|
Shimofunato Shell Mound
is an archaeological site consisting of a shell midden and the remains of an adjacent settlement dating from the Jōmon period, located in what is now the city of Ōfunato, Iwate Prefecture in the Tōhoku region of northern Japan. It has been protected by the central government as a National Historic Site since 1934. Overview During the early to middle Jōmon period (approximately 4000 to 2500 BC), sea levels were five to six meters higher than at present, and the ambient temperature was also 2 deg C higher. During this period, the Tōhoku region was inhabited by the Jōmon people, many of whom lived in coastal settlements. The middens associated with such settlements contain bone, botanical material, mollusc shells, sherds, lithics, and other artifacts and ecofacts associated with the now-vanished inhabitants, and these features, provide a useful source into the diets and habits of Jōmon society. Most of these middens are found along the Pacific coast of Japan. The rocky ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
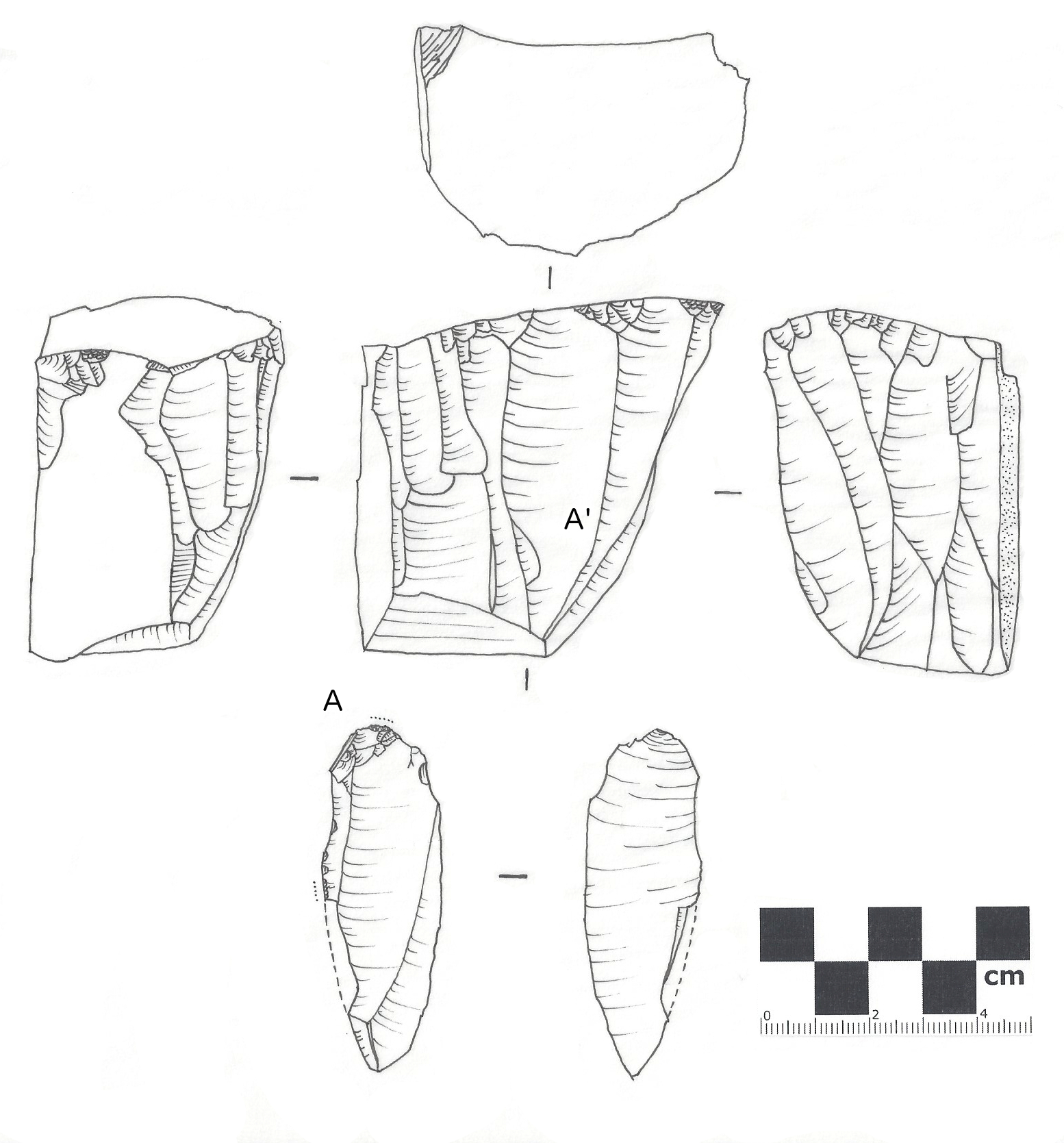
Lithic Flake
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and may also be referred to as simply a ''flake'', or collectively as debitage. The objective piece, or the rock being reduced by the removal of flakes, is known as a core.Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press Once the proper tool stone has been selected, a percussor or pressure flaker (e.g., an antler tine) is used to direct a sharp blow, or apply sufficient force, respectively, to the surface of the stone, often on the edge of the piece. The energy of this blow propagates through the material, often ( but not always) producing a Hertzian cone of force which causes the rock to fracture in a controllable fashion. Since cores are often struck on an edge with a suitable angle (<90°) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Historic Sites Of Japan (Iwate)
This list is of the Historic Sites of Japan located within the Prefecture of Iwate. National Historic Sites As of 24 December 2022, thirty-three Sites have been designated as being of national significance (including three *Special Historic Sites). , align="center", Nabekura Castle Site''Nabekura-jō ato'' , , Tōno , , , , , , , , , , - Prefectural Historic Sites As of 1 May 2022, thirty-seven Sites have been designated as being of prefectural importance. Municipal Historic Sites As of 1 May 2022, a further one hundred and eighty-four Sites have been designated as being of municipal importance. See also * Cultural Properties of Japan * Mutsu Province * Iwate Prefectural Museum * List of Places of Scenic Beauty of Japan (Iwate) * List of Cultural Properties of Japan - paintings (Iwate) This list is of the Cultural Properties of Japan designated in the category of for the Prefecture of Iwate. National Cultural Proper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shimofunato Station
was a JR East railway station located in Ōfunato, Iwate Prefecture, Japan. The station was closed after the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami and has now been replaced by a provisional bus rapid transit line. Lines Shimofunato Station was served by the Ōfunato Line, and was located 100.2 rail kilometers from the terminus of the line at Ichinoseki Station. Station layout Shimofunato Station had a single side platform serving traffic in both directions. The station was unattended. History Shimofunato Station opened on 3 September 1934. The station was absorbed into the JR East network upon the privatization of the Japan National Railways (JNR) on April 1, 1987. The station was closed after the 11 March 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami. Surrounding area * National Route 45 The following highways are numbered 45: International * Asian Highway 45 * European route E45 * AH45A, Asian Highway 45A Burma *National Road 45 (Burma) Canada * Alberta Highway 45 * Manitoba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JR East
The is a major passenger railway company in Japan and is the largest of the seven Japan Railways Group companies. The company name is officially abbreviated as JR-EAST or JR East in English, and as in Japanese. The company's headquarters are in Yoyogi, Shibuya, Tokyo, and next to the Shinjuku Station. It is listed in the Tokyo Stock Exchange (it formerly had secondary listings in the Nagoya and Osaka stock exchanges), is a constituent of the TOPIX Large70 index, and is also one of the three only Japan Railways Group constituents of the Nikkei 225 index, the other being JR Central and JR West. History JR East was incorporated on 1 April 1987 after being spun off from the government-run Japanese National Railways (JNR). The spin-off was nominally "privatization", as the company was actually a wholly owned subsidiary of the government-owned JNR Settlement Corporation for several years, and was not completely sold to the public until 2002. Following the breakup, JR East ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
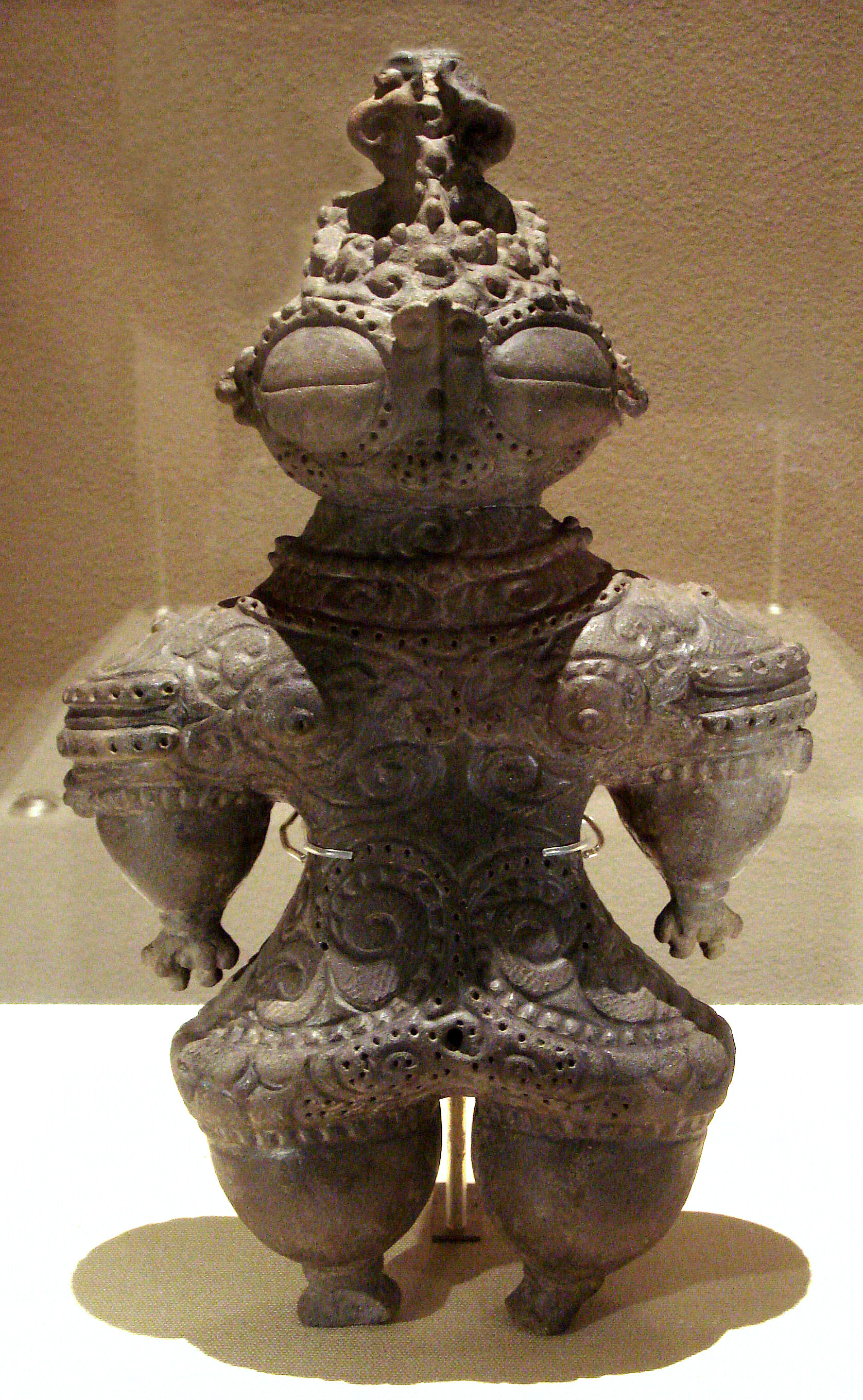
Dogū
