|
Sepik Hills
The Sepik () is the longest river on the island of New Guinea, and the second largest in Oceania by discharge volume after the Fly River. The majority of the river flows through the Papua New Guinea (PNG) provinces of Sandaun (formerly West Sepik) and East Sepik, with a small section flowing through the Indonesian province of Papua. The Sepik has a large catchment area, and landforms that include swamplands, tropical rainforests and mountains. Biologically, the river system is often said to be possibly the largest uncontaminated freshwater wetland system in the Asia-Pacific region. But, in fact, numerous fish and plant species have been introduced into the Sepik since the mid-20th century. Name In 1884, Germany asserted control over the northeast quadrant of the island of New Guinea, which became part of the German colonial empire. The colony was initially managed by the Deutsche Neuguinea-Kompagnie or German New Guinea Company, a commercial enterprise that christened the te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramu
The Ramu River is a major river in northern Papua New Guinea. The headwaters of the river are formed in the Kratke Range from where it then travels about northwest to the Bismarck Sea. Along the Ramu's course, it receives numerous tributaries from the Bismarck Range to the south and the Finisterre and Adelbert. History For many millennia, people have lived along the river, and the river has formed the basis for food, transport, and culture. German exploration The area encompassed by the Ramu was part of Kaiser-Wilhelmsland when Germany established German New Guinea in 1884. The Germans were quick to explore their territory, and the mouth of the Ramu was discovered in 1886 by Vice-Admiral Freiherr von Schleinitz after returning to Finschhafen from an expedition to the nearby Sepik.Souter (1963) p. 73 Schleinitz called the Ramu, ''Ottilien'' after his ship the ''Ottilie''. The course of the river was first discovered 10 years later in 1896 after Dr Carl Lauterbach, a bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Sepik
East Sepik is a province in Papua New Guinea. Its capital is Wewak. East Sepik has an estimated population of 433,481 people (2010 census) and is 43,426 km square in size. History Cherubim Dambui was appointed as East Sepik's first premier by Prime Minister Michael Somare upon the creation of the provincial government in 1976. Dambui remained interim premier until 1979, when he became East Sepik's permanent premier with a full term. He remained in office until 1983. Geography Wewak, the provincial capital, is located on the coast of East Sepik. There are a scattering of islands off shore, and coastal ranges dominate the landscape just inland of the coast. The remainder of the province's geography is dominated by the Sepik River, which is one of the largest rivers in the world in terms of water flow and is known for flooding—the river's level can alter by as much as five metres in the course of the year as it rises and falls. The southern areas of the province are taken up b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Depression, Papua New Guinea
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object. Central may also refer to: Directions and generalised locations * Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as Middle Africa * Central America, a region in the centre of America continent * Central Asia, a region in the centre of Eurasian continent * Central Australia, a region of the Australian continent * Central Belt, an area in the centre of Scotland * Central Europe, a region of the European continent * Central London, the centre of London * Central Region (other) * Central United States, a region of the United States of America Specific locations Countries * Central African Republic, a country in Africa States and provinces * Blue Nile (state) or Central, a state in Sudan * Central Department, Paraguay * Central Province (Kenya) * Central Province (Papua New Guinea) * Central Province (Solomon Islands) * Central Province, Sri Lank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telefomin
Telefomin is a station town on the border of Sandaun and Western Provinces in Papua New Guinea. The town started during the Second World War after Mick Leahy was assigned to engineer an air-strip in 1944 for the United States for use against the Imperial Japanese Army forces based in New Guinea. The Sepik River runs west-east south of the town. The Baptist Mission of Telefomin contains a notable museum and fossils that have been found in the area. The Telefomin peoples traditionally have carved designs onto tall boards for the entrances of their houses. In 1953 two Australian patrol officers and four police were killed by tribesman in the Telefomin Incident The Telefomin incident occurred in November 1953 in Papua New Guinea Papua New Guinea (abbreviated PNG; , ; tpi, Papua Niugini; ho, Papua Niu Gini), officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea ( tpi, Independen Stet bilong Pap .... References Populated places in Sandaun Province {{SandaunProvi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iatmul People
The Iatmul are a large ethnic group of about 10,000 people inhabiting some two-dozen politically autonomous villages along the middle Sepik River in Papua New Guinea. The communities are roughly grouped according to dialect of the Iatmül language as well as sociocultural affinities. The Iatmul are best known for their art, men's houses, male initiation, elaborate totemic systems, and a famous ritual called ''naven'', first studied by Gregory Bateson in the 1930s. More recently, Iatmul are known as a location for tourists and adventure travellers, and a prominent role in the 1988 documentary film ''Cannibal Tours''. File:Ancestor figure with skull, Papua New Guinea, Middle Sepik, Iatmul people, wood, skull, shells and human hair, HAA.jpg, Ancestor Iatmul figure with skull History In Iatmul legend, the original condition of the world was a primal sea. A wind stirred waves, and land surfaced. A large pit opened, and from it emerged the first generation of ancestral spirits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augusta Of Saxe-Weimar
Princess Augusta Marie Luise Katharina of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach (30 September 1811 – 7 January 1890) was the queen of Prussia and the first German empress as the consort of William I, German Emperor. Early life Augusta was the second daughter of Charles Frederick, Grand Duke of Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach, and Maria Pavlovna of Russia, a daughter of Paul I of Russia and Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg. While her father was an intellectually limited person, whose preferred reading up to the end of his life was fairy tales, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe spoke of Augusta's mother Marie as "one of the best and most significant women of her time." Augusta received a comprehensive education, including drawing lessons from the court painter, Luise Seidler, as well as music lessons from the court bandmaster, Johann Nepomuk Hummel. Meeting with Wilhelm Augusta was only fifteen years old when, in 1826, she first met her future husband, Prince Wilhelm (William), who was more than fourteen ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Finsch
Friedrich Hermann Otto Finsch (8 August 1839, Warmbrunn – 31 January 1917, Braunschweig) was a German ethnographer, natural history, naturalist and colonial explorer. He is known for a two-volume monograph on the parrots of the world which earned him a doctorate. He also wrote on the people of New Guinea and was involved in plans for German colonization in Southeast Asia. Several species of bird (such as ''Oenanthe finschii'', ''Alophoixus finschii'', ''Psittacula finschii'') are named after him as also the town of Finschhafen in Morobe Province, Papua New Guinea and a crater on the moon. Biography Finsch was born at Cieplice Śląskie-Zdrój, Bad Warmbrunn in Silesia to Mortiz Finsch and Mathilde née Leder. His father was in the glass trade and he too trained as a glass painter. An interest in birds led him to use his artistic skills for the purpose. Finsch went to Budapest in 1857 and studied at the Eötvös Loránd University, Royal Hungarian University, earning money by prep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
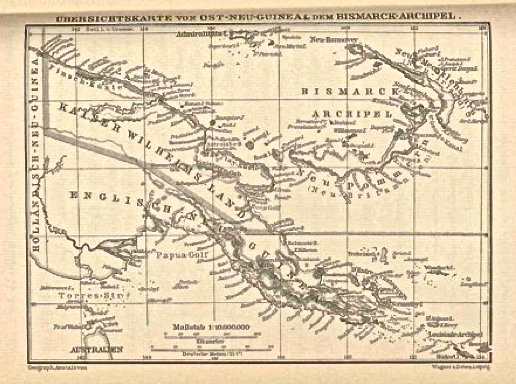
Kaiser-Wilhelmsland
Kaiser-Wilhelmsland ("Emperor William's Land") formed part of German New Guinea (german: Deutsch-Neuguinea), the South Pacific protectorate of the German Empire. Named in honour of Wilhelm I, who reigned as German Emperor () from 1871 to 1888, it included the northern part of present-day Papua New Guinea. From 1884 until 1920 the territory was a protectorate ( de , Schutzgebiet) of the German Empire. Kaiser-Wilhelmsland, the Bismarck Archipelago (including New Mecklenburg and New Pomerania), the northern Solomon Islands, the Caroline Islands, Palau, Nauru, the Northern Mariana Islands, and the Marshall Islands comprised German New Guinea. Most of the German settlers in Kaiser-Wilhelmsland worked as plantation owners, miners, or government functionaries; the number of European settlers, including non-Germans, was never very high. In 1885, Lutheran and Catholic congregations sent clergy to establish missions; they experienced moderate, but very slow, success with the indigenous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German New Guinea Company
The German New Guinea Company (german: Deutsche Neuguinea-Kompagnie) was a German Chartered Company which exploited insular territory in and near present Papua New Guinea. History In the 1870s and 1880s German commercial firms began to site trading stations in New Guinea. Agents of J.C. Godeffroy & Sohn reached the Bismarck Archipelago from the Caroline Islands in 1872. In 1875 Hersheim & Company moved to the Archipelago. In 1884, the New Guinea Company was founded in Berlin by Adolph von Hansemann and a syndicate of German bankers for the purpose of colonizing and exploiting resources on ''Neuguinea'' (German New Guinea), where German interest grew after British Queensland's annexation of part of eastern New Guinea. This expedition was with the knowledge and blessing of the German Chancellor, Count Otto von Bismarck, and with secrecy and speed an expedition was fitted out under Dr Otto Finsch, ornithologist and explorer. His task was to select land for plantation develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Colonial Empire
The German colonial empire (german: Deutsches Kolonialreich) constituted the overseas colonies, dependencies and territories of the German Empire. Unified in the early 1870s, the chancellor of this time period was Otto von Bismarck. Short-lived attempts at colonization by individual German states had occurred in preceding centuries, but Bismarck resisted pressure to construct a colonial empire until the Scramble for Africa in 1884. Claiming much of the left-over uncolonized areas of Africa, Germany built the third-largest colonial empire at the time, after the British and French. The German Colonial Empire encompassed parts of several African countries, including parts of present-day Burundi, Rwanda, Tanzania, Namibia, Cameroon, Gabon, Congo, Central African Republic, Chad, Nigeria, Togo, Ghana, as well as northeastern New Guinea, Samoa and numerous Micronesian islands. Including mainland Germany, the empire had a total land area of 3,503,352 square kilometers and pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |