|
Shipbuilding In Frindsbury, Kent
Frindsbury TQ744697 is a parish on the River Medway, on the opposite bank to Chatham Dockyard in Kent, England. It was a centre of ship building before 1820, building at least six 74 gun third rate ships of the line and many smaller vessels. From 1820, until recent times, the ship yards built over 100 Thames sailing barges. Shipbuilding has stopped but in 2006, one yard was still active in ship repair. Ships Quarry House Yard Edward Greaves and Nicholson set up at the Quarry House yard in c.1745. The full list of ships built is unknown but two of the later ones were:Merrily to Frendsbury-A History of the Parish of Frindsbury. Derek Barnard. Private Pub. City of Rochester Society. post 1994. *1785 —32 gun frigate was part of a squadron off the coast of Genoa in 1794 under the command of Captain Horatio Nelson. *1786 —74 gun designed by Sir Thomas Slade. Laid down in 1783, she was launched on 6 October 1786 and commissioned on 19 July 1790. Nicknamed the "Billy Ruffian". Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frindsbury
Frindsbury is part of the Medway Towns conurbation in Kent, southern England. It lies on the opposite side of the River Medway to Rochester, Kent, Rochester, and at various times in its history has been considered fully or partially part of the City of Rochester. Frindsbury today is part of the town of Strood and covers the most northern part of the town. Frindsbury refers to both a parish and a manorialism, manor. Within the civil parish of Frindsbury Extra are the villages of Frindsbury, Wainscott, Kent, Wainscott, and Upnor. Frindsbury was also the name given to an wards of the United Kingdom, electoral ward in the City of Rochester that straddled the parishes of Frindsbury and Strood. Topology Frindsbury lies on the northwest bank of the Medway at its lowest bridging point. After a narrow but marshy coastal strip, the land rises steeply to plateau at about . This was a sheet of chalk covered by brickearth covered with topsoil. Over the last two millennia, much of this was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheerness
Sheerness () is a town and civil parish beside the mouth of the River Medway on the north-west corner of the Isle of Sheppey in north Kent, England. With a population of 11,938, it is the second largest town on the island after the nearby town of Minster which has a population of 21,319. Sheerness began as a fort built in the 16th century to protect the River Medway from naval invasion. In 1665 plans were first laid by the Navy Board for Sheerness Dockyard, a facility where warships might be provisioned and repaired. The site was favoured by Samuel Pepys, then Clerk of the Acts of the navy, for shipbuilding over Chatham inland. After the raid on the Medway in 1667, the older fortification was strengthened; in 1669 a Royal Navy dockyard was established in the town, where warships were stocked and repaired until its closure in 1960. Beginning with the construction of a pier and a promenade in the 19th century, Sheerness acquired the added attractions of a seaside resort. Indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thames Sailing Barges
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the River Severn. The river rises at Thames Head in Gloucestershire, and flows into the North Sea near Tilbury, Essex and Gravesend, Kent, via the Thames Estuary. From the west it flows through Oxford (where it is sometimes called the Isis), Reading, Henley-on-Thames and Windsor. The Thames also drains the whole of Greater London. In August 2022, the source of the river moved five miles to beyond Somerford Keynes due to the heatwave in July 2022. The lower reaches of the river are called the Tideway, derived from its long tidal reach up to Teddington Lock. Its tidal section includes most of its London stretch and has a rise and fall of . From Oxford to the Estuary the Thames drops by 55 metres. Running through some of the drier parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy Dockyards In England
Royal may refer to: People * Royal (name), a list of people with either the surname or given name * A member of a royal family Places United States * Royal, Arkansas, an unincorporated community * Royal, Illinois, a village * Royal, Iowa, a city * Royal, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Royal, Nebraska, a village * Royal, Franklin County, North Carolina, an unincorporated area * Royal, Utah, a ghost town * Royal, West Virginia, an unincorporated community * Royal Gorge, on the Arkansas River in Colorado * Royal Township (other) Elsewhere * Mount Royal, a hill in Montreal, Canada * Royal Canal, Dublin, Ireland * Royal National Park, New South Wales, Australia Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Royal'' (Jesse Royal album), a 2021 reggae album * ''The Royal'', a British medical drama television series * ''The Royal Magazine'', a monthly British literary magazine published between 1898 and 1939 * ''Royal'' (Indian magazine), a men's lifestyle bimonthly * Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wouldham
Wouldham is a village on the bank of the River Medway in Kent, Great Britain. As of 2006 its population is approximately 1000 people, with the 11th-century church, one school, one village shop, and two public houses, The Medway Inn and The Waterman's Arms. History The tusk and teeth of a mammoth were excavated in Peters Pit and displayed in Rochester Guildhall Museum. In 1982, the skull of an 18-year-old man was excavated- it was dated as 1500 BC and the museum staff have had the face reconstructed. Oral history suggests that the village was occupied when the Romans arrived, and that they constructed a ford across the Medway. The site of a temple dedicated to Mithras has been excavated and occurs on old maps. On the Wouldham Marshes is ''Starkey House'' built in 1483: a now-restored Grade II listed medieval manor house called Starkey Castle. In the churchyard, is the grave of Walter Burke, who was present on board at the battle of Trafalgar and the man who held Nelson in his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burham
Burham is a village and civil parish in the borough of Tonbridge and Malling in Kent, England. According to the 2001 census it had a population of 1,251, decreasing to 1,195 at the 2011 Census. The village is near the Medway towns. The history of Burham can be traced to Roman times. AD43 saw the Battle of the Medway at the crossing point on the River Medway, where Burham is now, when the invading Roman legions, advancing west across Kent, were confronted by a massed army of the ancient British tribes. The Roman victory altered the course of history in Britain, and the remains of Roman buildings have been found in Burham and the neighbouring village of Eccles. There has been a Settlement in Burham since Saxon times, "ham" being the Saxon word for "settlement" — the "Bur" part of the name comes from "burgh", or borough, referring to the borough of Rochester. The name "Burham" means "the village near the borough". In the 11th century Burham belonged to Leofwine Godwinson, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
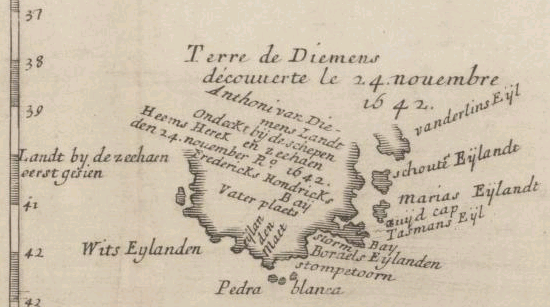
Van Diemen's Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colonial name of the island of Tasmania used by the British during the European exploration of Australia in the 19th century. A British settlement was established in Van Diemen's Land in 1803 before it became a separate colony in 1825. Its penal colonies became notorious destinations for the transportation of convicts due to the harsh environment, isolation and reputation for being inescapable. Macquarie Harbour and Port Arthur are among the most well-known penal settlements on the island. With the passing of the Australian Constitutions Act 1850, Van Diemen's Land (along with New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Victoria, and Western Australia) was granted responsible self-government with its own elected representative and parliament. On 1 January 1856, the colony of Van Diemen's Land was officially changed to Tasmania. The last penal settlement was closed in Tasmania in 1877. Toponym The island was named in honour of Anthony van Die ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Chesapeake (1799)
''Chesapeake'' was a 38-gun wooden-hull (watercraft), hulled, three-Mast (sailing), masted heavy frigate of the United States Navy. She was one of the original six frigates of the United States Navy, original six frigates whose construction was authorized by the Naval Act of 1794. Joshua Humphreys designed these frigates to be the young navy's capital ships. ''Chesapeake'' was originally designed as a 44-gun frigate, but construction delays, material shortages and budget problems caused builder Josiah Fox to alter his design to 38 guns. Launched at the Gosport Navy Yard on 2 December 1799, ''Chesapeake'' began her career during the Quasi-War with France and later saw service in the First Barbary War. On 22 June 1807 she was fired upon by of the Royal Navy for refusing to allow a search for deserters. The event, now known as the Chesapeake–Leopard affair, ''Chesapeake–Leopard'' affair, angered the American public and government and was a precipitating factor that l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Broke
Sir Philip Bowes Vere Broke, 1st Baronet (; 9 September 1776 – 2 January 1841) was a distinguished officer in the British Royal Navy. During his lifetime, he was often referred to as "Broke of the ''Shannon''", a reference to his notable command of in the War of 1812. His most famous military achievement was defeating and capturing the American frigate, USS ''Chesapeake''. Early life Broke was born at Broke Hall, Nacton, near Ipswich, the eldest son of Philip Bowes Broke, grandson of Philip Broke and descendant of Sir Richard Broke, who served as Chief Baron of the Exchequer. He was educated at Ipswich School, where a house was later named in his honour. Naval career Broke joined the Royal Naval Academy at Portsmouth Dockyard in 1788, and began active service as a midshipman in 1792. It was rather unusual for him to receive formal naval education – most of his contemporaries had only "on the job" training. He served as third lieutenant on the frigate during the bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thames And Medway Canal
The Thames and Medway Canal is a disused canal in Kent, south east England, also known as the Gravesend and Rochester Canal. It was originally some long and cut across the neck of the Hoo peninsula, linking the River Thames at Gravesend with the River Medway at Strood. The canal was first mooted in 1778 as a shortcut for military craft from Deptford and Woolwich Dockyards on the Thames to Chatham Dockyard on the Medway, avoiding the journey round the peninsula and through the Thames estuary. The canal was also intended to take commercial traffic between the two rivers. Construction The first practical attempt to build the canal began in 1799, when an engineer named Ralph Dodd published a pamphlet and began to solicit investment for the scheme. Dodd's plan was for a six-mile canal with locks and basins, taking two years to build and costing £24,576, part of the cost to be defrayed by selling the excavated chalk as agricultural lime. Dodd was confident that the canal would be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amy Lowell
Amy Lawrence Lowell (February 9, 1874 – May 12, 1925) was an American poet of the imagist school, which promoted a return to classical values. She posthumously won the Pulitzer Prize for Poetry in 1926. Life Amy Lowell was born on February 9, 1874, in Boston, Massachusetts, the daughter of Augustus Lowell and Katherine Bigelow Lowell. A member of the Brahmin Lowell family, her siblings included the astronomer Percival Lowell, the educator and legal scholar Abbott Lawrence Lowell, and Elizabeth Lowell Putnam, an early activist for prenatal care. They were the great-grandchildren of John Lowell and, on their mother's side, the grandchildren of Abbott Lawrence. School was a source of considerable despair for the young Amy Lowell. She considered herself to be developing "masculine" and "ugly" features and she was a social outcast. She had a reputation among her classmates for being outspoken and opinionated. Lowell never attended college because her family did not consider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career of Napoleon Bonaparte, successful campaigns during the French Revolutionary Wars, Revolutionary Wars. He was the ''de facto'' leader of the First French Republic, French Republic as First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then Emperor of the French from 1804 until 1814 and again in Hundred Days, 1815. Napoleon's political and cultural legacy endures to this day, as a highly celebrated and controversial leader. He initiated many liberal reforms that have persisted in society, and is considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. His wars and campaigns are studied by militaries all over the world. Between three and six million civilians and soldiers Napoleonic Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_-_Notman.jpg)
