|
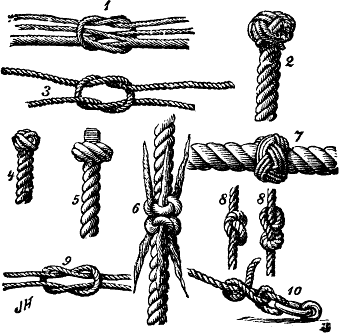
Seizing
Seizings are a class of stopping knots used to semi-permanently bind together two ropes, two parts of the same rope, or rope and another object. Akin to lashings, they use string or small-stuff to produce friction and leverage to immobilize larger ropes. Seizings are not recommended for heavy loads for critical use as strain reduces the diameter of the main rope and can permit slippage even with proper construction. According to ''The Ashley Book of Knots'', "A ''seizing'' holds several objects together."Ashley (1944), p.546. The other type of stopping knots are whipping knots. See also * Ropework Ropework or marlinespike seamanship are traditional umbrella terms for a skillset spanning the use, maintenance, and repair of rope. Included are tying knots, splicing, making lashings, whippings, and proper use and storage of rope. While th ... References Knots {{Knot-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small-stuff
This page explains commonly used terms related to knots. B Bend A bend is a knot used to join two lengths of rope. Bight A bight has two meanings in knotting. It can mean either any central part of a rope (between the standing end and the working end) or an arc in a rope that is at least as wide as a semicircle. "Any slack part of a rope between the two ends, particularly when curved or looped." In either case, a bight is a length of rope that does not cross itself. Knots that can be tied without use of the working end are called knots ''on the bight''. Binding knot Binding knots are knots that either constrict a single object or hold two objects snugly together. Whippings, seizings and lashings serve a similar purpose to binding knots, but contain too many wraps to be properly called a knot. In binding knots, the ends of rope are either joined together or tucked under the turns of the knot. Bitter end Another term for the working end. C Capsiz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whipping Knot
A whipping knot or whipping is a binding of twine or whipcord around the end of a rope to prevent its natural tendency to fray. Some whippings are finished cleanly, as by drawing the bitter end of the cordage beneath the whipping itself. Others are tied off or have the end(s) of the twine sewn through the rope. According to ''The Ashley Book of Knots'', "The purpose of a ''whipping'' is to prevent the end of a rope from fraying ... A whipping should be, in width, about equal to the diameter of the rope on which it is put ... wo sailmaker's whippings a short distance apart, are put in the ends of every reef point, where the constant "whipping" against the sail makes the wear excessive; this is said to be the source of the name ''whipping''."Ashley, Clifford W. (1944). ''The Ashley Book of Knots'', p.547. Doubleday. . The other type of stopping knot is a seizing knot. Whipping is suitable for synthetic and natural stranded and braided lines, including 3-strand rope, 4-strand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Round Turn
A turn is one round of rope on a pin or cleat, or one round of a coil. Turns can be made around various objects, through rings, or around the standing part of the rope itself or another rope. A turn also denotes a component of a knot. When the legs of a loop are brought together and crossed the rope has taken a turn. One distinguishes between single turn, round turn, and two round turns depending on the number of revolutions around an object. The benefit of round turns is best understood from the capstan equation. Riding turn A riding turn is a section of rope that passes on top of another section of rope, often parallel or at only a slight angle to the section below. Examples of riding turns can be seen in both the constrictor knot and the strangle knot. The second course of wrappings in some seizing knots can be referred to as riding turns. The formation of an unintentional riding turn on a sailing winch can cause it to jam. Single hitch A single hitch is a type of knot. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot
A knot is an intentional complication in cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including hitches, bends, loop knots, and splices: a ''hitch'' fastens a rope to another object; a ''bend'' fastens two ends of a rope to each another; a ''loop knot'' is any knot creating a loop; and ''splice'' denotes any multi-strand knot, including bends and loops. A knot may also refer, in the strictest sense, to a stopper or knob at the end of a rope to keep that end from slipping through a grommet or eye. Knots have excited interest since ancient times for their practical uses, as well as their topological intricacy, studied in the area of mathematics known as knot theory. History Knots and knotting have been used and studied throughout history. For example, Chinese knotting is a decorative handicraft art that began as a form of Chinese folk art in the Tang and Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD) in China, later popularized in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rope
A rope is a group of yarns, plies, fibres, or strands that are twisted or braided together into a larger and stronger form. Ropes have tensile strength and so can be used for dragging and lifting. Rope is thicker and stronger than similarly constructed cord, string, and twine. Construction Rope may be constructed of any long, stringy, fibrous material, but generally is constructed of certain natural or synthetic fibres. Synthetic fibre ropes are significantly stronger than their natural fibre counterparts, they have a higher tensile strength, they are more resistant to rotting than ropes created from natural fibres, and they can be made to float on water. But synthetic ropes also possess certain disadvantages, including slipperiness, and some can be damaged more easily by UV light. Common natural fibres for rope are Manila hemp, hemp, linen, cotton, coir, jute, straw, and sisal. Synthetic fibres in use for rope-making include polypropylene, nylon, polyesters (e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lashing (ropework)
A lashing is an arrangement of rope, wire, or webbing with linking device used to secure and fasten two or more items together in a somewhat rigid manner. Lashings are most commonly applied to timber poles, and are commonly associated with cargo, containerisation, the Scouting movement, and sailors. It has been imagined that the first lashing made by humans was wrapping a few strips of bark around a stone to hold it to a tree branch to make an ax to hunt and build with. In modern times, the same methods are used, but strips of bark and vines have been replaced with natural and synthetic fiber ropes. Scouts and campers use lashings to build camp gadgets and improve their campsites for comfort and convenience, including the building of rafts for transport and competitive events. Lashings are also used in pioneering, the art of creating structures such as bridges and towers, using ropes and wooden spars. There are still areas in the world where lashing spars (or poles) is the bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twine
Twine is a strong Thread (yarn), thread, light String (cord), string or cord composed of two or more thinner strands twisted, and then twisted together (Plying, plied). The strands are plied in the opposite direction to that of their twist, which adds torsional strength to the cord and keeps it from unravelling. This process is sometimes called reverse wrap. The same technique used for making twine is also used to make Thread (yarn), thread, which is thinner, yarn, and rope, which is stronger and thicker, generally with three or more strands. Natural fibres used for making twine include wool, cotton, sisal, jute, hemp, henequen, paper, and coir. A variety of synthetic fibres are also used. Twine is a popular substance used in modern-day crafting. Prehistoric The invention of twine is at least as important as the development of Stone tool, stone tools for early humans. Indeed, Elizabeth Wayland Barber has called the development of twine, which can be made far stronger and long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Ashley Book Of Knots
''The Ashley Book of Knots'' is an encyclopedia of knots written and illustrated by the American sailor and artist Clifford W. Ashley. First published in 1944, it was the culmination of over 11 years of work. The book contains 3,857 numbered entries (the final number, "3854", is added to by three "1/2" #s (794.5, 1034.5, & 2585.5) and, in later editions of the book, #1425a for Hunter's Bend; and one number has no entry) and approximately 7,000 illustrations. The entries include knot instructions, uses, and some histories, categorized by type or function. It remains one of the most important and comprehensive books on knots. Use as a reference Due to its scope and wide availability, ''The Ashley Book of Knots'' has become a significant reference work in the field of knotting. The numbers Ashley assigned to each knot can be used to unambiguously identify them. This helps to identify knots despite local colloquialisms or identification changes. Citations to Ashley numbers are usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deadeye
A deadeye is an item used in the standing and running rigging of traditional sailing ships. It is a smallish round thick wooden (usually lignum vitae) disc with one or more holes through it, perpendicular to the plane of the disc. Single and triple-hole deadeyes are most commonly seen. The three-holed blocks were called deadeyes because the position of the three holes resemble the eye and nose sockets of a sheep's skull. Single deadeyes (or bull's eyes) are used to guide and control a line and, particularly in older vessels, to change its direction. More modern systems would use a block for this purpose but in traditional rigs with many lines to deal with, designed when blocks were relatively expensive to make, a deadeye provided an acceptable compromise. When blocks came into common use for adjusting running rigging, deadeyes continued to be used for tensioning standing rigging. Triple deadeyes are used in pairs; a line called a lanyard is run back and forth between them, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ropework
Ropework or marlinespike seamanship are traditional umbrella terms for a skillset spanning the use, maintenance, and repair of rope. Included are tying knots, splicing, making lashings, whippings, and proper use and storage of rope. While the skill of a sailor in the Age of Sail was often judged by how well he knew marlinespike seamanship, the knowledge it embraces involving docking a craft, towing, making repairs underway, and more is still critical for modern seafarers. Whippings A whipping knot is a means of holding the cut end of a rope together to prevent fraying and ensure ease of use. The simplest form is the common whipping. Constrictor knots can serve as temporary whippings while cutting ropes, as can a few layers of adhesive tape. Other fray-prevention techniques include back-splicing, aglets, or the application of an rubberized adhesive coating, resin, or paint to the cut end. Some modern synthetic fibers, such as nylon and polyester can make use of alternati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |