|
Semni Karouzou
Semni Papaspyridi-Karouzou (; 1897 8 December 1994) was a Greek Classical archaeology, classical archaeologist who specialized in the study of pottery from ancient Greece. She was the first woman to join the Greek Archaeological Service; she excavated in Crete, Euboea, Thessaly, and the Argolis, Argolid, and worked as Curator of ceramic collections at the National Archaeological Museum, Athens, National Archaeological Museum in Athens for over thirty years. She experienced political persecution under the Greek junta, Greek military junta of 1967-1974. She has been described by the archaeologists Marianna Nikolaidou and Dimitra Kokkinidou as "perhaps the most important woman in Greek archaeology", and by the newspaper ''To Vima'' as "the last representative of the generation of great archaeologists".Marianna Nikolaidou & Dimitra Kokkinidou (1998), 'Greek women in archaeology: an untold story', in Margarita Díaz-Andreu & Marie Louise Stig Sorensen (eds), ''Excavating Women: A Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tripoli, Greece
Tripoli ( el, Τρίπολη, ''Trípoli'', formerly , ''Trípolis''; earlier ''Tripolitsá'') is a city in the central part of the Peloponnese, in Greece. It is the capital of the Peloponnese region as well as of the regional unit of Arcadia. The homonym municipality has around 47,000 inhabitants. Etymology In the Middle Ages the place was known as Drobolitsa, Droboltsá, or Dorboglitza, either from the Greek Hydropolitsa, 'Water City' or perhaps from the South Slavic for 'Plain of Oaks'. The association made by 18th- and 19th-century scholars with the idea of the "three cities" (Τρίπολις, τρεις πόλεις "three cities": variously Callia, Dipoena and Nonacris, mentioned by Pausanias without geographical context, or Tegea, Mantineia and Pallantium, or Mouchli, Tegea and Mantineia or Nestani, Mouchli and Thana), were considered paretymologies by G.C. Miles. An Italian geographical atlas of 1687 notes the fort of ''Goriza e Mandi et Dorbogliza''; a subsequent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christos Tsountas
Christos Tsountas ( el, Χρήστος Τσούντας; 1857 – 9 June 1934) was a Greece, Greek classical archaeologist. He was born in Thrace, Thracian Stenimachos, Ottoman Empire (present-day Asenovgrad in Bulgaria) and attended Zariphios School, Zariphios high school in Plovdiv. In 1886, he discovered and identified the Mycenaean Greece, Mycenean palace at Tiryns. He also conducted important excavations at the palace of Mycenae, and he conducted surveys of the Greek mainland and identified more Mycenean and early Bronze Age sites. Tsountas investigated burial sites on several islands of the Cyclades, such as the important site of Kastri (Syros), Kastri in Syros. Between 1898 and 1899, his investigations led him to coin the term "Cycladic civilization". He also conducted archaeological excavations at Sesklo, Agios Andreas, and Dimini. Tsountas also led the first scientific excavations at Amyclae. Tsountas died in Athens. Publications (selection) *Tsountas, Chrestos & Manatt, J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-figure Pottery
Black-figure pottery painting, also known as the black-figure style or black-figure ceramic ( grc, , }), is one of the styles of painting on antique Greek vases. It was especially common between the 7th and 5th centuries BCE, although there are specimens dating as late as the 2nd century BCE. Stylistically it can be distinguished from the preceding orientalizing period and the subsequent red-figure pottery style. Figures and ornaments were painted on the body of the vessel using shapes and colors reminiscent of silhouettes. Delicate contours were incised into the paint before firing, and details could be reinforced and highlighted with opaque colors, usually white and red. The principal centers for this style were initially the commercial hub Corinth, and later Athens. Other important production sites are known to have been in Laconia, Boeotia, eastern Greece, and Italy. Particularly in Italy individual styles developed which were at least in part intended for the Etruscan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amasis Painter
The Amasis Painter (active around 550–510 BC in Athens) was an ancient Greek vase painter who worked in the black-figure technique. He owes his name to the signature of the potter Amasis ("Amasis made me"), who signed twelve works painted by the same hand. At the time of the exhibition, "The Amasis Painter and His World" (1985), 132 vases had been attributed to this artist. Life and career As with any of the artisans working during the sixth century BC, very little is understood about the Amasis Painter's life or personality. Scholars do know that Amasis is a Greek version of an Egyptian name, more specifically of a contemporary Egyptian king, leading some to believe that the Amasis Painter—or at least the potter Amasis—may have been a foreigner, originally from Egypt. Other possibilities include that he was an Athenian with an Egyptian name, which is highly plausible, given close trade relations between Greece and Egypt, or that his signed name was a nickname given to hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ioannis Metaxas
Ioannis Metaxas (; el, Ιωάννης Μεταξάς; 12th April 187129th January 1941) was a Greek military officer and politician who served as the Prime Minister of Greece from 1936 until his death in 1941. He governed constitutionally for the first four months of his tenure, and thereafter as the strongman of the 4th of August Regime following his appointment by King George II. Born to an aristocratic family in Ithaca, Metaxas took part in the Greco-Turkish War of 1897 and the Balkan Wars (1912–13), and quickly rose through the ranks of the Hellenic Army. A Monarchist during the National Schism, Metaxas unsuccessfully opposed Prime Minister Eleftherios Venizelos and Greece's entry in World War I; thus he was exiled to Corsica in 1917. On his return, Metaxas moved into politics and founded the Freethinkers' Party, but had only limited success under the Second Hellenic Republic. The Greek monarchy was restored in 1935, and Metaxas was appointed Prime Minister in April 193 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nafplio
Nafplio ( ell, Ναύπλιο) is a coastal city located in the Peloponnese in Greece and it is the capital of the regional unit of Argolis and an important touristic destination. Founded in antiquity, the city became an important seaport in the Middle Ages during the Frankokratia as part of the lordship of Argos and Nauplia, held initially by the de la Roche following the Fourth Crusade before coming under the Republic of Venice and, lastly, the Ottoman Empire. The city was the second capital of the First Hellenic Republic and of the Kingdom of Greece, from 1827 until 1834. Name The name of the town changed several times over the centuries. The modern Greek name of the town is ''Nafplio'' (Ναύπλιο). In modern English, the most frequently used forms are ''Nauplia'' and ''Navplion''. In Classical Antiquity, it was known as ''Nauplia'' (Ναυπλία) in Attic GreekSee Liddell and Scott revised by Jones (1940), Ναυπλία. Retrieved 2012-01-26.See Liddell and Scott ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidaurus
Epidaurus ( gr, Ἐπίδαυρος) was a small city (''polis'') in ancient Greece, on the Argolid Peninsula at the Saronic Gulf. Two modern towns bear the name Epidavros: ''Palaia Epidavros'' and ''Nea Epidavros''. Since 2010 they belong to the new municipality of Epidaurus, part of the regional unit of Argolis. The seat of the municipality is the town Lygourio. The nearby sanctuary and ancient theatre were inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in 1988 because of their exemplary architecture and importance in the development and spread of healing sanctuaries and cults across the ancient Greek and Roman worlds. Name and etymology The name “Epidaurus” is of Greek origin. It was named after the hero Epidauros, son of Apollo. According to Strabo, the city was originally named Ἐπίκαρος (Epíkaros) under the Carians, (Aristotle claimed that Caria, as a naval empire, occupied Epidaurus and Hermione) before taking the name Ἐπίταυρος (Epítauros) when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avra Theodoropoulou
Avra Theodoropoulou ( el, Αύρα Θεοδωροπούλου; 3 November 1880 – 20 January 1963) was a Greek music teacher, pianist, suffragist and women's rights activist. She founded the League for Women's Rights in 1920 and served as its chairperson from 1920 to 1957. She was married to the poet . Early life Avra Drakopoulou was born on 3 November 1880 in Edirne, Ottoman Empire, to Eleni and Aristomenis Drakopoulos, who was a consul official for Greece in Turkey. Her sister, , was a well-known poet and actress. In their childhood, the family was posted in Turkey and then Crete before settling in Athens. Completing high school, Drakopoulou learned English, French and German and became involved as a volunteer nurse during the Greco-Turkish War of 1897. In 1900, she graduated from the Athens Conservatoire and that same year she met Spyros Theodoropoulos, who would become a politician and writer, using the pen name Agis Theros. They would marry in 1906, after overcoming her fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humboldt University Of Berlin
Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin (german: Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, abbreviated HU Berlin) is a German public research university in the central borough of Mitte in Berlin. It was established by Frederick William III on the initiative of Wilhelm von Humboldt, Johann Gottlieb Fichte and Friedrich Ernst Daniel Schleiermacher as the University of Berlin () in 1809, and opened in 1810, making it the oldest of Berlin's four universities. From 1828 until its closure in 1945, it was named Friedrich Wilhelm University (german: Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität). During the Cold War, the university found itself in East Berlin and was ''de facto'' split in two when the Free University of Berlin opened in West Berlin. The university received its current name in honour of Alexander and Wilhelm von Humboldt in 1949. The university is divided into nine faculties including its medical school shared with the Freie Universität Berlin. The university has a student enrollment of around 32 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Maximilian University Of Munich
The Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (simply University of Munich or LMU; german: Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München) is a public research university in Munich, Germany. It is Germany's sixth-oldest university in continuous operation. Originally established in Ingolstadt in 1472 by Duke Ludwig IX of Bavaria-Landshut, the university was moved in 1800 to Landshut by King Maximilian I of Bavaria when the city was threatened by the French, before being relocated to its present-day location in Munich in 1826 by King Ludwig I of Bavaria. In 1802, the university was officially named Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität by King Maximilian I of Bavaria in honor of himself and Ludwig IX. LMU is currently the second-largest university in Germany in terms of student population; in the 2018/19 winter semester, the university had a total of 51,606 matriculated students. Of these, 9,424 were freshmen while international students totalled 8,875 or approximately 17% of the student pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humboldt Fellowship
The Alexander von Humboldt Foundation (german: Alexander von Humboldt-Stiftung) is a foundation established by the government of the Federal Republic of Germany and funded by the Federal Foreign Office, the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, the Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development as well as other national and international partners; it promotes international academic cooperation between excellent scientists and scholars from Germany and from abroad. Description Every year, the Foundation grants more than 700 competitive research fellowships and awards, primarily going to academics from natural sciences (mathematics included) and the humanities. It allows scientists and scholars from all over the world to come to Germany to work on a research project they have chosen themselves together with a host and collaborative partner. Additionally it funds German scholars' via the Feodor Lynen Fellowships to go anywhere in the world to work on a research proj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
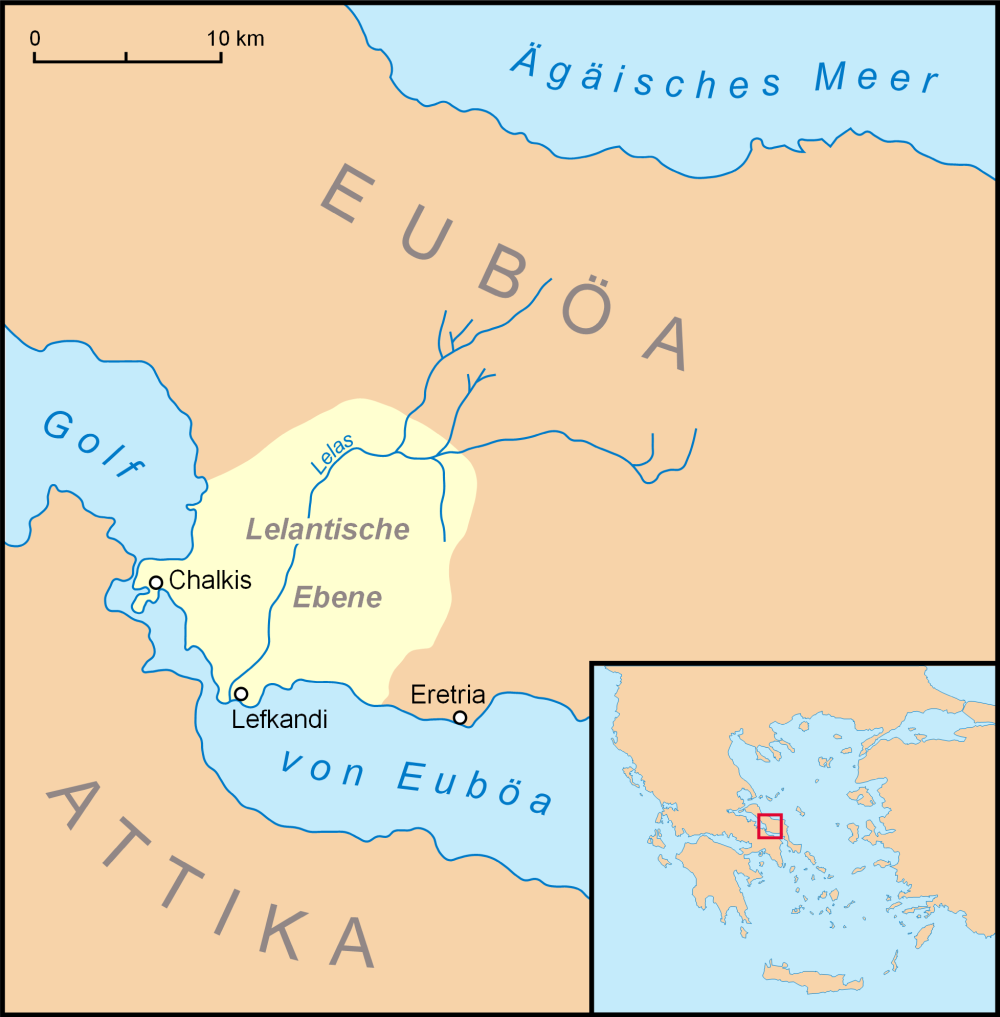
Eretria
Eretria (; el, Ερέτρια, , grc, Ἐρέτρια, , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers and actively involved in significant historical events. Excavations of the ancient city began in the 1890s and have been conducted since 1964 by the Greek Archaeological Service (11th Ephorate of Antiquities) and the Swiss School of Archaeology in Greece. History of Eretria Prehistory The first evidence for human activity in the area of Eretria are pottery shards and stone artifacts from the late Neolithic period (3500–3000 BC) found on the Acropolis as well as in the plain. No permanent structures have yet been found. It is therefore unclear whether a permanent settlement existed at that time. The first known settlement from the Early Helladic period (3000–2000 BC) was located on the plain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |