|
Sekbanbaşı Mosque
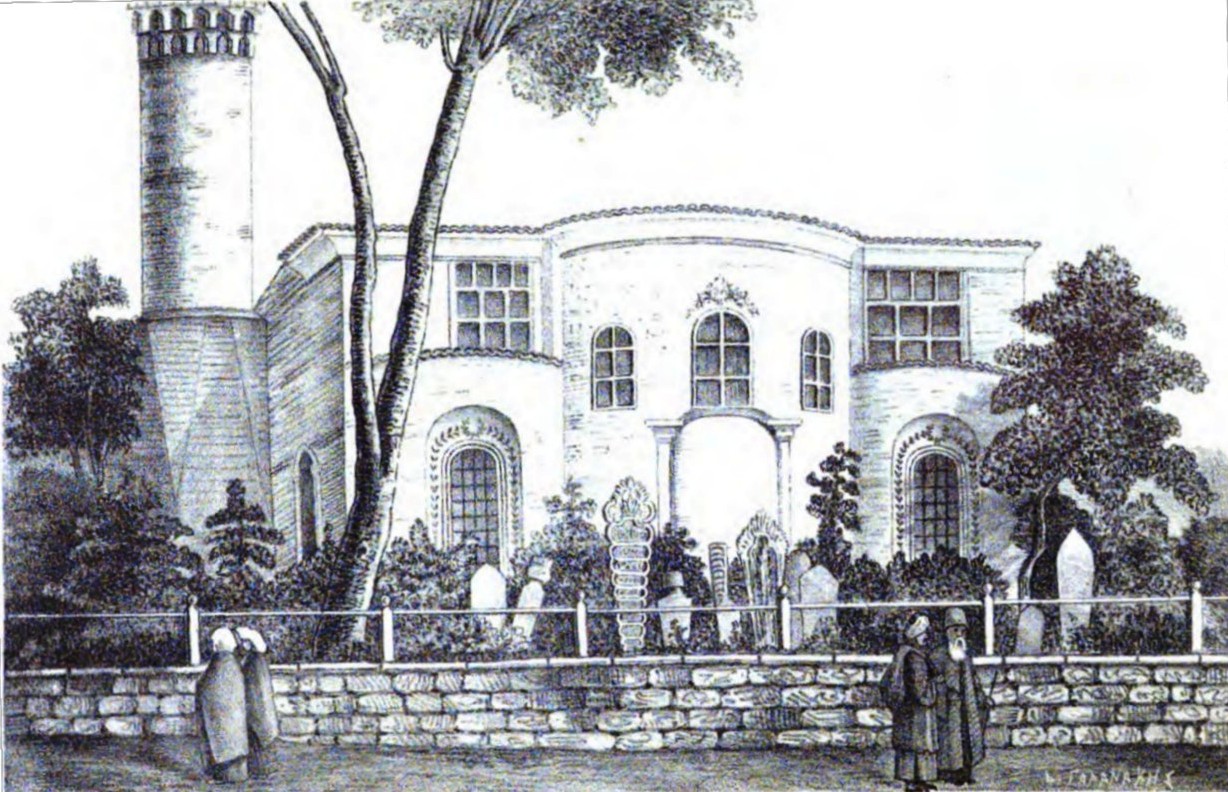
Sekbanbaşı Mosque was a mosque located in the Ottoman capital of Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul). It was originally a Byzantine church. According to the writings of Hafiz Hüseyin al-Ayvansarayî (''Hadîkatü’l-cevâmi‘''), the original Byzantine church had been converted by İbrahim Ağa (died 1496–7), the lieutenant of the Ottoman sekban regiments (''sekbanbaşı''). The building was located in Kendir Sokağı, in the Kırkçeşme quarter ( Fatih district), near the ancient aqueduct of Roman Emperor Valens. In 1838, the mosque was damaged by a fire, but underwent some restorations. In 1918, during the final few years of the Ottoman Empire, the mosque and the surrounding neighborhood were once again hit by a fire. This time, the mosque did not undergo reparations and was gradually abandoned. The heavily damaged fundament of the mosque was then completely torn down in 1943 as the Turkish Turkish may refer to: *a Turkic language spoken by the Turks * of or abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sekban Basi
The Sekban were mercenaries of peasant background in the Ottoman Empire. The term ''sekban'' initially referred to irregular military units, particularly those without guns, but ultimately it came to refer to any army outside the regular military. The sekbans were not only loyal to the Ottoman state, but they could become loyal to anyone who paid them a sufficient salary. These troops were maintained by raising a tax called the ''sekban aqçesi''. They were recruited in such numbers that they became the most numerous component of the imperial armies. The use of these troops ultimately led to grave consequences: the end of hostilities, as in the Ottoman–Safavid War (1578–1590), war against Persia in 1590 and the Long War (1591–1606), war against Austria in 1606, saw a large number of sekban without employment or means of livelihood. As a result, many of these soldiers took to brigandage and revolt, and they plundered much of Anatolia between 1596 and 1610. Rivalries between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, cultural and historic hub. The city straddles the Bosporus strait, lying in both Europe and Asia, and has a population of over 15 million residents, comprising 19% of the population of Turkey. Istanbul is the list of European cities by population within city limits, most populous European city, and the world's List of largest cities, 15th-largest city. The city was founded as Byzantium ( grc-gre, Βυζάντιον, ) in the 7th century BCE by Ancient Greece, Greek settlers from Megara. In 330 CE, the Roman emperor Constantine the Great made it his imperial capital, renaming it first as New Rome ( grc-gre, Νέα Ῥώμη, ; la, Nova Roma) and then as Constantinople () after himself. The city grew in size and influence, eventually becom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sekban
The Sekban were mercenaries of peasant background in the Ottoman Empire. The term ''sekban'' initially referred to irregular military units, particularly those without guns, but ultimately it came to refer to any army outside the regular military. The sekbans were not only loyal to the Ottoman state, but they could become loyal to anyone who paid them a sufficient salary. These troops were maintained by raising a tax called the ''sekban aqçesi''. They were recruited in such numbers that they became the most numerous component of the imperial armies. The use of these troops ultimately led to grave consequences: the end of hostilities, as in the war against Persia in 1590 and the war against Austria in 1606, saw a large number of sekban without employment or means of livelihood. As a result, many of these soldiers took to brigandage and revolt, and they plundered much of Anatolia between 1596 and 1610. Rivalries between the janissaries and the sekban ultimately resulted in a reb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatih
Fatih () is a district of and a municipality (''belediye'') in Istanbul, Turkey, and home to almost all of the provincial authorities (including the governor's office, police headquarters, metropolitan municipality and tax office) but not the courthouse. It encompasses the peninsula coinciding with old Constantinople. In 2009, the district of Eminönü, which had been a separate municipality located at the tip of the peninsula, was once again remerged into Fatih because of its small population. Fatih is bordered by the Golden Horn to the north and the Sea of Marmara to the south, while the Western border is demarked by the Theodosian wall and the east by the Bosphorus Strait. History Byzantine era Historic Byzantine districts encompassed by present-day Fatih include: ''Exokiónion'', ''Aurelianae'', ''Xerólophos'', '' ta Eleuthérou'', ''Helenianae'', ''ta Dalmatoú'', ''Sígma'', '' Psamátheia'', ''ta Katakalón'', ''Paradeísion'', ''ta Olympíou'', ''ta Kýrou'', '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqueduct Of Valens
The Aqueduct of Valens ( tr, Valens Su Kemeri, grc, Ἀγωγὸς τοῦ ὕδατος, translit=Agōgós tou hýdatos, lit=aqueduct) was a Roman aqueduct system built in the late 4th century AD, to supply Constantinople – the capital of the eastern Roman empire. Construction of the aqueduct began during the reign of the Roman emperor Constantius II () and was completed in 373 by the emperor Valens (). The aqueduct remained in use for many centuries. It was extended and maintained by the Byzantines and the Ottomans. Initially, the Aqueduct of Valens carried water from springs at Danımandere and Pınarca; the channels from each spring met at Dağyenice. This 4th-century first phase of the system was long. A second, 5th-century phase added a further of conduits that took water from Vize, away from Constantinople. The final and most visible aqueduct bridge in the system survives in the Fatih district of Istanbul, Turkey. Named in , it is an important landmark in the ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a East Thrace, small portion on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. It shares borders with the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia to the northeast; Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq to the southeast; Syria and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; the Aegean Sea to the west; and Greece and Bulgaria to the northwest. Cyprus is located off the south coast. Turkish people, Turks form the vast majority of the nation's population and Kurds are the largest minority. Ankara is Turkey's capital, while Istanbul is its list of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city and financial centre. One of the world's earliest permanently Settler, settled regions, present-day Turkey was home to important Neol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semavi Eyice
Mustafa Semavi Eyice (9 December 1922 in Istanbul, Turkey – 28 May 2018 in Istanbul, Turkey) was a Turkish art historian and archaeologist, who specialised in the study of Byzantine and Ottoman art in Istanbul. Professor Eyice is widely regarded as the pioneer of Byzantine studies in Turkey. Early life Born on 9 December 1922 at Kadıköy, Istanbul, to parents originating from Amasra, he grew up in Istanbul, where he attended the primary and secondary French schools in Kadıköy district, and graduated in 1943 from the Galatasaray Lisesi in Beyoğlu. During World War II, he went to Germany to learn the language. During the war years he attended in two different periods lectures in archeology, history and art history respectively at the Universities of Vienna and Berlin (at that time heavily bombed). In 1945, he was forced to leave Berlin, and was evacuated to Denmark and Sweden. In the same year, he returned to Turkey to undertake the study of art history at I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosques Converted From Churches In Istanbul
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers (sujud) are performed, including outdoor courtyards. The first mosques were simple places of prayer for Muslims, and may have been open spaces rather than buildings. In the first stage of Islamic architecture, 650-750 CE, early mosques comprised open and closed covered spaces enclosed by walls, often with minarets from which calls to prayer were issued. Mosque buildings typically contain an ornamental niche (''mihrab'') set into the wall that indicates the direction of Mecca ('' qiblah''), ablution facilities. The pulpit (''minbar''), from which the Friday ( jumu'ah) sermon ('' khutba'') is delivered, was in earlier times characteristic of the central city mosque, but has since become common in smaller mosques. Mosques typically have segregated spaces for m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

