|
Selected Ion Monitoring
Selected ion monitoring (SIM) is a mass spectrometry scanning mode in which only a limited mass-to-charge ratio range is transmitted/detected by the instrument, as opposed to the full spectrum range. This mode of operation typically results in significantly increased sensitivity. Due to their inherent nature, this technique is most effective—and therefore most common—on quadrupole mass spectrometers and Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometers. See also * Selected reaction monitoring Selected reaction monitoring (SRM), also called Multiple reaction monitoring, (MRM), is a method used in tandem mass spectrometry in which an ion of a particular mass is selected in the first stage of a tandem mass spectrometer and an ion product ... References {{Reflist Mass spectrometry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a '' mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass-to-charge Ratio
The mass-to-charge ratio (''m''/''Q'') is a physical quantity relating the ''mass'' (quantity of matter) and the ''electric charge'' of a given particle, expressed in units of kilograms per coulomb (kg/C). It is most widely used in the electrodynamics of charged particles, e.g. in electron optics and ion optics. It appears in the scientific fields of electron microscopy, cathode ray tubes, accelerator physics, nuclear physics, Auger electron spectroscopy, cosmology and mass spectrometry. The importance of the mass-to-charge ratio, according to classical electrodynamics, is that two particles with the same mass-to-charge ratio move in the same path in a vacuum, when subjected to the same electric and magnetic fields. On rare occasions, the thomson has been used as its unit in the field of mass spectrometry. Some disciplines use the charge-to-mass ratio (''Q''/''m'') instead, which is the multiplicative inverse of the mass-to-charge ratio. The CODATA recommended value fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrum
A mass spectrum is a histogram plot of intensity vs. ''mass-to-charge ratio'' (''m/z'') in a chemical sample, usually acquired using an instrument called a ''mass spectrometer''. Not all mass spectra of a given substance are the same; for example, some mass spectrometers break the analyte molecules into '' fragments''; others observe the intact molecular masses with little fragmentation. A mass spectrum can represent many different types of information based on the type of mass spectrometer and the specific experiment applied. Common fragmentation processes for organic molecules are the '' McLafferty rearrangement'' and '' alpha cleavage''. Straight chain alkanes and alkyl groups produce a typical series of peaks: 29 (CH3CH2+), 43 (CH3CH2CH2+), 57 (CH3CH2CH2CH2+), 71 (CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2+) etc. X-axis: ''m/z'' (mass-to-charge ratio) The x-axis of a mass spectrum represents a relationship between the mass of a given ion and the number of elementary charges that it carries. This is writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrupole Mass Analyzers
The quadrupole mass analyzer, originally conceived by Nobel Laureate Wolfgang Paul and his student Helmut Steinwedel, also known as quadrupole mass filter, is one type of mass analyzer used in mass spectrometry. As the name implies, it consists of four cylindrical rods, set parallel to each other. In a quadrupole mass spectrometer (QMS) the quadrupole is the ''mass analyzer'' - the component of the instrument responsible for selecting sample ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio (''m/z''). Ions are separated in a quadrupole based on the stability of their trajectories in the oscillating electric fields that are applied to the rods. Principle of operation The quadrupole consists of four parallel metal rods. Each opposing rod pair is connected together electrically, and a radio frequency (RF) voltage with a DC offset voltage is applied between one pair of rods and the other. Ions travel down the quadrupole between the rods. Only ions of a certain mass-to-charge ratio will reach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometers
Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry is a type of mass analyzer (or mass spectrometer) for determining the mass-to-charge ratio (''m''/''z'') of ions based on the cyclotron frequency of the ions in a fixed magnetic field. The ions are trapped in a Penning trap (a magnetic field with electric trapping plates), where they are excited (at their resonant cyclotron frequencies) to a larger cyclotron radius by an oscillating electric field orthogonal to the magnetic field. After the excitation field is removed, the ions are rotating at their cyclotron frequency in phase (as a "packet" of ions). These ions induce a charge (detected as an image current) on a pair of electrodes as the packets of ions pass close to them. The resulting signal is called a free induction decay (FID), transient or interferogram that consists of a superposition of sine waves. The useful signal is extracted from this data by performing a Fourier transform to give a mass spectrum. History F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
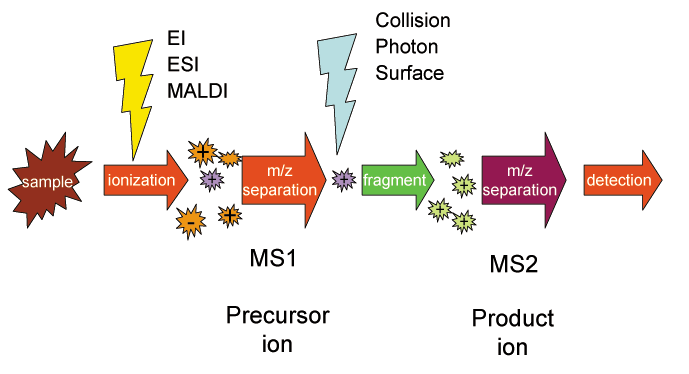
Selected Reaction Monitoring
Selected reaction monitoring (SRM), also called Multiple reaction monitoring, (MRM), is a method used in tandem mass spectrometry in which an ion of a particular mass is selected in the first stage of a tandem mass spectrometer and an ion product of a fragmentation reaction of the precursor ions is selected in the second mass spectrometer stage for detection. Variants A general case of SRM can be represented by :ABCD^+ \to AB + CD^+ where the precursor ion ABCD+ is selected by the first stage of mass spectrometry (MS1), dissociates into molecule AB and product ion CD+, and the latter is selected by the second stage of mass spectrometry (MS2) and detected. The precursor and product ion pair is called a SRM "transition." Consecutive reaction monitoring (CRM) is the serial application of three or more stages of mass spectrometry to SRM, represented in a simple case by :ABCD^+ \to AB + CD^+ \to C + D^+ where ABCD+ is selected by MS1, dissociates into molecule AB and ion CD+. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)