|
Shackleton (crater)
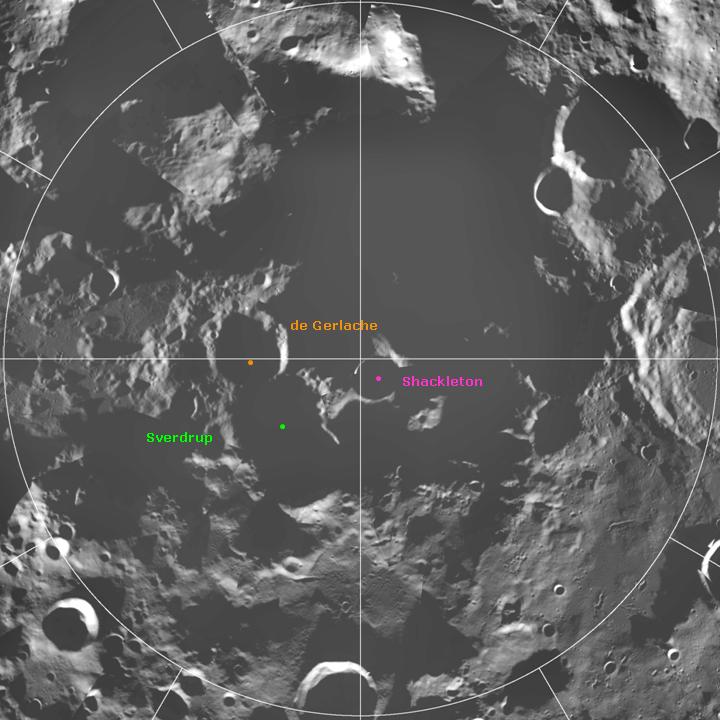
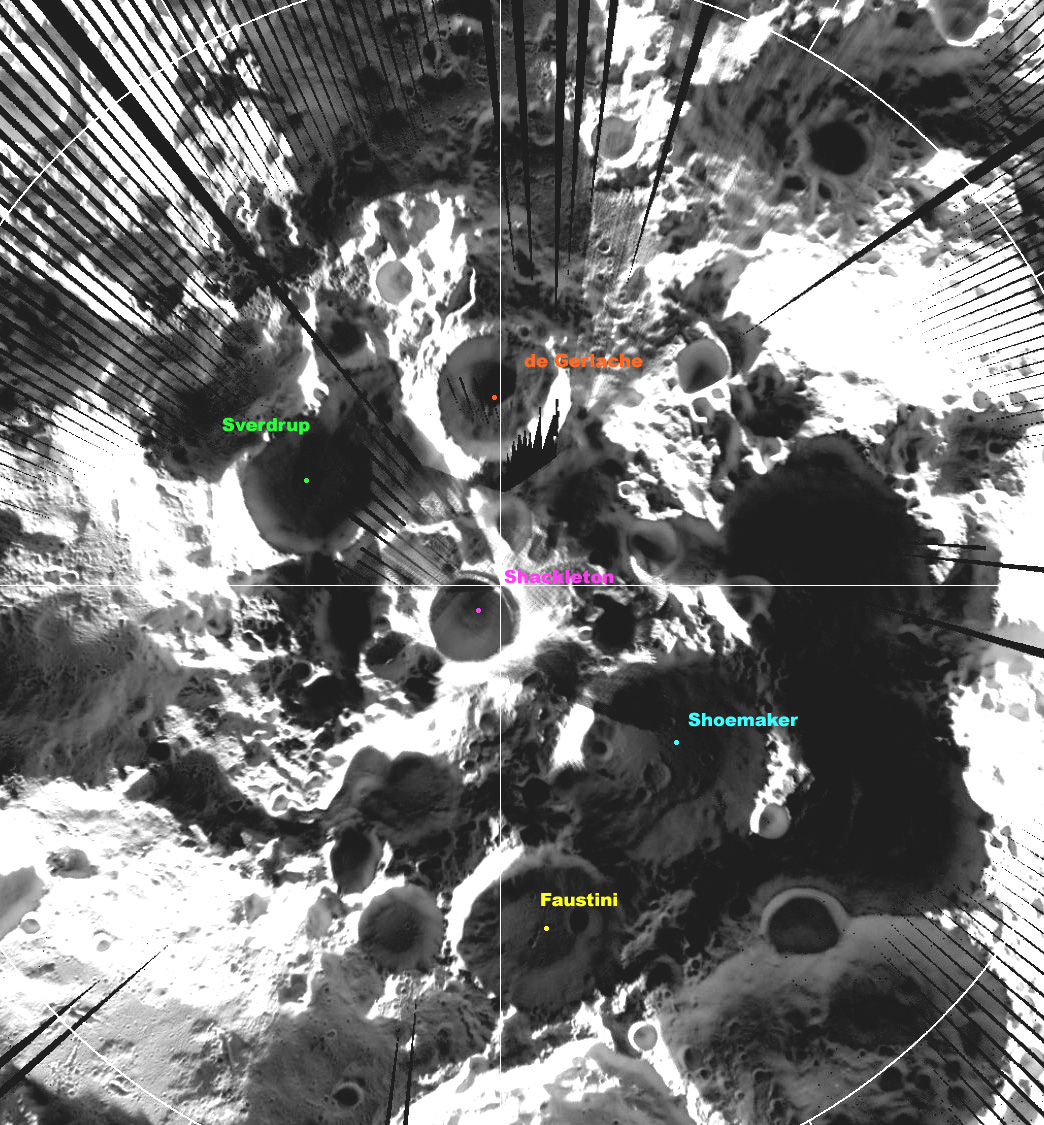
Shackleton is an impact crater that lies at the lunar south pole. The peaks along the crater's rim are exposed to almost continual sunlight, while the interior is perpetually in shadow. The low-temperature interior of this crater functions as a cold trap that may capture and freeze volatiles shed during comet impacts on the Moon. Measurements by the '' Lunar Prospector'' spacecraft showed higher than normal amounts of hydrogen within the crater, which may indicate the presence of water ice. The crater is named after Antarctic explorer Ernest Shackleton. Description The rotational axis of the Moon passes through Shackleton, near the rim. The crater is in diameter and deep. From the Earth, it is viewed edge-on in a region of rough, cratered terrain. It is located within the South Pole–Aitken basin on a massif. The rim is slightly raised about the surrounding surface and it has an outer rampart that has been only lightly impacted. No significant craters intersect the rim, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar South Pole
The lunar south pole is the southernmost point on the Moon, at 90°S. It is of special interest to scientists because of the occurrence of water ice in permanently shadowed areas around it. The lunar south pole region features craters that are unique in that the near-constant sunlight does not reach their interior. Such craters are cold traps that contain a fossil record of hydrogen, water ice, and other volatiles dating from the early Solar System. In contrast, the lunar north pole region exhibits a much lower quantity of similarly sheltered craters. Geography The lunar south pole is located on the center of the polar Antarctic Circle (80°S to 90°S).Lunar South Pole. NASA. 2017. Accessed on 16 July 2019. The lunar south pole has shifted 5 degrees from its original position billions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amundsen (crater)
Amundsen is a large lunar impact crater located near the south pole of the Moon, named after the Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen. It lies along the southern lunar limb, and so is viewed from the side by an observer on the Earth. To the northwest is the crater Scott, a formation of similar dimensions that is named for another Antarctic explorer. Nobile is attached to the western rim. The rim of Amundsen is slightly distended along the southern edge, and the terraced In agriculture, a terrace is a piece of sloped plane that has been cut into a series of successively receding flat surfaces or platforms, which resemble steps, for the purposes of more effective farming. This type of landscaping is therefore ... inner surface is wider at that point than elsewhere along the outer wall. The crater overlaps a smaller crater formation to the northwest, and Amundsen A is attached to the northern rim. Just to the south of Amundsen is the smaller crater Faustini. The inner floor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faustini (crater)
Faustini is a lunar impact crater that lies near the south pole of the Moon. It is located nearly due south of the much larger crater Amundsen, and is almost attached to Shoemaker to the southwest. About one crater diameter due south is the smaller crater Shackleton at the south pole. A small crater is attached to the eastern rim of Faustini. Due to its location, sunlight reaches the rim of this crater at a very low angle, leaving the interior in permanent darkness. As a result, the crater floor has never been observed by orbiting spacecraft, although it has been roughly mapped by radar. The lack of illumination by the Sun, the interior remains at a permanent temperature below 100 kelvins, cold enough to trap any water vapor that reaches the crater following comet impacts on the Moon. The Lunar Prospector spacecraft carried a neutron spectrometer that could be used to detect the presence of large concentrations of hydrogen Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slater (crater)
Slater is an impact crater near the south pole of the Moon. Like nearby Shackleton, the floor of the crater is in nearly perpetual darkness. The crater's name was adopted by the IAU The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach ... in May 2015, after the American planetary scientist David Charles Slater.Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature, International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN)Slater/ref> References * * * * * * * * * * * * Impact craters on the Moon {{Moon-crater-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sverdrup (crater)
Sverdrup is a lunar impact crater that is located about one crater diameter from the southern pole of the Moon. It lies on the far side of the Moon with respect to the Earth, in an area of the surface that is only illuminated by very oblique light from the Sun. The interior part of the crater is cloaked in perpetual darkness, and thus has not been mapped using photography. Portions of the rim are illuminated, however, and give the appearance of a worn formation that has been intruded upon by adjacent formations. The nearest craters of note to Sverdrup are de Gerlache to the east, and Shackleton at the south pole. References * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * {{cite news , title = Diviner lunar south pole image , publisher = UCLA The University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) is a public land-grant research university in Los Angeles, California. UCLA's academic roots were established in 1881 as a teachers college then known as the sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Gerlache (crater)
de Gerlache is a lunar impact crater that is located along the southern limb of the Moon, within a crater diameter of Shackleton at the south pole. From the Earth this crater is seen from the edge, and it lies in perpetual darkness. Thus little or no detail can be seen of this crater, other than the edge of the rim. However, the crater is clearly visible in Earth-based radar images. The crater is roughly circular, with some slight wear. No craters of note overlie the rim, although some formations may be attached to the southern and western edges. The crater was identified by Jean-Luc Margot and Donald B. Campbell who jointly proposed the name to the International Astronomical Union. The name, honoring the Belgian explorer Adrien de Gerlache, was adopted by the IAU The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haworth (crater)
Haworth is an impact crater that lies at the south pole of the Moon. The crater is named after British chemist Walter Haworth. Formation According to a 2015 study by Tye ''et al.'', Haworth was formed sometime during the Pre-Nectarian period, meaning it is at least 3.9 Ga (billion years) old. Physical features Due to Haworth's position near the lunar south pole, large amounts of the crater are permanently shadowed regions. These regions are very cold; many are believed to never reach temperatures above 40 Kelvin, making Haworth colder than nearby craters such as Shackleton and Faustini. Haworth and its surrounding low-lying areas are home to frost, which may be partly caused by these particularly low temperatures. See also * Lunar south pole References {{reflist , refs = {{cite web , date = January 16, 2009 , url = http://www.astronomy.com/asy/default.aspx?c=a&id=7833 , title = Chandrayaan-1 peeks inside Moon craters , publisher = Astronomy.com , accessdate = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoemaker (lunar Crater)
Shoemaker is a lunar craters, lunar impact crater located near the lunar south pole, southern pole of the Moon, within half a crater diameter of Shackleton (crater), Shackleton. Crater It lies to the south of the crater Malapert (crater), Malapert, to the east of Haworth (crater), Haworth, and just to the west of the similar-sized Faustini (crater), Faustini. The rim of Shoemaker is circular and worn, with some small craters along the inner wall. Due to the lack of illumination (it is a crater of eternal darkness), the albedo of the interior floor surface remains unknown. Prior to being given its current name by the International Astronomical Union, IAU, this formation had been informally named Mawson (after the Antarctic explorer Douglas Mawson). It was officially named Shoemaker in honor of Eugene Merle Shoemaker, Eugene Shoemaker, the geologist whose remains were on board the Lunar Prospector spacecraft that impacted this crater floor. Cold trap deposits This crater became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and development through global cooperation. It was founded in 1919 and is based in Paris, France. The IAU is composed of individual members, who include both professional astronomers and junior scientists, and national members, such as professional associations, national societies, or academic institutions. Individual members are organised into divisions, committees, and working groups centered on particular subdisciplines, subjects, or initiatives. As of 2018, the Union had over 13,700 individual members, spanning 90 countries, and 82 national members. Among the key activities of the IAU is serving as a forum for scientific conferences. It sponsors nine annual symposia and holds a triannual General Assembly that sets policy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Irish People
Anglo-Irish people () denotes an ethnic, social and religious grouping who are mostly the descendants and successors of the English Protestant Ascendancy in Ireland. They mostly belong to the Anglican Church of Ireland, which was the established church of Ireland until 1871, or to a lesser extent one of the English dissenting churches, such as the Methodist church, though some were Roman Catholics. They often defined themselves as simply "British", and less frequently "Anglo-Irish", "Irish" or "English". Many became eminent as administrators in the British Empire and as senior army and naval officers since Kingdom of England and Great Britain were in a real union with the Kingdom of Ireland until 1800, before politically uniting into the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland) for over a century. The term is not usually applied to Presbyterians in the province of Ulster, whose ancestry is mostly Lowland Scottish, rather than English or Irish, and who are sometimes id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |