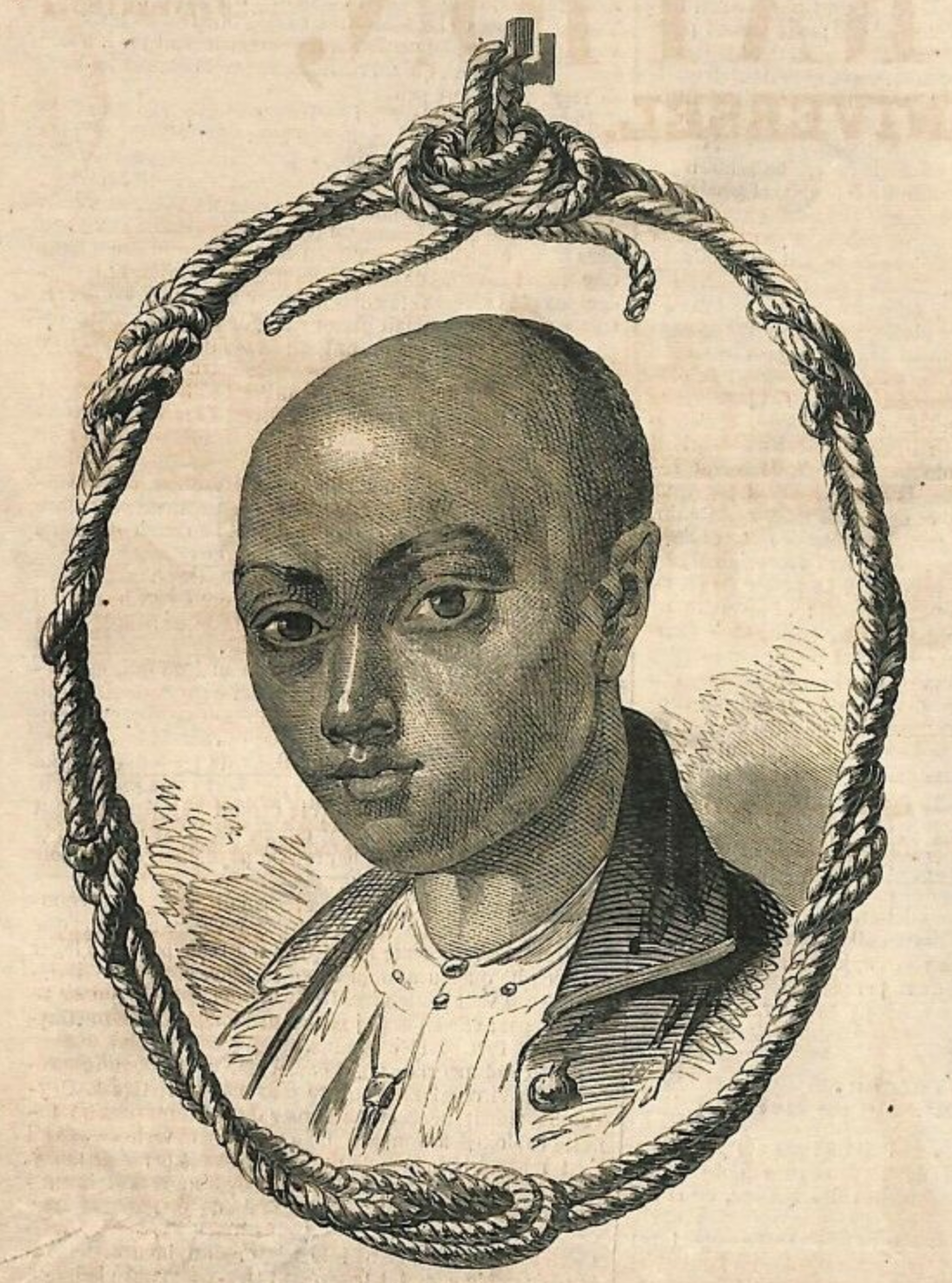
Han Kik Ko
Han Kik Ko, Majoor der Chinezen, Regent van Probolinggo (1766 – 1813), also known as Han Tik Ko in European sources, was a Peranakan Chinese magnate, government official and landlord in East Java. He is remembered today as a pioneer of the sugar industry in East Java, and for his acquisition and despotic rule of the district of Probolinggo. Family background Han Kik Ko ''Sia'' was born in Surabaya in 1767, the fifth of twelve sons, to Han Bwee Kong (1727–1778), and was as such a grandson of the Chinese migrant Han Siong Kong (1673–1743), founder of the powerful Han family of Lasem. His father, Han Bwee Kong, held the civil government post of ''Kapitein der Chinezen'', which gave him legal and political authority over the Chinese community of Surabaya. As the son of a Chinese officer, Han Kik Ko bore the hereditary title 'Sia'. Other prominent members of his family include his elder brother and fellow landlord, Han Chan Piet, Majoor der Chinezen (1759–1827); his uncle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scholar-gentry
The "gentry Gentry (from Old French ''genterie'', from ''gentil'', "high-born, noble") are "well-born, genteel and well-bred people" of high social class, especially in the past. Word similar to gentle [simple and decent] families ''Gentry'', in its widest ...", or "landed gentry" in China was the elite who held privileged status through passing the Imperial exams, which made them eligible to hold office. These literati, or scholar-officials, (''shenshi'' 紳士 or ''jinshen'' 縉紳), also called 士紳 ''shishen'' "scholar gentry" or 鄉紳 ''xiangshen'' "local gentry", held a virtual monopoly on office holding, and overlapped with an unofficial elite of the wealthy. The Tang dynasty, Tang and Song Dynastys expanded the Imperial examination, civil service exam to replace the nine-rank system which favored hereditary and largely military Chinese nobility, aristocrats. As a social class they included retired mandarin (China), mandarins or their families and descendants. Owni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiong Hoa Hwee Koan
Tiong Hoa Hwee Koan (THHK, ) was an Indonesian Chinese organization founded on March 17, 1900 in Batavia, Dutch East Indies. Its founders included former classmates Lie Kim Hok and Phoa Keng Hek ''Sia'', both of whom had been educated at Sierk Coolsma's missionary school in the Dutch East Indies. At first its mission was to renew and spread Confucian Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a Religious Confucianism, religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, ... ideas and the general level of knowledge among the Chinese-Indonesian population of the Indies.Overseas Chinese Nationalism, Lea E. Williams, MIT, 1960. References {{SEAsia-hist-stub Indonesian people of Chinese descent 1900 establishments in the Dutch East Indies 20th century in Jakarta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kong Koan
A kong koan (; Dutch: ''Chinese Raad''; Indonesian: ''Raad Tjina'') or "chinese council", was a high government body in the major capitals of the Dutch East Indies, consisting of all incumbent Chinese officers in those cities. It acted as both a judicial and executive authority and constituted part of the Dutch colonial system of indirect rule. The ''rechtszitting'', or official seat or building, housing the kong koan was called a kong tong (; literally "tribunal" or "law court"). Overview The Kong Koan as a government body was inseparable from the institution of Chinese officers, who were high-ranking civil administrators, appointed by the Dutch colonial authorities to govern the local Chinese community in colonial Indonesia. In the larger cities, the active officers sat as a council, the Kong Koan, in order to adjudicate justice, govern the local Chinese community and implement the directives of the colonial government. In executing these responsibilities, the Kong Koan had its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoa Liong Gie
Phoa Liong Gie Sia (: born in Bandung on June 4, 1905 – died on January 14, 1983 in Switzerland) was an Indonesian-born Swiss jurist, politician and newspaper owner of the late colonial era in the Dutch East Indies. Background and education He was born in 1905 into a prominent family of Peranakan Chinese roots, part of the ''Cabang Atas'' or the Chinese gentry of colonial Indonesia. His great-grandfather, Phoa Tjeng Tjoan, served as ''Kapitein der Chinezen'' of Buitenzorg (now Bogor) from 1866 until 1878. This was a post in the colonial civil administration with political and legal jurisdiction over the local Chinese community. Phoa was styled 'Sia' from birth as the descendant of a Chinese officer. Phoa was also a great-nephew of the prominent community leader and landlord, Phoa Keng Hek ''Sia''. The younger Phoa was educated at the ''Europeesche Lagere School'' (European lower school) in Garut, and at the '' Hogere Burgerschool'' (higher civic school) in Batavia. Both ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kwee Thiam Tjing
Kwee Thiam Tjing Sia (February 9, 1900 – May 28, 1974), also known by his pen name Tjamboek Bērdoeri Thorn Whip' was a prominent Indonesian writer, journalist and left-wing political activist. He is best remembered for his 1947 book, ' Indonesia dalem Api dan Bara', and for his role as a co-founder of the Partai Tionghoa Indonesia he 'Chinese-Indonesian Party'in 1932. Life Born in 1900 in Pasuruan, East Java, Kwee hailed on both sides of his family from old ''Peranakan'' lineages of the 'Cabang Atas' gentry with roots in the Chinese officership, which formed the Chinese bureaucratic elite of the Dutch East Indies. His father, Kwee Tjiong Khing, was a paternal grandson of Kwee Sioe Liem, ''Kapitein der Chinezen'' of Pasuruan, and a great-grandson of Kwee Sam Hway, the first ''Luitenant der Chinezen'' of Malang (1801–1865), as well as a maternal grandson of the Surabaya landowner Tan Tong Liep (1831–1907). Kwee Thiam Tjing's mother, Liem Liang Nio, was the daughter of Liem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loa Sek Hie
Loa Sek Hie Sia (born in Batavia in 1898 - died in The Hague in 1965) was a colonial Indonesian politician, parliamentarian and the founding ''Voorzitter'' or chairman of the controversial, ethnic-Chinese self-defense force Pao An Tui (1946 - 1949). He was a ''Peranakan'' of Chinese-Indonesian, Austrian and Javanese descent. In his political career, he campaigned against racial discrimination and demanded better healthcare and education for ethnic Chinese in the Dutch East Indies. History Family and education Loa was born in Pasar Baru, Batavia in 1898 into one of the city's most prominent families, part of the 'Cabang Atas' or ''Peranakan'' Chinese gentry of Java. His grandfather was the tycoon Loa Po Seng, oJalan Posengin Pasar Baru, while his father, Loa Tiang Hoei, served as ''Kapitein der Chinezen'' of Pasar Baru. This was a civil government appointment with legal and political authority over the local Chinese community. Loa's mother, Louise Goldman, came from an Indo-E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hok Hoei Kan
Kan Hok Hoei Sia (; 6 January 1881 - 1 March 1951), generally known as Hok Hoei Kan or in short H. H. Kan, was a prominent public figure, statesman and patrician landowner of Peranakan Chinese descent in the Dutch East Indies (today known as Indonesia). He was the founding president of Chung Hwa Hui (CHH), a Chinese-Indonesian political party, and sat as its leading parliamentary representative in the Volksraad. He advocated cooperation with the Dutch colonial authorities in order to attain racial and legal equality for the colony's Chinese community, but was criticised for his pro-Dutch sentiments and perceived elite indifference to poorer Indonesians. Family and early life Kan was born Han Khing Tjiang Sia in Batavia, capital of the Dutch East Indies, into the heart of the 'Cabang Atas' or the Chinese gentry of Java. His father, Han Oen Lee (1856—1893), served as '' Luitenant der Chinezen'' of Bekasi, an important administrative post in the colonial bureaucracy, and hail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khouw Kim An
Khouw Kim An, 5th Majoor der Chinezen (; 1875 – February 13, 1945) was a high-ranking Chinese Indonesian bureaucrat, public figure and landlord who served as the fifth and last ''Majoor der Chinezen'' ("Major of the Chinese") of Batavia, Dutch East Indies (now Jakarta). The Chinese Mayoralty was the highest-ranking, Chinese government position in the East Indies with considerable political and judicial jurisdiction over the colony's Chinese subjects. The Batavian Mayoralty was one of the oldest public institutions in the Dutch colonial empire, perhaps second only in antiquity to the viceregal post of Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies. Family and background Khouw Kim An Sia was born in Batavia in 1875 to the ninth concubine of his father, Khouw Tjeng Tjoan, ''Luitenant-titulair der Chinezen'' (died in 1880). Khouw's father and uncles, Khouw Tjeng Kee and Khouw Tjeng Po, were the sons of the late eighteenth-century magnate, Khouw Tian Sek (died in 1843), patriar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oen Giok Khouw
Khouw Oen Giok Sia (1874 – 1927), later more popularly known as Oen Giok Khouw or O. G. Khouw, was a philanthropist and landowner in the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia). He gained notoriety for acquiring Dutch citizenship, thus breaking down the race barriers of colonial society. Today, he is best remembered for his extravagant mausoleum in Petamburan, Jakarta. Family Born in 1874 in Batavia (now Jakarta), he was a scion of the Khouw family of Tamboen, part of the ''Cabang Atas'' or the Chinese gentry (''baba bangsawan'') of colonial Indonesia. His father, Khouw Tjeng Kee, ''Luitenant-titulair der Chinezen'' (died in 1883), was a prominent landlord and community leader. Khouw's father and uncles, Luitenant Khouw Tjeng Tjoan and Luitenant Khouw Tjeng Po, were the sons of the late eighteenth-century magnate, Luitenant Khouw Tian Sek (died in 1843). The Chinese lieutenancies of Khouw's father, uncles and grandfather were honorary appointments without any of the entailed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoa Keng Hek
Phoa Keng Hek Sia (; 1857–1937) was a Chinese Indonesian ''Landheer'' (landlord), social activist and founding president of Tiong Hoa Hwe Koan, an influential Confucian educational and social organisation meant to better the position of ethnic Chinese in the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia). He was also one of the founders of Institut Teknologi Bandung. Biography Early life and family background Phoa was born in Buitenzorg (now Bogor), Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia), in 1857 into an influential ''Peranakan'' Chinese family, part of the ''Cabang Atas'' or the Chinese gentry of colonial Indonesia. His father, Phoa Tjeng Tjoan, held the post of '' Kapitein der Chinezen'' of Buitenzorg from 1866 until 1878. This was a civil government position in the Dutch colonial administration with legal and political jurisdiction over the local Chinese community. His mother, Thung Tiauw Nio, was the daughter and elder sister of prominent community leaders in Buitenzorg, Thung Tiang Mih and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_and_his_family.png)

