|
Selenite Peak
Selenite Peak is a summit located in Pershing County, Nevada, United States. Description Selenite Peak is the fifth-highest peak of the Selenite Range which is a subset of the Great Basin Ranges. This peak is set on land managed by the Bureau of Land Management, and is the highest point of the BLM's Selenite Mountains Wilderness Study Area. It is situated southeast of the town of Gerlach, and northeast of Empire. Topographic relief is significant as the summit rises above the valley floor in three miles. This landform's toponym has been officially adopted by the U.S. Board on Geographic Names. Climate Selenite Peak is set in the Black Rock Desert which has hot summers and cold winters. The desert is an example of a cold desert climate The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk''), is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenite Range
The Selenite Range is a mountain range in western Pershing County, Nevada. The range is a north–south trending feature approximately long and wide. The Fox Range lies to the west across the San Emidio Desert valley and the south end of the Black Rock Desert playa. Gerlach and Empire are two communities on the foothills and just to the northwest of the range. These communities supported the gypsum Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywal ... mines in the range during their active period. The large Empire gypsum quarry lies just west of Luxor Peak at 40° 30' N; 119° 18' W just northwest of Kumiva Peak.Empire, NV 7.5 minute quadrangle, USGS, 1990Kumiva Peak, NV 7.5 minute quadrangle, USGS, 1990 The range was named for deposits of selenite, a variety of gypsum. Named Pea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Nevada
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Pershing County, Nevada
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
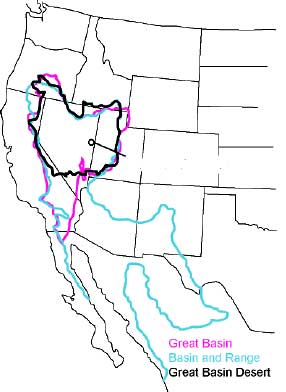
Great Basin
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic basin, endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California. It is noted for both its arid climate and the basin and range topography that varies from the North American low point at Badwater Basin in Death Valley to the highest point of the contiguous United States, less than away at the summit of Mount Whitney. The region spans several physical geography, physiographic divisions, biomes, ecoregions, and deserts. Definition The term "Great Basin" is applied to hydrography, hydrographic, ecology, biological, floristic province, floristic, physiographic, topography, topographic, and Ethnography, ethnographic geographic areas. The name was originally coined by John C. Frémont, who, based on information gleaned from Joseph R. Walker as well as his own travels, recognized the hydrographic nature o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diurnal Temperature Variation
In meteorology, diurnal temperature variation is the variation between a high air temperature and a low temperature that occurs during the same day. Temperature lag Temperature lag is an important factor in diurnal temperature variation: peak daily temperature generally occurs ''after'' noon, as air keeps net absorbing heat even after noon, and similarly minimum daily temperature generally occurs substantially after midnight, indeed occurring during early morning in the hour around dawn, since heat is lost all night long. The analogous annual phenomenon is seasonal lag. As solar energy strikes the Earth's surface each morning, a shallow layer of air directly above the ground is heated by conduction. Heat exchange between this shallow layer of warm air and the cooler air above is very inefficient. On a warm summer's day, for example, air temperatures may vary by from just above the ground to waist height. Incoming solar radiation exceeds outgoing heat energy for many hours afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desert Climate
The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk''), is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in desert climates are dry and hold little moisture, quickly evaporating the already little rainfall they receive. Covering 14.2% of earth's land area, hot deserts are the second most common type of climate on earth after the polar climate. There are two variations of a desert climate according to the Köppen climate classification: a hot desert climate (''BWh''), and a cold desert climate (''BWk''). To delineate "hot desert climates" from "cold desert climates", there are three widely used isotherms: most commonly a mean annual temperature of , or sometimes the coldest month's mean temperature of , so that a location with a ''BW'' type climate with the appropriate temperature above whichever isotherm is being used is classified as "hot arid sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topographic Relief
Terrain or relief (also topographical relief) involves the vertical and horizontal dimensions of land surface. The term bathymetry is used to describe underwater relief, while hypsometry studies terrain relative to sea level. The Latin word (the root of ''terrain'') means "earth." In physical geography, terrain is the lay of the land. This is usually expressed in terms of the elevation, slope, and orientation of terrain features. Terrain affects surface water flow and distribution. Over a large area, it can affect weather and climate patterns. Importance The understanding of terrain is critical for many reasons: * The terrain of a region largely determines its suitability for human settlement: flatter alluvial plains tend to have better farming soils than steeper, rockier uplands. * In terms of environmental quality, agriculture, hydrology and other interdisciplinary sciences; understanding the terrain of an area assists the understanding of watershed boundaries, drai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire, Nevada
Empire is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Washoe County, Nevada, with a population estimated at 65 (2021). Empire mine bought out by investor and reopened on a smaller scale. It is part of the Reno– Sparks Metropolitan Statistical Area; before the 2010 census, it was part of the Gerlach–Empire census-designated place. The nearest town, Nixon, is to the south on a reservation owned by the Pyramid Lake Paiute Tribe. For 63 years, from 1948 to 2011, Empire was a company town of the US Gypsum Corporation, a manufacturer of gypsum based construction sheetrock, and once had a population of more than 750 people. US Gypsum closed the mine and the town in 2011; the mine and town were bought in 2016 by the Empire Mining Company (EMC), a manufacturer of gypsum based agricultural and construction additives. In 2016, the town again became a company town under the new auspices of EMC. Since that date both the town and the mine have been partially re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerlach, Nevada
Gerlach, Nevada is a census-designated place (CDP) in Washoe County, Nevada, United States. The population was 107 at the 2018 American Community Survey. It is part of the Reno–Sparks Metropolitan Statistical Area. Prior to 2010, Gerlach was part of the Gerlach–Empire census-designated place. The town of Empire is now a separate CDP. The next nearest town, Nixon, is to the south on a reservation owned by the Pyramid Lake Paiute Tribe. The Fly Geyser is located near Gerlach. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the Gerlach CDP has a total area of , all land. Its elevation is . Gerlach is approximately north of Reno, Nevada. Demographics Climate Gerlach has a steppe climate (Bsk). Economy The economy of Gerlach focuses on tourism in the nearby Black Rock Desert, and hunting. Gypsum mining was the historic staple of the local economy. Nearby Empire was a company town of the United States Gypsum Corporation (USG) until the plant closed on January 31, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bureau Of Land Management
The Bureau of Land Management (BLM) is an agency within the United States Department of the Interior responsible for administering federal lands. Headquartered in Washington DC, and with oversight over , it governs one eighth of the country's landmass. President Harry S. Truman created the BLM in 1946 by combining two existing agencies: the General Land Office and the Grazing Service. The agency manages the federal government's nearly of subsurface mineral estate located beneath federal, state and private lands severed from their surface rights by the Homestead Act of 1862. Most BLM public lands are located in these 12 western states: Alaska, Arizona, California, Colorado, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, Oregon, Utah, Washington and Wyoming. The mission of the BLM is "to sustain the health, diversity, and productivity of the public lands for the use and enjoyment of present and future generations." Originally BLM holdings were described as "land nobody wanted" because home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basin And Range Province
The Basin and Range Province is a vast physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, characterized by abrupt changes in elevation, alternating between narrow faulted mountain chains and flat arid valleys or basins. The physiography of the province is the result of tectonic extension that began around 17 million years ago in the early Miocene epoch. The numerous ranges within the province in the United States are collectively referred to as the "Great Basin Ranges", although many are not actually in the Great Basin. Major ranges include the Snake Range, the Panamint Range, the White Mountains, and the Sandia Mountains. The highest point fully within the province is White Mountain Peak in California, while the lowest point is the Badwater Basin in Death Valley at . The province's climate is arid, with numerous ecoregions. Most North American deserts are located within it. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |