|
Shubnikov–de Haas Effect
An oscillation in the conductivity of a material that occurs at low temperatures in the presence of very intense magnetic fields, the Shubnikov–de Haas effect (SdH) is a macroscopic manifestation of the inherent quantum mechanical nature of matter. It is often used to determine the effective mass of charge carriers (electrons and electron holes), allowing investigators to distinguish among majority and minority carrier populations. The effect is named after Wander Johannes de Haas and Lev Shubnikov. Physical process At sufficiently low temperatures and high magnetic fields, the free electrons in the conduction band of a metal, semimetal, or narrow band gap semiconductor will behave like simple harmonic oscillators. When the magnetic field strength is changed, the oscillation period of the simple harmonic oscillators changes proportionally. The resulting energy spectrum is made up of Landau levels separated by the cyclotron energy. These Landau levels are further split by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive or Periodic function, periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of Mechanical equilibrium, equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum and alternating current. Oscillations can be used in physics to approximate complex interactions, such as those between atoms. Oscillations occur not only in mechanical systems but also in dynamic systems in virtually every area of science: for example the beating of the human heart (for circulation), business cycles in economics, predator–prey population cycles in ecology, geothermal geysers in geology, vibration of strings in guitar and other string instruments, periodic firing of nerve cells in the brain, and the periodic swelling of Cepheid variable stars in astronomy. The term ''vibration'' is precisely used to describe a mechanical oscillation. Oscillation, especially rapid oscillation, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Harmonic Oscillator
In mechanics and physics, simple harmonic motion (sometimes abbreviated ) is a special type of periodic motion of a body resulting from a dynamic equilibrium between an inertial force, proportional to the acceleration of the body away from the static equilibrium position and a restoring force on the moving object that is directly proportional to the magnitude of the object's displacement and acts towards the object's equilibrium position. It results in an oscillation, described by a sinusoid which continues indefinitely, if uninhibited by friction or any other dissipation of energy. Simple harmonic motion can serve as a mathematical model for a variety of motions, but is typified by the oscillation of a mass on a spring when it is subject to the linear elastic restoring force given by Hooke's law. The motion is sinusoidal in time and demonstrates a single resonant frequency. Other phenomena can be modeled by simple harmonic motion, including the motion of a simple pendulum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
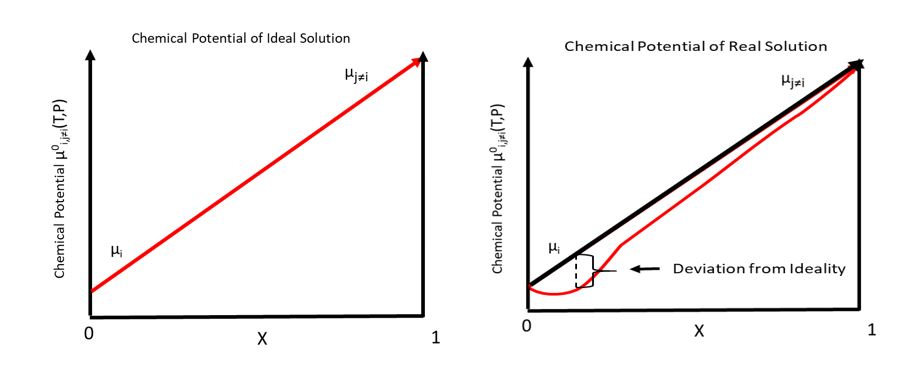
Chemical Potential
In thermodynamics, the chemical potential of a species is the energy that can be absorbed or released due to a change of the particle number of the given species, e.g. in a chemical reaction or phase transition. The chemical potential of a species in a mixture is defined as the rate of change of free energy of a thermodynamic system with respect to the change in the number of atoms or molecules of the species that are added to the system. Thus, it is the partial derivative of the free energy with respect to the amount of the species, all other species' concentrations in the mixture remaining constant. When both temperature and pressure are held constant, and the number of particles is expressed in moles, the chemical potential is the partial molar Gibbs free energy. At chemical equilibrium or in phase equilibrium, the total sum of the product of chemical potentials and stoichiometric coefficients is zero, as the free energy is at a minimum. In a system in diffusion equilibrium, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi Level
The Fermi level of a solid-state body is the thermodynamic work required to add one electron to the body. It is a thermodynamic quantity usually denoted by ''µ'' or ''E''F for brevity. The Fermi level does not include the work required to remove the electron from wherever it came from. A precise understanding of the Fermi level—how it relates to electronic band structure in determining electronic properties, how it relates to the voltage and flow of charge in an electronic circuit—is essential to an understanding of solid-state physics. In band structure theory, used in solid state physics to analyze the energy levels in a solid, the Fermi level can be considered to be a hypothetical energy level of an electron, such that at thermodynamic equilibrium this energy level would have a ''50% probability of being occupied at any given time''. The position of the Fermi level in relation to the band energy levels is a crucial factor in determining electrical properties. The Fermi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sketch Energy Edge Channels
Sketch or Sketches may refer to: * Sketch (drawing), a rapidly executed freehand drawing that is not usually intended as a finished work Arts, entertainment and media * Sketch comedy, a series of short scenes or vignettes called sketches Film and television * ''Sketch'' (2007 film), a Malayalam film * ''Sketch'' (2018 film), a Tamil film * ''Sketch'' (TV series), a 2018 South Korean series * "Sketch", a 2008 episode of ''Skins'' ** Sketch (''Skins'' character) * Sketch with Kevin McDonald, a 2006 CBC television special Literature * Sketch story, or sketch, a very short piece of writing * ''Daily Sketch'', a British newspaper 1909–1971 * ''The Sketch'', a British illustrated weekly journal 1893–1959 Music * Sketch (music), an informal document prepared by a composer to assist in composition * The Sketches, a Pakistani Sufi folk rock band * ''Sketch'' (album), by Ex Norwegian, 2011 * ''Sketch'' (EP), by Hyomin, 2016 * ''Sketches'' (album), by Bert Jansch, 1990 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Work Function
In solid-state physics, the work function (sometimes spelt workfunction) is the minimum thermodynamic work (i.e., energy) needed to remove an electron from a solid to a point in the vacuum immediately outside the solid surface. Here "immediately" means that the final electron position is far from the surface on the atomic scale, but still too close to the solid to be influenced by ambient electric fields in the vacuum. The work function is not a characteristic of a bulk material, but rather a property of the surface of the material (depending on crystal face and contamination). Definition The work function for a given surface is defined by the difference :W = -e\phi - E_, where is the charge of an electron, is the electrostatic potential in the vacuum nearby the surface, and is the Fermi level ( electrochemical potential of electrons) inside the material. The term is the energy of an electron at rest in the vacuum nearby the surface. In practice, one directly controls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinusoidal
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the '' sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function. It occurs often in mathematics, as well as in physics, engineering, signal processing and many other fields. Formulation Its most basic form as a function of time (''t'') is: y(t) = A\sin(2 \pi f t + \varphi) = A\sin(\omega t + \varphi) where: * ''A'', ''amplitude'', the peak deviation of the function from zero. * ''f'', '' ordinary frequency'', the ''number'' of oscillations (cycles) that occur each second of time. * ''ω'' = 2''f'', '' angular frequency'', the rate of change of the function argument in units of radians per second. * \varphi, '' phase'', specifies (in radians) where in its cycle the oscillation is at ''t'' = 0. When \varphi is non-zero, the entire waveform appears to be shifted in time by the amount ''φ''/''ω'' seconds. A negative val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamic
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws of thermodynamics which convey a quantitative description using measurable macroscopic physical quantities, but may be explained in terms of microscopic constituents by statistical mechanics. Thermodynamics applies to a wide variety of topics in science and engineering, especially physical chemistry, biochemistry, chemical engineering and mechanical engineering, but also in other complex fields such as meteorology. Historically, thermodynamics developed out of a desire to increase the efficiency of early steam engines, particularly through the work of French physicist Sadi Carnot (1824) who believed that engine efficiency was the key that could help France win the Napoleonic Wars. Scots-Irish physicist Lord Kelvin was the first to for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport Phenomena
In engineering, physics, and chemistry, the study of transport phenomena concerns the exchange of mass, energy, charge, momentum and angular momentum between observed and studied systems. While it draws from fields as diverse as continuum mechanics and thermodynamics, it places a heavy emphasis on the commonalities between the topics covered. Mass, momentum, and heat transport all share a very similar mathematical framework, and the parallels between them are exploited in the study of transport phenomena to draw deep mathematical connections that often provide very useful tools in the analysis of one field that are directly derived from the others. The fundamental analysis in all three subfields of mass, heat, and momentum transfer are often grounded in the simple principle that the total sum of the quantities being studied must be conserved by the system and its environment. Thus, the different phenomena that lead to transport are each considered individually with the knowled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi Energy
The Fermi energy is a concept in quantum mechanics usually referring to the energy difference between the highest and lowest occupied single-particle states in a quantum system of non-interacting fermions at absolute zero temperature. In a Fermi gas, the lowest occupied state is taken to have zero kinetic energy, whereas in a metal, the lowest occupied state is typically taken to mean the bottom of the conduction band. The term "Fermi energy" is often used to refer to a different yet closely related concept, the Fermi ''level'' (also called electrochemical potential).The use of the term "Fermi energy" as synonymous with Fermi level (a.k.a. electrochemical potential) is widespread in semiconductor physics. For example:''Electronics (fundamentals And Applications)''by D. Chattopadhyay''Semiconductor Physics and Applications''by Balkanski and Wallis. There are a few key differences between the Fermi level and Fermi energy, at least as they are used in this article: * The Fermi energ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeeman Effect
The Zeeman effect (; ) is the effect of splitting of a spectral line into several components in the presence of a static magnetic field. It is named after the Dutch physicist Pieter Zeeman, who discovered it in 1896 and received a Nobel prize for this discovery. It is analogous to the Stark effect, the splitting of a spectral line into several components in the presence of an electric field. Also similar to the Stark effect, transitions between different components have, in general, different intensities, with some being entirely forbidden (in the dipole approximation), as governed by the selection rules. Since the distance between the Zeeman sub-levels is a function of magnetic field strength, this effect can be used to measure magnetic field strength, e.g. that of the Sun and other stars or in laboratory plasmas. The Zeeman effect is very important in applications such as nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, electron spin resonance spectroscopy, magnetic resonan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |