|
Sergeant York Gun
The M247 Sergeant York DIVAD (Division Air Defense) was a self-propelled anti-aircraft gun (SPAAG), developed by Ford Aerospace in the late 1970s. Based on the M48 Patton tank, it replaced the Patton's turret with a new one that featured twin radar-directed Bofors 40 mm rapid-fire guns. The vehicle was named after Sergeant Alvin York, a famous World War I hero. The Sergeant York was intended to fight alongside the M1 Abrams and M2 Bradley in the U.S. Army, in a role similar to the Soviet ZSU-23-4 and German Flakpanzer Gepard. It would replace the M163 Vulcan Air Defense System SPAAG and MIM-72 Chaparral missile, ''ad hoc'' systems of limited performance that had been introduced when the more advanced MIM-46 Mauler missile failed to mature. Despite the use of many off the shelf technologies that were intended to allow rapid and low-cost development, a series of technical problems and massive cost overruns resulted in the cancelation of the project in 1985. History Prior ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-propelled Antiaircraft Gun
An anti-aircraft vehicle, also known as a self-propelled anti-aircraft gun (SPAAG) or self-propelled air defense system (SPAD), is a mobile vehicle with a dedicated anti-aircraft capability. Specific weapon systems used include machine guns, autocannons, larger guns, or missiles, and some mount both guns and longer-ranged missiles (e.g. the Pantsir-S1). Platforms used include both trucks and heavier combat vehicles such as armored personnel carriers and tanks, which add protection from aircraft, artillery, and small arms fire for front line deployment. Anti-aircraft guns are usually mounted in a quickly-traversing turret with a high rate of elevation, for tracking fast-moving aircraft. They are often in dual or quadruple mounts, allowing a high rate of fire. In addition, most anti-aircraft guns can be used in a direct-fire role against surface targets to great effect. Today, missiles (generally mounted on similar turrets) have largely supplanted anti-aircraft guns, but they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bofors 40 Mm Automatic Gun L/60
The Bofors 40 mm Automatic Gun L/60 (often referred to simply as the "Bofors 40 mm gun", the "Bofors gun" and the like, see name) is an anti-aircraft autocannon, designed in the 1930s by the Swedish arms manufacturer AB Bofors. The gun was designed as an intermediate anti-aircraft gun, filling the gap between fast firing close-range small calibre anti-aircraft guns and slower firing long-range high calibre anti-aircraft guns, a role which previously was filled by older outdated guns. The Bofors 40 mm L/60 was for its time perfectly suited for this role and outperformed competing designs in the years leading up to World War II in both effectiveness and reliability. It entered the export market around 1932 and was in service with 18 countries by 1939. Throughout World War II it became one of the most popular and widespread medium-weight anti-aircraft guns. It was used by the majority of the western Allies and some Axis powers such as Nazi Germany and Hungary. In the pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLIR
Forward-looking infrared (FLIR) cameras, typically used on military and civilian aircraft, use a thermographic camera that senses infrared radiation. The sensors installed in forward-looking infrared cameras, as well as those of other thermal imaging cameras, use detection of infrared radiation, typically emitted from a heat source (thermal radiation), to create an image assembled for video output. They can be used to help pilots and drivers steer their vehicles at night and in fog, or to detect warm objects against a cooler background. The wavelength of infrared that thermal imaging cameras detect is 3 to 12 μm and differs significantly from that of night vision, which operates in the visible light and near-infrared ranges (0.4 to 1.0 μm). Design Infrared light falls into two basic ranges: ''long-wave'' and ''medium-wave''. Long-wave infrared (LWIR) cameras, sometimes called "far-infrared", operate at 8 to 12 μm and can see heat sources, such as hot e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Front Line
A front line (alternatively front-line or frontline) in military terminology is the position(s) closest to the area of conflict of an armed force's personnel and equipment, usually referring to land forces. When a front (an intentional or unintentional boundary) between opposing sides forms, the front line is the area where each side's forces are engaged in conflict. Leaders have often fought at the front lines either purposefully or due to a collapse in battle formation. While a calculated risk, fighting on the front has in instances reduced communication and heightened morale. All branches of the United States Armed Forces use the related technical terms, Forward Line of Own Troops (FLOT) and Forward Edge of Battle Area (FEBA). These terms are used as battlespace control measures that designate the forward-most friendly maritime or land forces on the battlefield at a given point in time during an armed conflict. FLOT/FEBA may include covering and screening forces. The Forwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gama Goat
The Gama Goat was a six-wheel drive semi-amphibious off-road vehicle originally developed for use by the US military in the Vietnam War. The Goat uses an articulated chassis, so that from distance it appears to be a four-wheel drive vehicle pulling a two-wheel trailer, but it is a single six-wheel vehicle with a four-wheel steering arrangement with the front and rear wheels turning in opposite directions. It was famous for its ability to travel over exceptionally rough and muddy terrain. The vehicle's nickname came from two sources: "Gama" from the name of the inventor of its powered articulated joint, Roger Gamaunt, and "Goat" for its mountain goat-like off-road ability. Its military designation was M561, 6×6 tactical 1¼-ton truck. There was also an ambulance version known as the M792. The vehicle was replaced by a variety of Commercial Utility Cargo Vehicles (CUCV) and Humvees (HMMWV) History The concept for the vehicle came when the French Army reported that the United Stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AN/MPQ-49 Forward Area Alerting Radar
The AN/MPQ-49 Forward Area Alerting Radar (FAAR) is a lightweight early warning radar system consisting of the AN/TPQ-43 radar, AN/TPX-50 Mark XII IFF receiver, a 5 kW generator set, and a Gama Goat providing mobility."AN/MPQ-49 Forward Area Alerting Radar (FAAR)" GlobalSecurity.org Development FAAR was developed by the in the 1960s to support their field weapons, the ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AIM-9 Sidewinder
The AIM-9 Sidewinder (where "AIM" stands for "Air Intercept Missile") is a short-range air-to-air missile which entered service with the US Navy in 1956 and subsequently was adopted by the US Air Force in 1964. Since then the Sidewinder has proved to be an enduring international success, and its latest variants remain standard equipment in most Western-aligned air forces. The Soviet K-13 (AA-2 'Atoll'), a reverse-engineered copy of the AIM-9B, was also widely adopted by a number of nations. Low-level development started in the late 1940s, emerging in the early 1950s as a guidance system for the modular Zuni rocket. This modularity allowed for the introduction of newer seekers and rocket motors, including the AIM-9C variant, which used semi-active radar homing and served as the basis of the AGM-122 Sidearm anti-radar missile. Originally a tail-chasing system, early models saw extensive use during the Vietnam War but had a low success rate. This led to all-aspect capabilities in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M61 Vulcan
The M61 Vulcan is a hydraulically, electrically, or pneumatically driven, six-barrel, air-cooled, electrically fired Gatling-style rotary cannon which fires rounds at an extremely high rate (typically 6,000 rounds per minute). The M61 and its derivatives have been the principal cannon armament of United States military fixed-wing aircraft for over sixty years. The M61 was originally produced by General Electric. After several mergers and acquisitions, it is currently produced by General Dynamics. Development At the end of World War II, the United States Army Air Forces began to consider new directions for future military aircraft guns. The higher speeds of jet-powered fighter aircraft meant that achieving an effective number of hits would be extremely difficult without a much higher volume of fire. While captured German designs (principally the Mauser MG 213C) showed the potential of the single-barrel revolver cannon, the practical rate of fire of such a design was still lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
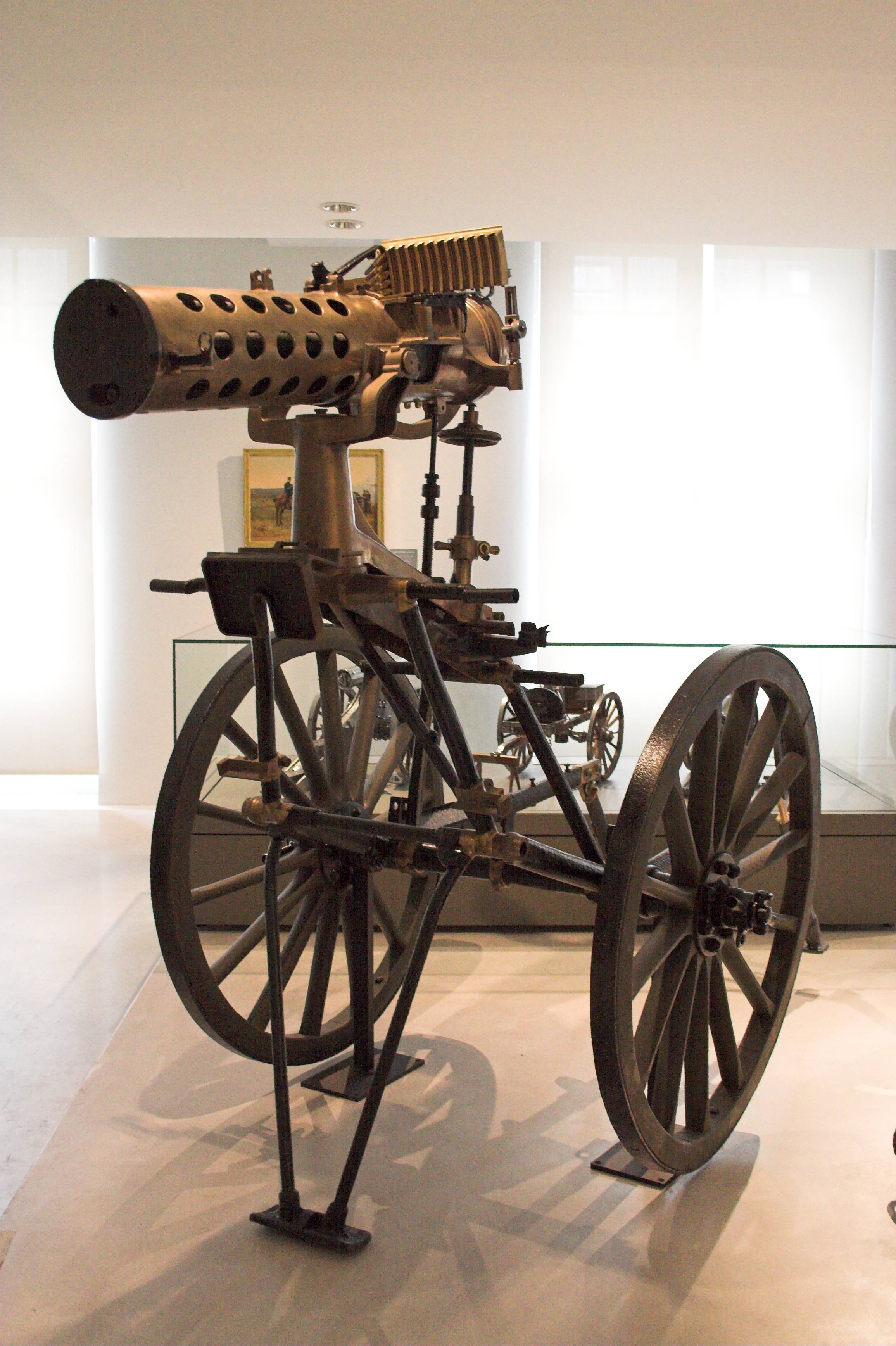
Gatling Gun
The Gatling gun is a rapid-firing multiple-barrel firearm invented in 1861 by Richard Jordan Gatling. It is an early machine gun and a forerunner of the modern electric motor-driven rotary cannon. The Gatling gun's operation centered on a cyclic multi-barrel design which facilitated cooling and synchronized the firing-reloading sequence. As the handwheel is cranked, the barrels rotate and each barrel sequentially loads a single cartridge from a top-mounted magazine, fires off the shot when it reaches a set position (usually at 4 o'clock), then ejects the spent casing out of the left side at the bottom, after which the barrel is empty and allowed to cool until rotated back to the top position and gravity-fed another new round. This configuration eliminated the need for a single reciprocating bolt design and allowed higher rates of fire to be achieved without the barrels overheating quickly. One of the best-known early rapid-fire firearms, the Gatling gun saw occasional use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T249 Vigilante
The T249 Vigilante was a prototype 37 mm self-propelled anti-aircraft gun (SPAAG) designed as a replacement for the Bofors 40 mm gun and M42 Duster in US Army service. The system consisted of a 37 mm T250 six-barrel Gatling gun mounted on a lengthened M113 armored personnel carrier platform. By the early 1960s, the US Army declared that gun-based systems were outdated, and canceled further development in favor of the MIM-46 Mauler missile system that also failed to enter service. The designer, the Sperry Utah Engineering Laboratory, later revived the Vigilante, rechambering it for NATO-standard 35×228mm rounds and mounting it on a M48 Patton tank chassis for the Division Air Defense (DIVAD) contest. However, it ultimately lost to Ford's M247 Sergeant York that also failed to enter service. Development Very little information exists of the T249 Vigilante and its T250 cannon. The conceptual design for the T250 cannon was initiated in 1956. While the design of can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (also known by #Names, other names) was a conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. It was the second of the Indochina Wars and was officially fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. The north was supported by the Soviet Union, China, and other communist states, while the south was United States in the Vietnam War, supported by the United States and other anti-communism, anti-communist Free World Military Forces, allies. The war is widely considered to be a Cold War-era proxy war. It lasted almost 20 years, with direct U.S. involvement ending in 1973. The conflict also spilled over into neighboring states, exacerbating the Laotian Civil War and the Cambodian Civil War, which ended with all three countries becoming communist states by 1975. After the French 1954 Geneva Conference, military withdrawal from Indochina in 1954 – following their defeat in the First Indochina War – the Viet Minh to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)