are small humanoid and animal figurines made during the later part of the Jōmon period (14,000–400 BC) of prehistoric Japan. ''Dogū'' come exclusively from the Jōmon period, and were no longer made by the following Yayoi period. There are various styles of ''dogū'', depending on the exhumation area and time period. The National Museum of Japanese History estimates that the total number of dogū is approximately 15,000, with The Japan Times placing the figure at approximately 18,000. ''Dogū'' were made across all of Japan, except Okinawa. Most of the ''dogū'' have been found in eastern Japan and it is rare to find one in western Japan. The purpose of the ''dogū'' remains unknown and should not be confused with the clay haniwa funerary objects of the Kofun period (250 – 538 C.E.). Everyday ceramic items from the period are called Jōmon pottery. Origins Some scholars theorize the ''dogū'' acted as Effigy, effigies of people, that manifested some kind of sympathet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ria Coast
A ria (; gl, ría) is a coastal inlet formed by the partial submergence of an unglaciated river valley. It is a drowned river valley that remains open to the sea. Definitions Typically rias have a dendritic, treelike outline although they can be straight and without significant branches. This pattern is inherited from the dendritic drainage pattern of the flooded river valley. The drowning of river valleys along a stretch of coast and formation of rias results in an extremely irregular and indented coastline. Often, there are naturally occurring islands, which are summits of partly submerged, pre-existing hill peaks. (Islands may also be artificial, such as those constructed for the Chesapeake Bay Bridge-Tunnel.) A ria coast is a coastline having several parallel rias separated by prominent ridges, extending a distance inland.Goudie, A. (2004) ''Encyclopedia of Geomorphology.'' Routledge. London, England.Bird, E.C.F. (2008) ''Coastal Geomorphology: An Introduction'', 2nd ed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |
Diet (nutrition)
In nutrition, diet is the sum of food consumed by a person or other organism. The word diet often implies the use of specific intake of nutrition for health or weight-management reasons (with the two often being related). Although humans are omnivores, each culture and each person holds some food preferences or some food taboos. This may be due to personal tastes or ethical reasons. Individual dietary choices may be more or less healthy. Complete nutrition requires ingestion and absorption of vitamins, minerals, essential amino acids from protein and essential fatty acids from fat-containing food, also food energy in the form of carbohydrate, protein, and fat. Dietary habits and choices play a significant role in the quality of life, health and longevity. Health A healthy diet can improve and maintain health, which can include aspects of mental and physical health. Specific diets, such as the DASH diet, can be used in treatment and management of chronic conditions. Dietar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feature (archaeology)
In archaeological excavation, a feature is a collection of one or more contexts representing some human non-portable activity, such as a hearth or wall. Features serve as an indication that the area in which they are found has been interfered with in the past, usually by humans. Features are distinguished from artifacts in that they cannot be separated from their location without changing their form. Artifacts are portable, while features are non-portable. Artifacts and features can both be made from any available material, with the primary distinction being portability. Features and artifacts differ from ecofacts. Ecofacts are natural remains, such as plants and animals. Types Features are categorized by the time period, as either historic or prehistoric. Prehistoric archaeology refers to the time in history before human life was recorded or documented, while historic archaeology refers to the time period where there was a documented human past. In relation to site stra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecofact
In archaeology, a biofact (more commonly known as an ecofact) is any organic material including flora or fauna material found at an archaeological site that has not been technologically altered by humans yet still has cultural relevance. Biofacts/ecofacts can include but are not limited to plants, seeds, pollen, animal bones, insects, fish bones and mollusks. The study of biofacts/ecofacts, alongside other archaeological remains such as artifacts are a key element to understanding how past societies interacted with their surrounding environment and with each other. Biofacts/ecofacts also play a role in helping archaeologists understand questions of subsistence and reveals information about the domestication of certain plant species and animals which demonstrates, for example, the transition from a hunter-gatherer society to a farming society. Biofacts/ecofacts are differentiated from artifacts in that artifacts are typically considered anything purposefully manipulated or made by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_V2.jpg)
.jpg)

