|
Shan–Thai Terrane
The Shan–Thai or Sibumasu Terrane is a mass of continental crust extending from Tibet into Southeast Asia sharing a similar geological history. The Shan–Thai Terrane rifted from Australia in the Permian and collided with the Indochina terrane in the Triassic. It extends from Malaysia, through peninsular Thailand, Myanmar, West Yunnan, to Lhasa. Shan–Thai is long and bounded by the Indochina terrane to the east and the South China terrane to the north. It is one of a series of continental blocks or terranes that were rifted off eastern Gondwana during the Ordovician (), long before the formation of Pangaea. Today these blocks form south-east Asia but the different timing of their journeys has given them distinct geologic histories. Shan–Thai was an archipelago on the Paleo-Tethys Ocean spread over several latitudes. It can therefore be subdivided into several portions with different palaeo-geographical histories. The internal "Thai" elements, bordering the Indochin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
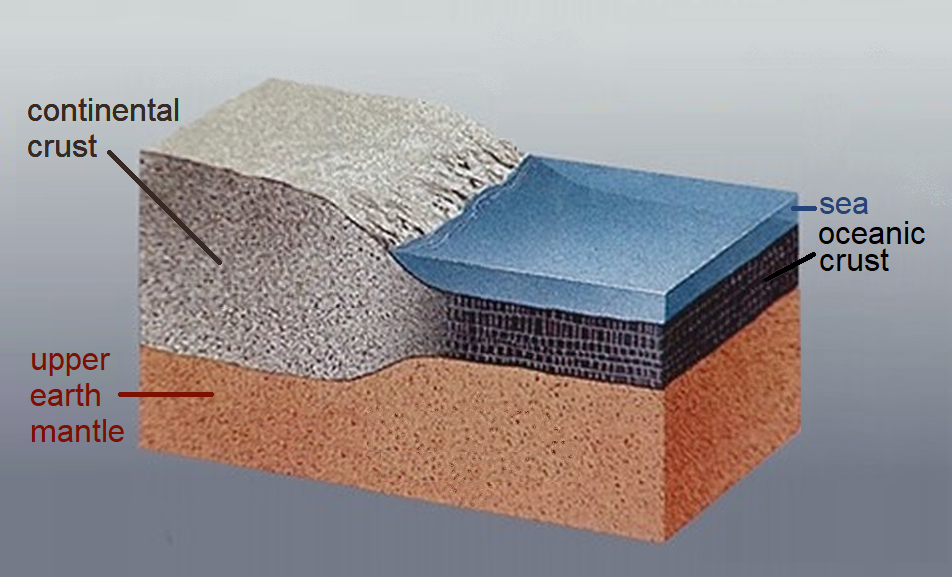
Continental Crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called ''sial'' because its bulk composition is richer in aluminium silicates (Al-Si) and has a lower density compared to the oceanic crust, called ''sima'' which is richer in magnesium silicate (Mg-Si) minerals. Changes in seismic wave velocities have shown that at a certain depth (the Conrad discontinuity), there is a reasonably sharp contrast between the more felsic upper continental crust and the lower continental crust, which is more mafic in character. The continental crust consists of various layers, with a bulk composition that is intermediate (SiO2 wt% = 60.6). The average density of continental crust is about , less dense than the ultramafic material that makes up the mantle, which has a density of around . Continental crust is also less dense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages of break-up, involving the separation of Antarctica from South America (forming the Drake Passage) and Australia, occurred during the Paleogene. Gondwana was not considered a supercontinent by the earliest definition, since the landmasses of Baltica, Laurentia, and Siberia were separated from it. To differentiate it from the Indian region of the same name (see ), it is also commonly called Gondwanaland. Gondwana was formed by the accretion of several cratons. Eventually, Gondwana became the largest piece of continental crust of the Palaeozoic Era, covering an area of about , about one-fifth of the Earth's surface. During the Carboniferous Period, it merged with Laurasia to form a larger supercontinent called Pangaea. Gondwana (and Pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Geology
Historical geology or palaeogeology is a discipline that uses the principles and methods of geology to reconstruct the geological history of Earth. Historical geology examines the vastness of geologic time, measured in billions of years, and investigates changes in the Earth, gradual and sudden, over this deep time. It focuses on geological processes, such as plate tectonics, that have changed the Earth's surface and subsurface over time and the use of methods including stratigraphy, structural geology, paleontology, and sedimentology to tell the sequence of these events. It also focuses on the evolution of life during different time periods in the geologic time scale. Historical development During the 17th century, Nicolas Steno was the first to observe and propose a number of basic principles of historical geology, including three key stratigraphic principles: the law of superposition, the principle of original horizontality, and the principle of lateral continuity. 18th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Tectonic Plates
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonic Plates
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large tectonic plates which have been slowly moving since about 3.4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of ''continental drift'', an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be generally accepted by geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid to late 1960s. Earth's lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of the planet (the crust and upper mantle), is broken into seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates or "platelets". Where the plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of plate boundary: '' convergent'', '' divergent'', or ''transform''. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic tren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facies
In geology, a facies ( , ; same pronunciation and spelling in the plural) is a body of rock with specified characteristics, which can be any observable attribute of rocks (such as their overall appearance, composition, or condition of formation), and the changes that may occur in those attributes over a geographic area. A facies encompasses all of the characteristics of a rock including its chemical, physical, and biological features that distinguish it from adjacent rock. The term facies was introduced by the Swiss geologist Amanz Gressly in 1838 and was part of his significant contribution to the foundations of modern stratigraphy, which replaced the earlier notions of Neptunism. Types of facies Sedimentary facies Ideally, a Sedimentary structures, sedimentary facies is a distinctive rock unit that forms under certain conditions of sedimentation, reflecting a particular process or environment. Sedimentary facies are either descriptive or interpretative. Sedimentary facies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathaysia
Cathaysia was a microcontinent or a group of terranes that rifted off Gondwana during the Late Paleozoic. They mostly correspond to modern territory of China, which were split into the North China and South China blocks. Terminology The terms "Cathaysia", "Cathaysialand" and "Cathaysia Terrane" have been used by various authors for different continental blocks or terranes and assemblages thereof. During the Devonian, the South China and Indochina continents had separated from Gondwana and they collided during the Carboniferous to finally form a superterrane in the Permian. "Cathaysia" has been used for some or all of the constellations involved in this tectonic journey. For example, in South China formed from the amalgamation of the "Yangtse and Cathaysia Blocks", whilst groups North China, South China, and Indochina into the "Cathaysian terranes". Cathaysia, ''sensu'' Scotese, are a few of the almost 70 microcontinents that are involved in the formation of Asia. Furthermore, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleo-Tethys Ocean
The Paleo-Tethys or Palaeo-Tethys Ocean was an ocean located along the northern margin of the paleocontinent Gondwana that started to open during the Middle Cambrian, grew throughout the Paleozoic, and finally closed during the Late Triassic; existing for about 400 million years. Paleo-Tethys was a precursor to the Tethys Ocean (also called the Neo-Tethys) which was located between Gondwana and the Hunic terranes (continental fragments that broke-off Gondwana and moved north). It opened as the Proto-Tethys Ocean subducted under these terranes and closed as the Cimmerian terranes (that also broke-off Gondwana and moved north) gave way to the Tethys Ocean. Confusingly, the Neo-Tethys is sometimes defined as the ocean south of a hypothesised mid-ocean ridge separating Greater Indian from Asia, in which case the ocean between Cimmeria and this hypothesised ridge is called the Meso-Tethys, i.e. the "Middle-Tethys". The so-called Hunic terranes are divided into the ''European Hunic' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million years ago, and began to break apart about 200 million years ago, at the end of the Triassic and beginning of the Jurassic. In contrast to the present Earth and its distribution of continental mass, Pangaea was centred on the equator and surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa and the Paleo-Tethys Ocean, Paleo-Tethys and subsequent Tethys Ocean, Tethys Oceans. Pangaea is the most recent supercontinent to have existed and the first to be reconstructed by geologists. Origin of the concept The name "Pangaea" is derived from Ancient Greek ''pan'' (, "all, entire, whole") and ''Gaia (mythology), Gaia'' or Gaea (, "Mother goddess, Mother Earth, land"). The concept that the continents once formed a contiguous land mass was hypothesised, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its own distinctive geologic history, which is different from that of the surrounding areas—hence the term "exotic" terrane. The suture zone between a terrane and the crust it attaches to is usually identifiable as a fault. A sedimentary deposit that buries the contact of the terrane with adjacent rock is called an overlap formation. An igneous intrusion that has intruded and obscured the contact of a terrane with adjacent rock is called a stitching pluton. Older usage of ''terrane'' simply described a series of related rock formations or an area having a preponderance of a particular rock or rock groups. Overview A tectonostratigraphic terrane is not necessarily an independent microplate in origin, since it may not contain the full thickness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

