|
Separation Range
Separation Range () is the northeastern branch of the Commonwealth Range in the Queen Maud Mountains, Antarctica. The branch starts at about 84°20'S, and forms two chains of mountains separated by Hood Glacier. The Separation Range, about long, terminates to the north at the Ross Ice Shelf. Named by the New Zealand Alpine Club Antarctic Expedition, 1959–60. Location The Separation range lies to the east of the northern part of the Commonwealth Range, and runs from south to north between that range and the Canyon Glacier to the east. The Cunningham Glacier enters the Canyon Glacier just south of the southern end of the Searation Range. The northern end adjoins the Ross Ice Shelf. The Hood Glacier Hood Glacier () is a glacier about long draining northward from Siege Dome in the Commonwealth Range of Antarctica. It enters the Ross Ice Shelf between the Commonwealth Range and the Separation Range. The glacier was discovered by the Southern ... defines its western edge. Fea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Maud Mountains
The Queen Maud Mountains are a major group of mountains, ranges and subordinate features of the Transantarctic Mountains, lying between the Beardmore and Reedy Glaciers and including the area from the head of the Ross Ice Shelf to the Antarctic Plateau in Antarctica. Captain Roald Amundsen and his South Pole party ascended Axel Heiberg Glacier near the central part of this group in November 1911, naming these mountains for the Norwegian queen Maud of Wales. Despite the name, they are not located within Queen Maud Land. Elevations bordering the Beardmore Glacier, at the western extremity of these mountains, were observed by the British expeditions led by Ernest Shackleton (1907–09) and Robert Falcon Scott (1910-13), but the mountains as a whole were mapped by several American expeditions led by Richard Evelyn Byrd (1930s and 1940s), and United States Antarctic Program (USARP) and New Zealand Antarctic Research Program (NZARP) expeditions from the 1950s through the 1970s. Featu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Range
The Commonwealth Range is a north-south trending range of rugged mountains, long, located within the Queen Maud Mountains on the Dufek Coast of the continent of Antarctica. The range borders the eastern side of Beardmore Glacier from the Ross Ice Shelf to Keltie Glacier. The range was discovered by the British Antarctic Expedition (1907–09) and named by the expedition after the Commonwealth of Australia, which gave much assistance to the expedition. Key features Its highest peak is Flat Top at 4000 meters or 13,123 feet. Other peaks within the range include: * |
Hood Glacier
Hood Glacier () is a glacier about long draining northward from Siege Dome in the Commonwealth Range of Antarctica. It enters the Ross Ice Shelf between the Commonwealth Range and the Separation Range. The glacier was discovered by the Southern Polar Party of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1907–09, under Ernest Shackleton, and was named for Admiral Sir Horace Hood, under whom Jameson Adams, a member of the party, had served in HMS ''Berwick''. The outcropping known as the Chevron Rocks Chevron Rocks () is a distinctive rock outcrop at the north end of Retrospect Spur, near the head of Hood Glacier in the Queen Maud Mountains. A New Zealand New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Oc ... is located near the head of Hood Glacier. References Glaciers of Dufek Coast {{DufekCoast-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
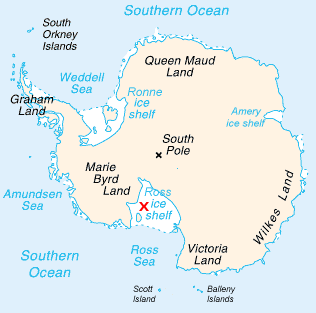
Ross Ice Shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between high above the water surface. Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface. Most of Ross Ice Shelf is in the Ross Dependency claimed by New Zealand. It floats in, and covers, a large southern portion of the Ross Sea and the entire Roosevelt Island located in the east of the Ross Sea. The ice shelf is named after Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered it on 28 January 1841. It was originally called "The Barrier", with various adjectives including "Great Ice Barrier", as it prevented sailing further south. Ross mapped the ice front eastward to 160° W. In 1947, the U.S. Board on Geographic Names applied the name "Ross Shelf Ice" to this feature and published it in the original U.S. Antarctic Gazetteer. In Januar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canyon Glacier
Canyon Glacier () is a narrow glacier, long, flowing to the Ross Ice Shelf. It drains the northwest slopes of Mount Wexler and moves northward between steep canyon walls of the Separation Range and Hughes Range to join the ice shelf immediately west of Giovinco Ice Piedmont. The glacier was observed from nearby Mount Patrick Mount Patrick () is a massive, largely ice-covered mountain in the Commonwealth Range of Antarctica, rising to just east of Wedge Face Wedge Face () is a descriptive name for the prominent wedge-shaped rock spur that projects from Mount Patric ... by the New Zealand Alpine Club Antarctic Expedition (1959–60) who gave the descriptive name. References Glaciers of Dufek Coast {{DufekCoast-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cunningham Glacier
Canyon Glacier () is a narrow glacier, long, flowing to the Ross Ice Shelf. It drains the northwest slopes of Mount Wexler and moves northward between steep canyon walls of the Separation Range and Hughes Range to join the ice shelf immediately west of Giovinco Ice Piedmont. The glacier was observed from nearby Mount Patrick by the New Zealand Alpine Club Antarctic Expedition New is an adjective referring to something recently made, discovered, or created. New or NEW may refer to: Music * New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz Albums and EPs * ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013 * ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, ... (1959–60) who gave the descriptive name. References Glaciers of Dufek Coast {{DufekCoast-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Ranges
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arisen from the same cause, usually an orogeny. Mountain ranges are formed by a variety of geological processes, but most of the significant ones on Earth are the result of plate tectonics. Mountain ranges are also found on many planetary mass objects in the Solar System and are likely a feature of most terrestrial planets. Mountain ranges are usually segmented by highlands or mountain passes and valleys. Individual mountains within the same mountain range do not necessarily have the same geologic structure or petrology. They may be a mix of different orogenic expressions and terranes, for example thrust sheets, uplifted blocks, fold mountains, and volcanic landforms resulting in a variety of rock types. Major ranges Most geologically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Ranges Of Antarctica
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |