|
Seder Ha-Mishmarah
The Seder ha-Mishmarah is a study cycle devised by the Ben Ish Ḥai and used by some Mizrahi Jews (Jews of Near and Middle Eastern origin) for reading the whole of the Hebrew Bible and the Mishnah in the course of a year. It depends on the cycle of the weekly Torah portions read in the synagogue. Some communities have a custom of public reading, whereby on each Shabbat afternoon the whole of the ''mishmarah'' for the following Shabbat is read out loud. In others, individuals use it as a basis for private study. The usual form of the cycle is set out in the table below. This cycle is unrelated to that for '' Chok l'Yisrael'', which is a study cycle based on the works of Rabbi Hayyim ben Joseph Vital and revised by Rabbi Chaim Joseph David Azulai. This too is often published in book form and is widely popular among Near and Middle Eastern Jews. Differences between the two are: * The Seder ha-Mishmarah does not include Targum or commentaries on the Torah portion; ''Chok l'Yi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ben Ish Chai
Yosef Hayim (1 September 1835 – 30 August 1909) ( Iraqi Hebrew: Yoseph Ḥayyim; he, יוסף חיים מבגדאד) was a leading Baghdadi ''hakham'' (Sephardi rabbi), authority on ''halakha'' (Jewish law), and Master Kabbalist. He is best known as author of the work on ''halakha'' ''Ben Ish Ḥai'' () ("Son of Man (who) Lives"), a collection of the laws of everyday life interspersed with mystical insights and customs, addressed to the masses and arranged by the weekly Torah portion. Biography Hayim initially studied in his father's library, and, at the age of 10, he left ''midrash'' ("school room") and began to study with his uncle, David Hai Ben Meir, who later founded the Shoshanim LeDavid Yeshiva in Jerusalem. In 1851, he married Rachel, the niece of Abdallah Somekh, his prime mentor, with whom he had a daughter and two sons. When Hayim was only twenty-five years old, his father died. Despite his youth, the Jews of Baghdad accepted him to fill his father's place as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pe'ah
Pe'ah ( he, פֵּאָה, lit. "Corner") is the second tractate of ''Seder Zeraim'' ("Order of Seeds") of the Mishnah and of the Talmud. This tractate begins the discussion of topics related to agriculture, the main focus of this ''seder'' (order) of the Mishnah. The tractate discusses the laws of gifts to the poor when a person harvests their field, vineyards or trees, based on commandments in the Torah. The tractate also deals with the laws of giving charity in general. The tractate is called Pe'ah because the first part of the tractate deals with the laws of Pe'ah, while the remaining part of the tractate deals with a number of other related topics. In addition to the Mishnah, a tractate Pe'ah exists in the Jerusalem Talmud (commenting on the Mishnah tractate), but not in the Babylonian Talmud. Topics This tractate discusses the gifts due to the poor when fields, vineyards or trees are harvested, and the laws of giving charity in general. Six categories of obligations are discu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mikva'ot
Tractate Miqwaʾoth (Hebrew: מקואות, lit. "Pools of Water"; in Talmudic Hebrew: ''Miqwaʾoth'') is a section of the Mishna discussing the laws pertaining to the building and maintenance of a mikvah, a Jewish ritual bath. Like most of Seder Tohorot, Mikva'ot is present only in its mishnaic form and has no accompanying gemara in either the Babylonian or Jerusalem Talmud The Jerusalem Talmud ( he, תַּלְמוּד יְרוּשַׁלְמִי, translit=Talmud Yerushalmi, often for short), also known as the Palestinian Talmud or Talmud of the Land of Israel, is a collection of rabbinic notes on the second-century .... It contains 10 chapters, with 83 paragraphs total. References External links Online text of Mishna Mikvaot (in Hebrew) {{Judaism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miketz (parsha)
Miketz or Mikeitz (—Hebrew for "at the end", the second word, and first distinctive word of the ''parashah'') is the tenth weekly Torah portion (, ''parashah'') in the annual Jewish cycle of Torah reading. It constitutes . The parashah tells of Joseph's interpretation of Pharaoh's dreams, Joseph's rise to power in Egypt, and Joseph's testing of his brothers. The parashah has the most letters (although not the most words or verses) of any of the weekly Torah portions in the Book of Genesis. It is made up of 7,914 Hebrew letters, 2,022 Hebrew words, 146 verses, and 255 lines in a Torah Scroll (, '' Sefer Torah''). (In the Book of Genesis, Parashat Vayeira has the most words, and Parashiyot Noach and Vayishlach have the most verses.) Jews read Parashat Miketz on the tenth Sabbath after Simchat Torah, generally in December, or rarely in late November or early January, usually during Chanukah. Readings In traditional Sabbath Torah reading, the parashah is divided into seven read ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yevamot
Yevamot ( he, יבמות, "Brother's Widow", also pronounced Yevamos, or Yavmus) is a tractate of the Talmud that deals with, among other concepts, the laws of Yibbum (, loosely translated in English as levirate marriage), and, briefly, with conversion to Judaism. This tractate is the first in the order of Nashim (, "Women"). Yevamot, along with Eruvin and Niddah, is considered one of the three most difficult tractates in the Babylonian Talmud. A Hebrew mnemonic for the three is (''ani'', meaning "poverty").Jacob Emden, ''Mitpachat Sefarim'' 4:174 Contents ''Yibbum'' is the Torah law () by which the brother of a man who died without children is allowed and expected to marry the widow. This law only applies to paternal brothers, i.e., brothers by the same father; whether they have the same mother or different mothers is irrelevant. The deceased's widow(s) is forbidden to marry anyone else while waiting for one of the brothers to marry her, or release to her by performing a cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vayeshev (parsha)
Vayeshev, Vayeishev, or Vayesheb (—Hebrew for "and he lived," the first word of the parashah) is the ninth weekly Torah portion (, ''parashah'') in the annual Jewish cycle of Torah reading. The parashah constitutes . The parashah tells the stories of how Jacob's other sons sold Joseph into captivity in Egypt, how Judah wronged his daughter-in-law Tamar who then tricked him into fulfilling his oath, and how Joseph served Potiphar and was imprisoned when falsely accused of assaulting Potiphar's wife. The parashah is made up of 5,972 Hebrew letters, 1,558 Hebrew words, 112 verses, and 190 lines in a Torah Scroll (, ''Sefer Torah''). Jews read it the ninth Sabbath after Simchat Torah, in late November or December. Readings In traditional Sabbath Torah reading, the parashah is divided into seven readings, or , '' aliyot''. In the Masoretic Text of the Tanakh (Hebrew Bible), Parashat Vayeshev has three "open portion" (, ''petuchah'') divisions (roughly equivalent to paragraphs, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horayot
Horayot ( he, הוֹרָיוֹת; "Decisions") is a tractate in Seder Nezikin in the Talmud. In the Mishnah, this is the tenth and last tractate in Nezikin; in the Babylonian Talmud the ninth tractate; in the Jerusalem Talmud the eighth. It consists of three chapters in the Mishnah and two in the Tosefta. The tractate mainly discusses laws pertaining to erroneous rulings by a Jewish court, as well as unwitting actions performed by leading authorities of the Jewish people, and the sacrificial offerings (Hebrew korban, plural ''korbanot'') that might be brought as a consequence of these actions. The conclusion of the tractate (12a-13b) deals with the prioritization of korbanot in the temple and explores the question of how to quantify human life in emergency situations. Mishnah The Mishnah of Horayot is the final work of Nezikin. Horayot contains three chapters. There are twenty paragraphs of Mishna, or twenty ''mishnayot'', within the three chapters. These chapters deal with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mo'ed Katan
Mo'ed Katan or Mo'ed Qatan (Hebrew: מועד קטן, lit. "little festival") is the eleventh tractate of ''Seder Moed'' of the Mishnah and the Talmud. It is concerned with the laws of the days between the first and last days of Passover and Sukkot (as both of these festivals are a week in length). These days are also known as " Chol HaMoed" days. Mo'ed Katan also discusses the laws of Aveilus (Bereavement). Consisting of only three chapters, it has a Gemara from both Babylonian Talmud and the Jerusalem Talmud. Summary In the Babylonian Talmud: *The first 2 chapters deal with Chol HaMoed *The 3rd chapter deals primarily with the laws of mourning, as well as the laws of excommunication, and various accounts of the deaths of Amoraim. Permitted Activities on Chol HaMoed The Mishnah Berurah sums up the important principles that come out of Mo'ed Katan. In Mishnah Berurah 530:1 it lists the activities permitted on Chol HaMoed: * ''Davar Ha'Aved''- One may do work in order to avoid a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
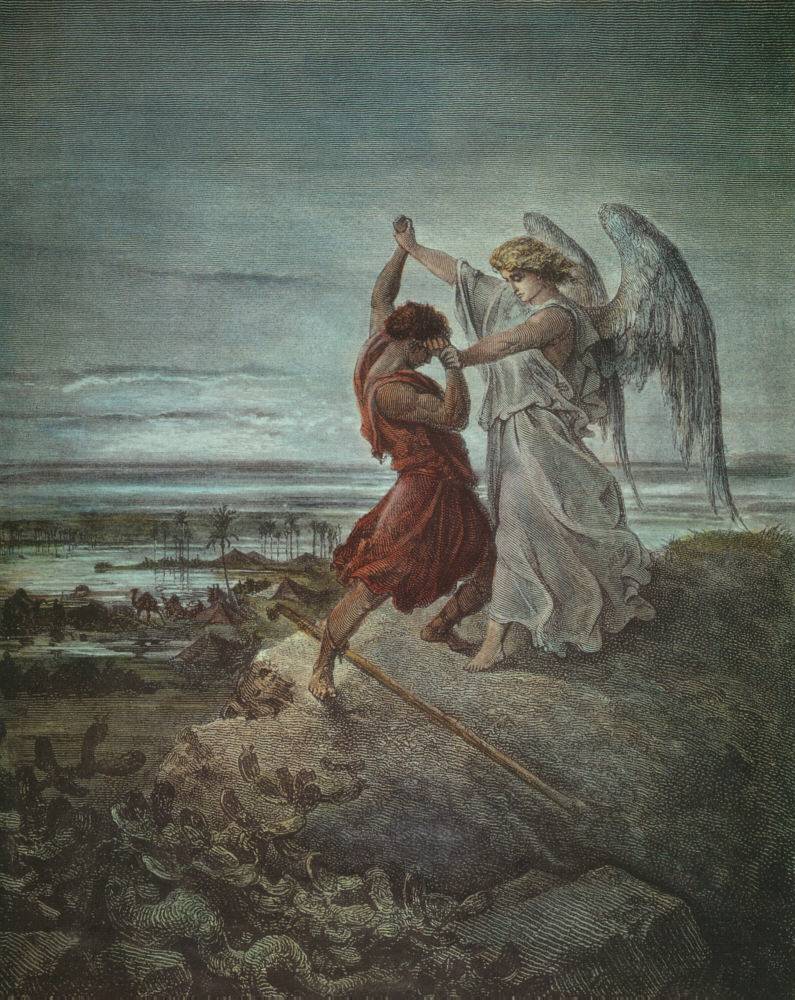
Vayishlach (parsha)
Vayishlach or Vayishlah ( — Hebrew language, Hebrew for "and he sent," the incipit, first word of the parashah) is the eighth weekly Torah portion (, ) in the annual Judaism, Jewish cycle of Torah reading. In the parashah, Jacob reconciles with Esau after wrestling with a "man." The prince Shechem (biblical figure), Shechem rapes Dinah, whose brothers sack the city of Shechem in revenge. In the family's subsequent flight, Rachel gives birth to Benjamin and dies in childbirth. The parashah constitutes . The parashah has the most Chapters and verses of the Bible, verses of any weekly Torah portion in the Book of Genesis (Parashat Miketz has the most letters, Parashat Vayeira has the most words, and Parashat Noach (parsha), Noach has an equal number of verses as Parashat Vayishlach). It is made up of 7,458 Hebrew letters, 1,976 Hebrew words, 153 verses, and 237 lines in a Torah Scroll (''Sefer Torah''). Jews read it the eighth Shabbat, Sabbath after Simchat Torah, in November or De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketubot (Talmud)
Ketubot ( he, כְּתוּבּוׂת) is a tractate of the Mishnah and the Talmud in the order of Nashim. It deals with a variety of marital responsibilities, especially those intended for the marital contract, also named the ''ketubah''. Due to the wide breadth of subjects discussed in this tractate, Ketubot is often referred to as the ''Shas katan (the miniature Talmud)''. A ketubah (plural: ketubot) (in Hebrew: כְּתוּבָּה; plural: כְּתוּבּוׂת) is a special type of Jewish prenuptial agreement. It is considered an integral part of a traditional Jewish marriage, and describes the groom's rights and responsibilities towards the bride. Currently, the ketubah does not have a monetary value, however, it has legal value in Israel. " Broyde, Michael and Jonathan Reiss. Journal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vayetze (parsha)
Vayetze, Vayeitzei, or Vayetzei (—Hebrew for 'and he left', the first word in the parashah) is the seventh weekly Torah portion (, ) in the annual Jewish cycle of Torah reading. It constitutes . The parashah tells of Jacob's travels to, life in, and return from Harran. The parashah recounts Jacob's dream of a ladder to heaven, Jacob's meeting of Rachel at the well, Jacob's time working for Laban and living with Rachel and Leah, the birth of Jacob's children, and the departure of Jacob's family from Laban. The parashah is made up of 7,512 Hebrew letters, 2,021 Hebrew words, 148 verses, and 235 lines in a Torah Scroll (, ''Sefer Torah''). Jews read it the seventh Sabbath after Simchat Torah, generally in November or December. Readings In traditional Sabbath Torah reading, the parashah is divided into seven readings, or , '' aliyot''. In the Masoretic Text of the Tanakh (Hebrew Bible), Parashah Vayetze is unusual in that it is entirely contained in one single "open portion" (, ) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berakhot (Talmud)
Berakhot ( he, בְּרָכוֹת, Brakhot, lit. "Blessings") is the first tractate of ''Seder Zeraim'' ("Order of Seeds") of the Mishnah and of the Talmud. The tractate discusses the rules of prayers, particularly the Shema and the Amidah, and blessings for various circumstances. Since a large part of the tractate is concerned with the many ''berakhot'' ( en, blessings), all comprising the formal liturgical element beginning with words "Blessed are you, Lord our God….", it is named for the initial word of these special form of prayer. ''Berakhot'' is the only tractate in ''Seder Zeraim'' to have Gemara – rabbinical analysis of and commentary on the Mishnah – in the Babylonian Talmud. There is however Jerusalem Talmud on all the tractates in ''Seder Zeraim''. There is also a Tosefta for this tractate. The Jewish religious laws detailed in this tractate have shaped the liturgies of all the Jewish communities since the later Talmudic period and continue to be observed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |