|
Sense Of Direction
Sense of direction is the ability to know one's location and perform wayfinding. It is related to cognitive maps, spatial awareness, and spatial cognition. Sense of direction can be impaired by brain damage, such as in the case of topographical disorientation. Humans create spatial maps whenever they go somewhere. Neurons called place cells inside the hippocampus fire individually while a person makes their way through an environment. This was first discovered in rats, when the neurons of the hippocampus were recorded. Certain neurons fired whenever the rat was in a certain area of its environment. These neurons form a grid when they are all put together on the same plane. Santa Barbara Sense-of-Direction Scale Sense of direction can be measured with the Santa Barbara Sense-of-Direction Scale, a self-assessed psychometric test designed in 2002. This scale has been used to study sense of direction in many contexts, such as driving. See also * Direction determination * Personal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wayfinding
Wayfinding (or way-finding) encompasses all of the ways in which people (and animals) orient themselves in physical space and navigate from place to place. Wayfinding software is a self-service computer program that helps users to find a location, usually used indoors and installed on interactive kiosks or smartphones. Basic process The basic process of wayfinding involves four stages: # ''Orientation'' is the attempt to determine one's location, in relation to objects that may be nearby and the desired destination. # ''Route decision'' is the selection of a course of direction to the destination. # ''Route monitoring'' is checking to make sure that the selected route is heading towards the destination. # ''Destination recognition'' is when the destination is recognized. Historical Historically, wayfinding refers to the techniques used by travelers over land and sea to find relatively unmarked and often mislabeled routes. These include but are not limited to dead reckoning, map ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Map
A cognitive map is a type of mental representation which serves an individual to acquire, code, store, recall, and decode information about the relative locations and attributes of phenomena in their everyday or metaphorical spatial environment. The concept was introduced by Edward Tolman in 1948. He tried to explain the behavior of rats that appeared to learn the spatial layout of a maze, and subsequently the concept was applied to other animals, including humans. The term was later generalized by some researchers, especially in the field of operations research, to refer to a kind of semantic network representing an individual's personal knowledge or schemas. Overview Cognitive maps have been studied in various fields, such as psychology, education, archaeology, planning, geography, cartography, architecture, landscape architecture, urban planning, management and history. Because of the broad use and study of cognitive maps, it has become a colloquialism for just about any ment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Awareness
Spatial contextual awareness consociates contextual information such as an individual's or sensor's location, activity, the time of day, and proximity to other people or objects and devices.Chen, Guanling, and David Kotz. 2000. A Survey of Context-Aware Mobile Computing Research. Dartmouth Computer Science Technical Report TR2000-381. It is also defined as the relationship between and synthesis of information garnered from the spatial environment, a cognitive agent, and a cartographic map. The spatial environment is the physical space in which the orientation or wayfinding task is to be conducted; the cognitive agent is the person or entity charged with completing a task; and the map is the representation of the environment which is used as a tool to complete the task.Freksa, Christian, Alexander Klippel, and Stephan Winter. 2005. A Cognitive Perspective on Spatial Context. Dagstuhl Seminar Proceedings 05491. An incomplete view of spatial contextual awareness would render it as si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Cognition
Spatial cognition is the acquisition, organization, utilization, and revision of knowledge about spatial environments. It is most about how animals including humans behave within space and the knowledge they built around it, rather than space itself. These capabilities enable individuals to manage basic and high-level cognitive tasks in everyday life. Numerous disciplines (such as cognitive psychology, neuroscience, artificial intelligence, geographic Information science, cartography, etc.) work together to understand spatial cognition in different species, especially in humans. Thereby, spatial cognition studies also have helped to link cognitive psychology and neuroscience. Scientists in both fields work together to figure out what role spatial cognition plays in the brain as well as to determine the surrounding neurobiological infrastructure. In humans, spatial cognition is closely related to how people talk about their environment, find their way in new surroundings, and plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topographical Disorientation
Topographical disorientation is the inability to orient oneself in one's surroundings, sometimes as a result of focal brain damage. This disability may result from the inability to make use of selective spatial information (e.g., environmental landmarks) or to orient by means of specific cognitive strategies such as the ability to form a mental representation of the environment, also known as a cognitive map. It may be part of a syndrome known as visuospatial dysgnosia. Classification Topographical disorientation is the inability to find one's way through an environment due to cognitive impairment. Topographical disorientation has been studied for decades using case studies of patients who have selectively lost their ability to find their way within large-scale, locomotor environments. Several dozen case reports of topographical disorientation have been presented over the last century. Studying these people will aid in the understanding of the complex, multi-component behavior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables navigation. The hippocampus is located in the allocortex, with neural projections into the neocortex in humans, as well as primates. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In humans, it contains two main interlocking parts: the hippocampus proper (also called ''Ammon's horn''), and the dentate gyrus. In Alzheimer's disease (and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of the brain to suffer damage; short-term memory loss and disorientation are included among the early symptoms. Damage to the hippocampus can also result from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direction Determination
Direction determination refers to the ways in which a cardinal direction or compass point can be determined in navigation and wayfinding. The most direct method is using a compass (magnetic compass or gyrocompass), but indirect methods exist, based on the Sun path (unaided or by using a watch or sundial), the stars, and satellite navigation.U.S. Army, ''Advanced Map and Aerial Photograph Reading'', Headquarters, War Department, Washington, D.C. (17 September 1941), "DETERMINATION OF DIRECTION BY FIELD EXPEDIENTSCompass The Earth has a magnetic field which is approximately aligned with its axis of rotation. A magnetic compass is a device that uses this field to determine the cardinal directions. Magnetic compasses are widely used, but only moderately accurate. The north pole of the magnetic needle points toward the geographic north pole of the earth and vice versa. This is because the geographic north pole of the earth lies very close to the magnetic south pole of the earth. This so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
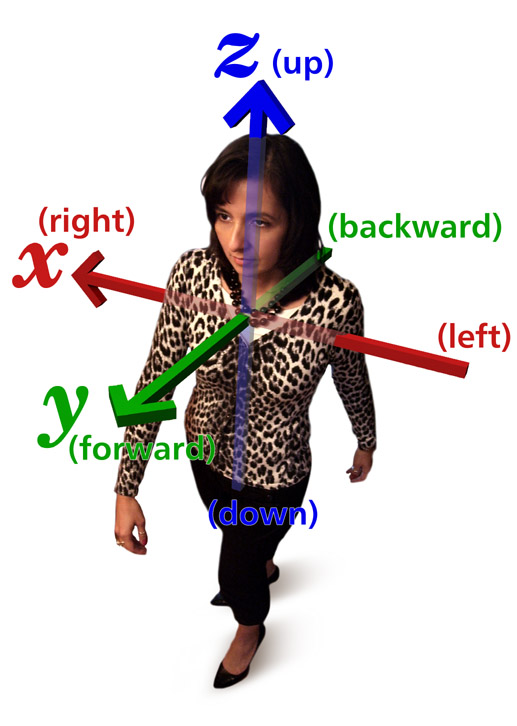
Personal Relative Direction
Body relative directions (also known as egocentric coordinates) are geometrical orientations relative to a body such as a human person's. The most common ones are: left and right; forward(s) and backward(s); up and down. They form three pairs of orthogonal axes. Traditions and conventions Since definitions of left and right based on the geometry of the natural environment are unwieldy, in practice, the meaning of relative direction words is conveyed through tradition, acculturation, education, and direct reference. One common definition of up and down uses gravity and the planet Earth as a frame of reference. Since there is a very noticeable force of gravity acting between the Earth and any other nearby object, down is defined as that direction which an object moves in reference to the Earth when the object is allowed to fall freely. Up is then defined as the opposite direction of down. Another common definition uses a human body, standing upright, as a frame of reference. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Disorientation
Spatial disorientation results in a person being unable to determine their position or relative motion, commonly occurring during periods of challenging visibility, since vision is the dominant sense for orientation. The auditory system, vestibular system (within the inner ear), and proprioceptive system (sensory receptors located in the skin, muscles, tendons and joints) collectively work to coordinate movement with balance, and can also create illusory nonvisual sensations, resulting in spatial disorientation in the absence of strong visual cues. In aviation, spatial disorientation can result in improper perception of the a of the aircraft, referring to the motion of the aircraft (whether turning, ascending or descending). For aviators, proper recognition of aircraft attitude is most critical at night or in poor weather, when there is no visible horizon, and spatial disorientation has led to numerous aviation accidents. Spatial disorientation can occur in other situations where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Ability
Spatial ability or visuo-spatial ability is the capacity to understand, reason, and remember the visual and spatial relations among objects or space. Visual-spatial abilities are used for everyday use from navigation, understanding or fixing equipment, understanding or estimating distance and measurement, and performing on a job. Spatial abilities are also important for success in fields such as sports, technical aptitude, mathematics, natural sciences, engineering, economic forecasting, meteorology, chemistry and physics. Not only do spatial abilities involve understanding the outside world, but they also involve processing outside information and reasoning with it through representation in the mind. Definition and types Spatial ability is the capacity to understand, reason and remember the visual and spatial relations among objects or space. There are four common types of spatial abilities which include spatial or visuo-spatial perception, spatial visualization, mental folding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychology is the scientific study of mental processes such as attention, language use, memory, perception, problem solving, creativity, and reasoning. Cognitive psychology originated in the 1960s in a break from behaviorism, which held from the 1920s to 1950s that unobservable mental processes were outside the realm of empirical science. This break came as researchers in linguistics and cybernetics, as well as applied psychology, used models of mental processing to explain human behavior. Work derived from cognitive psychology was integrated into other branches of psychology and various other modern disciplines like cognitive science, linguistics, and economics. The domain of cognitive psychology overlaps with that of cognitive science, which takes a more interdisciplinary approach and includes studies of non-human subjects and artificial intelligence. History Philosophically, ruminations on the human mind and its processes have been around since the times of the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Behavioural Sciences
Behavioral sciences explore the cognitive processes within organisms and the behavioral interactions between organisms in the natural world. It involves the systematic analysis and investigation of human and animal behavior through naturalistic observation, controlled scientific experimentation and mathematical modeling. It attempts to accomplish legitimate, objective conclusions through rigorous formulations and observation.Klemke, E. D., Hollinger, R., and Kline, A. D., (1980), Introduction to the book in 'Introductory Readings in the Philosophy of Science': Buffalo, New York, Prometheus Books p 11-12 Examples of behavioral sciences include psychology, psychobiology, anthropology, economics, and cognitive science. Generally, behavioral science primarily has shown how human action often seeks to generalize about human behavior as it relates to society and its impact on society as a whole. Categories Behavioral sciences include two broad categories: neural ''Information sciences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |