|
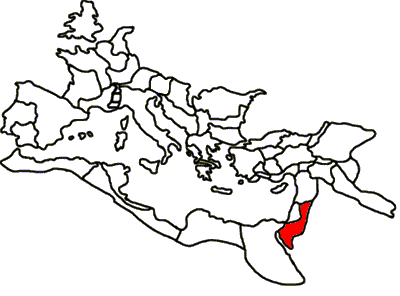
Sela (Edom)
Sela ( he, סֶּלַע, transliteration ''Sela‛'', meaning '' rock''; ar, السلع, ''es-Sela‛''; el, πέτρα, 'Petra'; la, petra) is a geographical name encountered several times in the Hebrew Bible, and applicable to a variety of locations. One site by this name is placed by the Second Book of Kings in Edom. It has been widely identified with the archaeological site of es-Sela' or as-Sila‛ in Jordan's Tafilah Governorate. Hebrew Bible Book of Judges In the Book of Judges there is a mention of a place called Sela, "the rock", on the southern border of the lands still inhabited by the Amorites after the partial conquest of Canaan by the Israelites (). Second Book of Kings 2 Kings sets "Sela" in the great valley extending from the Dead Sea to the Red Sea (). It was near Mount Hor, close by the desert of Zin. In the story of King Amaziah of Judah, a place called Sela is mentioned. Amaziah is described as throwing 10,000 Edomites to their death from the heights of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan River. Jordan is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south and east, Iraq to the northeast, Syria to the north, and the Palestinian West Bank, Israel, and the Dead Sea to the west. It has a coastline in its southwest on the Gulf of Aqaba's Red Sea, which separates Jordan from Egypt. Amman is Jordan's capital and largest city, as well as its economic, political, and cultural centre. Modern-day Jordan has been inhabited by humans since the Paleolithic period. Three stable kingdoms emerged there at the end of the Bronze Age: Ammon, Moab and Edom. In the third century BC, the Arab Nabataeans established their Kingdom with Petra as the capital. Later rulers of the Transjordan region include the Assyrian, Babylonian, Roman, Byzantine, Rashidun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joktheel
Joktheel is a geographic name used in the Hebrew Bible, meaning "God-subdued". In Judah A place named Joktheel is mentioned in the Book of Joshua and the ] as located in the Shephelah, low country of Judah between Mizpah and Lachish (). In Edom (Sela) A different place, located in Edom Edom (; Edomite: ; he, אֱדוֹם , lit.: "red"; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Egyptian: ) was an ancient kingdom in Transjordan, located between Moab to the northeast, the Arabah to the west, and the Arabian Desert to the south and east.N ... and originally called Sela, is renamed as Joktheel by King Amaziah of Judah after his conquest of the area (, ). The Second Book of Chronicles offers a clearer explanation of how that name, which means "God-subdued", was chosen due to the fact that Amaziah attributed his victory to God.http://biblehub.com/topical/j/joktheel.htm Biblehub References Hebrew Bible places {{Bible-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Gruyter
Walter de Gruyter GmbH, known as De Gruyter (), is a German scholarly publishing house specializing in academic literature. History The roots of the company go back to 1749 when Frederick the Great granted the Königliche Realschule in Berlin the royal privilege to open a bookstore and "to publish good and useful books". In 1800, the store was taken over by Georg Reimer (1776–1842), operating as the ''Reimer'sche Buchhandlung'' from 1817, while the school’s press eventually became the ''Georg Reimer Verlag''. From 1816, Reimer used the representative Sacken'sche Palace on Berlin's Wilhelmstraße for his family and the publishing house, whereby the wings contained his print shop and press. The building became a meeting point for Berlin salon life and later served as the official residence of the president of Germany. Born in Ruhrort in 1862, Walter de Gruyter took a position with Reimer Verlag in 1894. By 1897, at the age of 35, he had become sole proprietor of the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Society Of Overseas Research
The American Society of Overseas Research (ASOR), founded in 1900 as the American School of Oriental Study and Research in Palestine, is a non-profit 501(c)(3) organization based in Alexandria, Virginia which supports the research and teaching of the history and cultures of the Near East and Middle Eastern countries. ASOR supports scholarship, research, exploration, and archeological fieldwork and offers avenues of disseminating this research through their publications. ASOR also provides support for undergraduates and graduates in institutions of higher education around the world pursuing studies of the history and cultures of the Near and Middle East. As of January 2020, Sharon Herbert, is the president of ASOR. Her predecessor, Susan Ackerman served as President from 2014-2019. ASOR collaborates with the following independent overseas institutes: * Albright Institute of Archaeological Research, Jerusalem – former directors of which include Millar Burrows who was instrumenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the List of kings of Babylon, King of Babylon in 626 BC and being firmly established through the fall of the Neo-Assyrian Empire in 612 BC, the Neo-Babylonian Empire was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid Persian Empire in 539 BC, marking the collapse of the Chaldean dynasty less than a century after its founding. The defeat of the Neo-Assyrian Empire and subsequent transfer of power to Babylon marked the first time that the city, and Lower Mesopotamia, southern Mesopotamia in general, had risen to dominate the ancient Near East since the collapse of the Old Babylonian Empire (under Hammurabi) nearly a thousand years earlier. The period of Neo-Babylonian rule thus saw unprecedented economic and population growth throughout Babylonia, as well as a renaissance of cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabonidus
Nabonidus (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-naʾid'', meaning "May Nabu be exalted" or "Nabu is praised") was the last king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling from 556 BC to the fall of Babylon to the Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great in 539 BC. Nabonidus was the last native ruler of ancient Mesopotamia, the end of his reign marking the end of thousands of years of Sumer, Sumero-Akkadian language, Akkadian states, kingdoms and empires. One of the most vibrant and individualistic rulers of his time, Nabonidus is remembered as the last independent king of Babylon, and he is characterised by some scholars as an unorthodox religious reformer and as the first archaeologist. The origins of Nabonidus, his connection to previous royalty, and subsequently what claim he had to the throne remain unclear, given that Nabonidus made no genealogical claims of kinship to previous kings. This suggests that he was neither related nor connected to the Chaldean dynasty of Babylonian rulers. Howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataean
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; Arabic: , , singular , ; compare grc, Ναβαταῖος, translit=Nabataîos; la, Nabataeus) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Raqmu (present-day Petra, Jordan)—gave the name ''Nabatene'' ( grc, Ναβατηνή, translit=Nabatēnḗ) to the Arabian borderland that stretched from the Euphrates to the Red Sea. The Nabateans emerged as a distinct civilization and political entity between the 4th and 2nd centuries BCE,Taylor, Jane (2001). ''Petra and the Lost Kingdom of the Nabataeans''. London: I.B.Tauris. pp. 14, 17, 30, 31. . Retrieved 8 July 2016. with their kingdom centered around a loosely controlled trading network that brought considerable wealth and influence across the ancient world. Described as fiercely independent by contemporary Greco-Roman accounts, the Nabataeans were annexed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia (modern Iraq, southeast Turkey, southwest Iran and northeastern Syria), ancient Egypt, ancient Iran ( Elam, Media, Parthia and Persis), Anatolia/Asia Minor and the Armenian highlands (Turkey's Eastern Anatolia Region, Armenia, northwestern Iran, southern Georgia, and western Azerbaijan), the Levant (modern Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine, and Jordan), Cyprus and the Arabian Peninsula. The ancient Near East is studied in the fields of Ancient Near East studies, Near Eastern archaeology and ancient history. The history of the ancient Near East begins with the rise of Sumer in the 4th millennium BC, though the date it ends varies. The term covers the Bronze Age and the Iron Age in the region, until either the conquest by the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC, that by the Macedonian Empire in the 4th century BC, or the Muslim conquest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tophel
Tophel or Tofel (תפל) was an Edomite town mentioned in the Hebrew Bible: "These are the words Moses spoke to all Israel in the desert east of the Jordan — that is, in the Arabah — opposite Suph, between Paran and Tophel, Laban, Hazeroth and Dizahab." (Deuteronomy 1:1). It is identified as Tafilah in Jordan north to Petra Petra ( ar, ٱلْبَتْرَاء, Al-Batrāʾ; grc, Πέτρα, "Rock", Nabataean: ), originally known to its inhabitants as Raqmu or Raqēmō, is an historic and archaeological city in southern Jordan. It is adjacent to the mountain of Ja .... External linksThe Columbia Encyclopedia, Sixth Edition Hebrew Bible cities {{Tanakh-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tafilah
Tafilah ( ar, الطفيلة, 'aṭ-Ṭafīlah, ), also spelled Tafila, is a town with a population of 27,559 people in southern Jordan, located southwest of Amman. It is the capital of Tafilah Governorate. It is well known for having green gardens which contain olive and ficus, fig trees, and grape-vines. Tafilah was first built by the Edomites and was called Tophel. There are more than 360 natural springs in the at-Tafilah area, including the natural reservoir of Dana (Jordan), Dana and hot natural springs at Afra and Burbeita. There are two phosphate and cement mines in at-Tafilah, which are one of the country's main income sources. History Iron Age to Crusader period The oldest state formation established in the region on Tafilah was the kingdom of Edom, and Tafilah lies on the ruins of the Edomite city of Tophel. The capital of Edom was at Bozrah, Busairah 23 km to the south of Tafilah. Tafilah was later annexed by the Nabatean kingdom who, had its capital at Petra. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obadiah
Obadiah (; he, עֹבַדְיָה – ''ʿŌḇaḏyā'' or – ''ʿŌḇaḏyāhū''; "servant of Yah", or "Slave of Yah HVH) is a biblical prophet. The authorship of the Book of Obadiah is traditionally attributed to the prophet Obadiah. Biblical account Dating The Interpreters' Bible states that: Rabbinic tradition According to the Talmud, Obadiah is said to have been a convert to Judaism from Edom, Translated by Michael L. Rodkinson a descendant of Eliphaz, the friend of Job. He is identified with the Obadiah who was the servant of Ahab, and was chosen to prophesy against Edom because he was himself an Edomite. Obadiah is supposed to have received the gift of prophecy for having hidden the "hundred prophets" from the persecution of Jezebel. He hid the prophets in two caves, so that if those in one cave should be discovered those in the other might yet escape. Obadiah was very rich, but all his wealth was expended in feeding the poor prophets, unt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaiah
Isaiah ( or ; he, , ''Yəšaʿyāhū'', "God is Salvation"), also known as Isaias, was the 8th-century BC Israelite prophet after whom the Book of Isaiah is named. Within the text of the Book of Isaiah, Isaiah himself is referred to as "the prophet", but the exact relationship between the Book of Isaiah and the actual prophet Isaiah is complicated. The traditional view is that all 66 chapters of the book of Isaiah were written by one man, Isaiah, possibly in two periods between 740 BC and c. 686 BC, separated by approximately 15 years, and that the book includes dramatic prophetic declarations of Cyrus the Great in the Bible, acting to restore the nation of Israel from Babylonian captivity. Another widely held view is that parts of the first half of the book (chapters 1–39) originated with the historical prophet, interspersed with prose commentaries written in the time of King Josiah a hundred years later, and that the remainder of the book dates from immediately before an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |