|
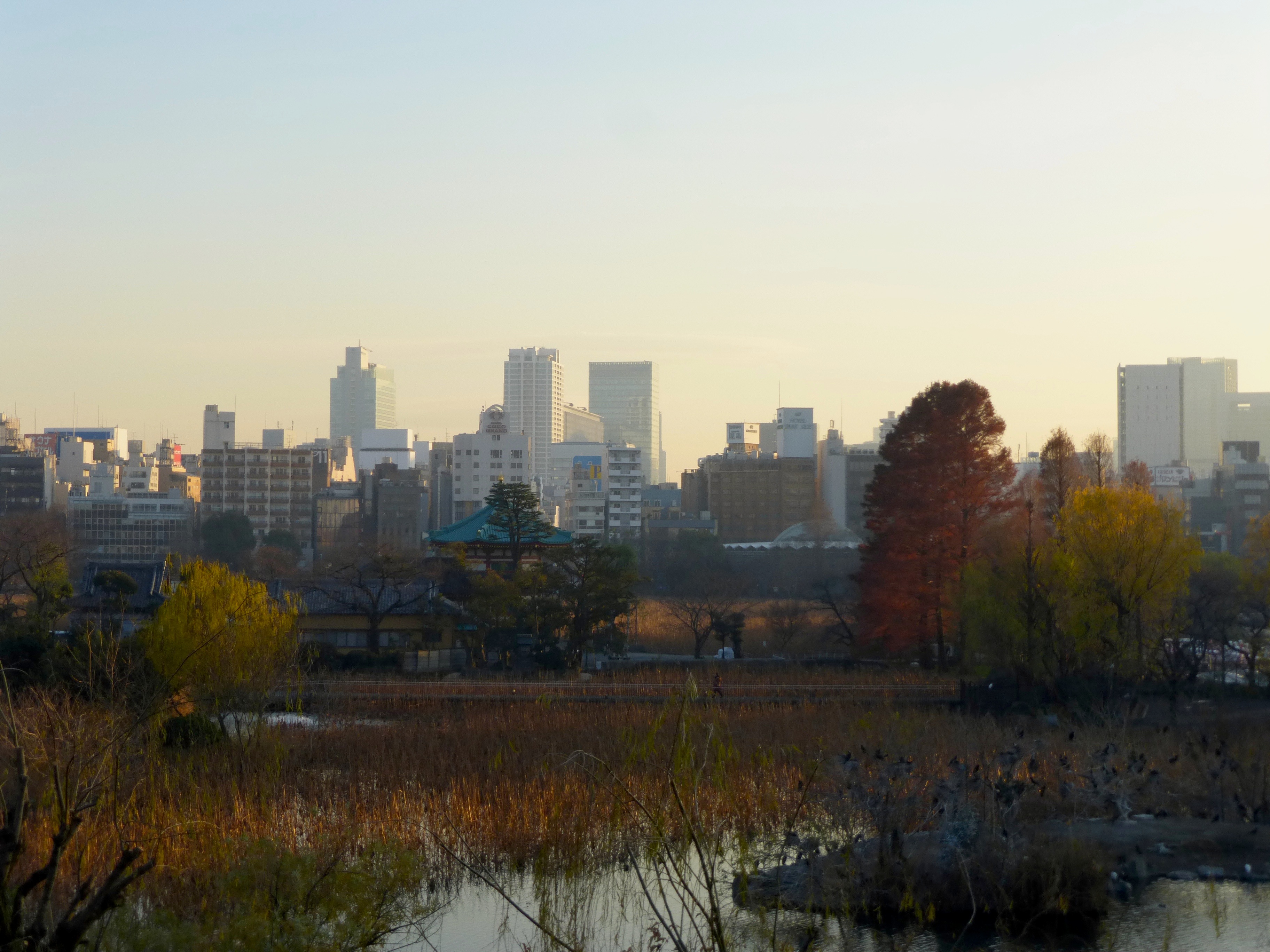
Shinobazu Pond
The is a pond within Ueno Park (a spacious public park located in the Ueno section of Taitō, Tokyo, Japan), and a historically prominent Shitamachi feature often appearing in history and works of art. The park occupies the site of the former Kan'ei-ji, a temple closely associated with the Tokugawa ''shōguns'', who had built it to guard Edo Castle against the northeast, a direction believed to be unlucky by traditional geomancy. The temple was destroyed during the Boshin War. The pond, although modified many times and even once drained, is natural. Position and Dimensions Situated in the south of Ueno Park, the pond is divided in three sections (see map), one called because of the plants that during the summer completely cover its surface, one called from the rental boats it hosts, and the third called , which lies within the limits of the Ueno Zoo and takes its name from the birds that inhabit it. The pond has a circumference of about 2 km and a surface of about 1,10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tufted Ducks
The tufted duck or tufted pochard (''Aythya fuligula'') is a small diving duck with a population of close to one million birds, found in northern Eurasia. The scientific name is derived from Ancient Greek '' aithuia'', an unidentified seabird mentioned by authors including Hesychius and Aristotle, and ''Latin'' ''fuligo'' "soot" and ''gula'' "throat". Description The adult male is all black except for white flanks and a blue-grey bill with gold-yellow eyes, along with a thin crest on the back of its head. It has an obvious head tuft that gives the species its name. The adult female is brown with paler flanks, and is more easily confused with other diving ducks. In particular, some have white around the bill base which resembles the scaup species, although the white is never as extensive as in those ducks. The females' call is a harsh, growling "karr", mostly given in flight. The males are mostly silent but they make whistles during courtship based on a simple "wit-oo". The onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo Metro Chiyoda Line
The is a subway line owned and operated by Tokyo Metro in Tokyo, Japan. On average, the line carries 1,447,730 passengers daily (2017), the second highest of the Tokyo Metro network, behind the Tozai Line (1,642,378).Tokyo Metro station ridership in 2010 ''Train Media (sourced from Tokyo Metro)'' Retrieved July 23, 2018. The line was named after the Chiyoda ward, under which it passes. On maps, diagrams and signboards, the line is shown using the color green (), and its stations are given numbers using the letter "C". Overview The 24.0 km line serves the wards of[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Of Japan
The Emperor of Japan is the monarch and the head of the Imperial House of Japan, Imperial Family of Japan. Under the Constitution of Japan, he is defined as the symbol of the Japanese state and the unity of the Japanese people, and his position is derived from "the will of the people with whom resides sovereign power". Imperial Household Law governs the line of Succession to the Japanese throne, imperial succession. The emperor is sovereign immunity, immune from prosecution by the Supreme Court of Japan. He is also the head of the Shinto religion. In Japanese language, Japanese, the emperor is called , literally "Emperor of heaven or "Heavenly Sovereign". The Japanese Shinto religion holds him to be the direct descendant of the sun goddess Amaterasu. The emperor is also the head of all national Orders, decorations, and medals of Japan, Japanese orders, decorations, medals, and awards. In English, the use of the term for the emperor was once common but is now considered obsolete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiji Era
The is an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868 to July 30, 1912. The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonization by Western powers to the new paradigm of a modern, industrialized nation state and emergent great power, influenced by Western scientific, technological, philosophical, political, legal, and aesthetic ideas. As a result of such wholesale adoption of radically different ideas, the changes to Japan were profound, and affected its social structure, internal politics, economy, military, and foreign relations. The period corresponded to the reign of Emperor Meiji. It was preceded by the Keiō era and was succeeded by the Taishō era, upon the accession of Emperor Taishō. The rapid modernization during the Meiji era was not without its opponents, as the rapid changes to society caused many disaffected traditionalists from the former samurai cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
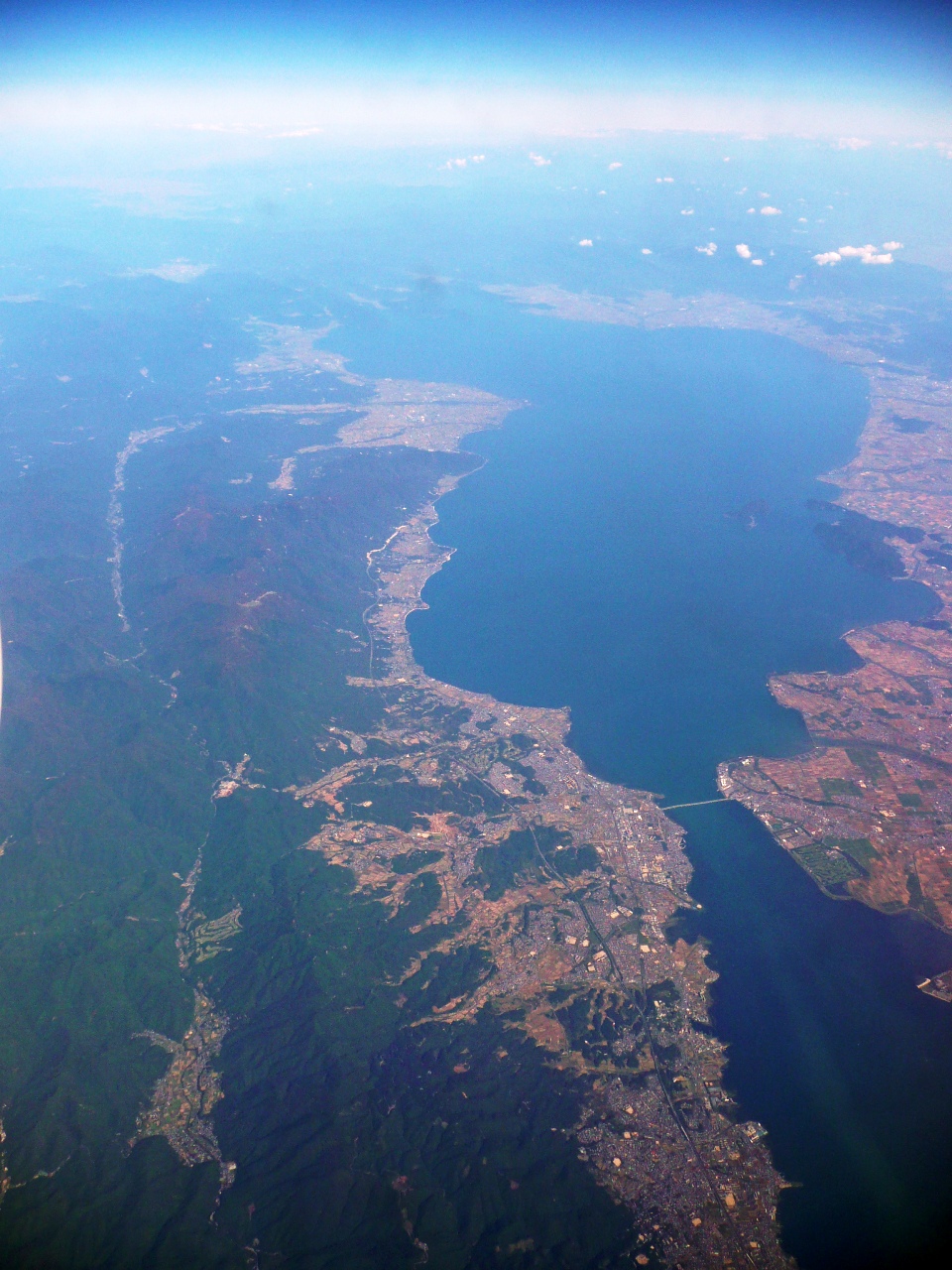
Lake Biwa
is the largest freshwater lake in Japan, located entirely within Shiga Prefecture (west-central Honshu), northeast of the former capital city of Kyoto. Lake Biwa is an ancient lake, over 4 million years old. It is estimated to be the 13th oldest lake in the world. Because of its proximity to Kyoto, references to Lake Biwa appear frequently in Japanese literature, particularly in poetry and in historical accounts of battles. Name The name ''Biwako'' was established in the Edo period. There are various theories about the origin of the name ''Biwako'', but it is generally believed to be so named because of the resemblance of its shape to that of a stringed instrument called the ''biwa''. Kōsō, a learned monk of Enryaku-ji in the 14th century, gave a clue to the origin of the name ''Biwako'' in his writing: "The lake is the Pure land of the goddess Benzaiten because she lives on Chikubu Island and the shape of the lake is similar to that of the ''biwa'', her favorite instrume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenkai
was a Japanese Tendai Buddhist monk of the Azuchi-Momoyama and early Edo periods. He achieved the rank of ''Daisōjō'', the highest rank of the priesthood. His Buddhist name was first , which he changed to Tenkai in 1590. Also known as , he died on 13 November 1643, and was granted the posthumous title of in 1648. Tenkai was at Kita-in (then written 北院) in Kawagoe in 1588, and became abbot in 1599. He was on the advisor of Tokugawa Ieyasu, and served as a liaison between the Tokugawa Shogunate and the Imperial Court in Kyoto. One of his projects was the rebuilding of Enryaku-ji, which had been devastated by Oda Nobunaga. He also revitalized Kita-in, and changed the characters of its name to 喜多院. Nearing death in 1616, Ieyasu entrusted Tenkai with his last will regarding matters of his funeral and his posthumous name. Tenkai selected ''gongen'' rather than ''myōjin,'' and after death Ieyasu became known as Tōshō Daigongen. Tenkai continued to serve as a consul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enryakuji
is a Tendai monastery located on Mount Hiei in Ōtsu, overlooking Kyoto. It was first founded in 788 during the early Heian period (794–1185) by Saichō (767–822), also known as Dengyō Daishi, who introduced the Tendai sect of Mahayana Buddhism to Japan from China. The temple complex has undergone several reconstruction efforts since then, with the most significant (that of the main hall) taking place in 1642 under Tokugawa Iemitsu. Enryaku-ji is the headquarters of the Tendai sect and one of the most significant monasteries in Japanese history. As such, it is part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site "Historic Monuments of Ancient Kyoto (Kyoto, Uji and Otsu Cities)". The founders of Jōdo-shū, Jōdo Shinshū, Sōtō Zen, and Nichiren Buddhism all spent time at the monastery. Enryaku-ji is also the center for the practice of kaihōgyō (aka the "marathon monks"). History With the support of Emperor Kanmu, the Buddhist monk Saichō ordained a hundred disciples in 807. Main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hieizan
is a mountain to the northeast of Kyoto, lying on the border between the Kyoto and Shiga Prefectures, Japan. The temple of Enryaku-ji, the first outpost of the Japanese Tendai (Chin. Tiantai) sect of Buddhism, was founded atop Mount Hiei by Saichō in 788 and rapidly grew into a sprawling complex of temples and buildings that were roughly divided into three areas: # The area near the summit, and technically in Kyoto Prefecture. # The area, also near the summit, where Enryaku-ji Temple was first founded, and located just within Shiga Prefecture. # The area near the northernmost end of Mount Hiei. Due to its remoteness, as a temple complex it experienced periods of revival and decline, starting with Ennin, later revived by Ryōgen and made famous by the scholar-monk Genshin. Due to its position north-east of the ancient capital of Kyoto, it was thought in ancient geomancy practices to be a protective bulwark against negative influences on the capital, which along with the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Tokugawa-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 978.Nussbaum"''Edo-jidai''"at p. 167. The Tokugawa shogunate was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after victory at the Battle of Sekigahara, ending the civil wars of the Sengoku period following the collapse of the Ashikaga shogunate. Ieyasu became the ''shōgun,'' and the Tokugawa clan governed Japan from Edo Castle in the eastern city of Edo (Tokyo) along with the ''daimyō'' lords of the ''samurai'' class.Nussbaum"Tokugawa"at p. 976. The Tokugawa shogunate organized Japanese society under the strict Tokugawa class system and banned most foreigners under the isolationist policies of '' Sakoku'' to promote political stability. The Tokugawa shoguns governed Japan in a feudal system, with each ''daimyō'' administering a ''han'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |