|
Second Battle Of Sackett's Harbor
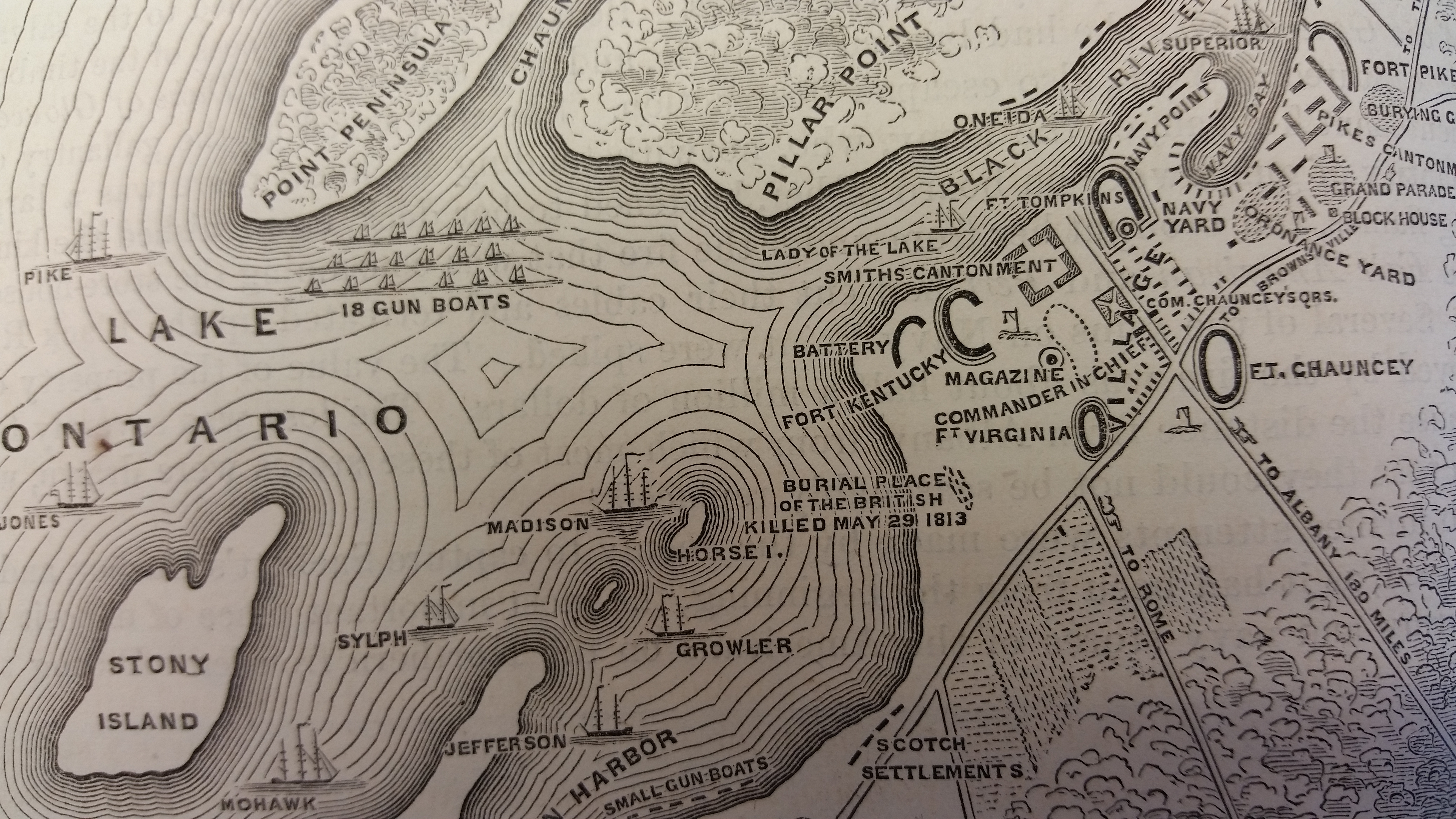
The Second Battle of Sacket's Harbor or simply the Battle of Sacket's Harbor, took place on 29 May 1813, during the War of 1812. A British force was transported across Lake Ontario and attempted to capture the town, which was the principal dockyard and base for the American naval squadron on the lake. Twelve warships were built here. The British were repulsed by American regulars, militia, marines and sailors. Background In the early weeks of the War, the British had seized control of the Great Lakes. In September 1812 U.S. Navy Captain Isaac Chauncey was ordered to assume command of naval forces on Lakes Ontario and Erie with the directive to "...use every exertion to obtain control of them this fall." Within three weeks he had directed and brought 149 ships' carpenters, 700 Seamen and Marines, and some 100 cannon, along with a good quantity of muskets and other supplies, to Sacket's Harbor on Lake Ontario where there was already a small navy yard. At the start of the campaign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It began when the United States declared war on 18 June 1812 and, although peace terms were agreed upon in the December 1814 Treaty of Ghent, did not officially end until the peace treaty was ratified by Congress on 17 February 1815. Tensions originated in long-standing differences over territorial expansion in North America and British support for Native American tribes who opposed US colonial settlement in the Northwest Territory. These escalated in 1807 after the Royal Navy began enforcing tighter restrictions on American trade with France and press-ganged men they claimed as British subjects, even those with American citizenship certificates. Opinion in the US was split on how to respond, and although majorities in both the House and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of regular, full-time military personnel; or, historically, to members of a warrior-nobility class (e.g. knights or samurai). Generally unable to hold ground against regular forces, militias commonly support regular troops by skirmishing, holding fortifications, or conducting irregular warfare, instead of undertaking offensive campaigns by themselves. Local civilian laws often limit militias to serve only in their home region, and to serve only for a limited time; this further reduces their use in long military campaigns. Beginning in the late 20th century, some militias (in particular officially recognized and sanctioned militias of a government) act as professional forces, while still being "part-time" or "on-call" organizations. For instan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Admiralty
The Admiralty was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom responsible for the command of the Royal Navy until 1964, historically under its titular head, the Lord High Admiral – one of the Great Officers of State. For much of its history, from the early 18th century until its abolition, the role of the Lord High Admiral was almost invariably put "in commission" and exercised by the Lords Commissioner of the Admiralty, who sat on the governing Board of Admiralty, rather than by a single person. The Admiralty was replaced by the Admiralty Board in 1964, as part of the reforms that created the Ministry of Defence and its Navy Department (later Navy Command). Before the Acts of Union 1707, the Office of the Admiralty and Marine Affairs administered the Royal Navy of the Kingdom of England, which merged with the Royal Scots Navy and the absorbed the responsibilities of the Lord High Admiral of the Kingdom of Scotland with the unification of the Kingdom of Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort George, Ontario
Fort George was a military fortification in Niagara-on-the-Lake, Ontario, Canada. The fort was used by the British Army, the Canadian militia, and the United States Armed Forces for a brief period. The fort was mostly destroyed during the War of 1812. The site of the fort has been a National Historic Site of Canada since 1921, and features a reconstruction of Fort George. The British established Fort George in the 1790s to replace Fort Niagara. Many of its structures were demolished in May 1813, during the Battle of Fort George. After the battle, American forces occupied the fort for seven months before withdrawing in December 1813. Although the British regained the fort shortly afterwards, little effort was put into its reconstruction after they captured Fort Niagara the following week. The poor wartime design of Fort George led its replacement by Fort Mississauga in the 1820s, although the grounds of Fort George saw some use by the military until the end of the First World Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niagara River
The Niagara River () is a river that flows north from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario. It forms part of the border between the province of Ontario in Canada (on the west) and the state of New York (state), New York in the United States (on the east). There are differing theories as to the origin of the river's name. According to Iroquoian scholar Bruce Trigger, ''Niagara'' is derived from the name given to a branch of the locally residing native Neutral Nation, Neutral Confederacy, who are described as being called the ''Niagagarega'' people on several late-17th-century French maps of the area. According to George R. Stewart, it comes from the name of an Iroquois town called ''Ongniaahra'', meaning "point of land cut in two". The river, which is occasionally described as a strait, is about long and includes Niagara Falls in its course. The falls have moved approximately upstream from the Niagara Escarpment in the last 12,000 years, resulting in a gorge below the falls. Today, the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Niagara
Fort Niagara is a fortification originally built by New France to protect its interests in North America, specifically control of access between the Niagara River and Lake Ontario, the easternmost of the Great Lakes. The fort is on the river's eastern bank at its mouth on Lake Ontario. Youngstown, New York, later developed near here. The British took over the fort in 1759 during the French and Indian War. Although the United States was ostensibly ceded the fort after it gained independence in the American Revolutionary War, the British stayed until 1796. Transfer to the U.S. came after signing of the Jay Treaty that reaffirmed and implemented the legal border with British Canada. Although the US Army deactivated the fort in 1963, the Coast Guard continues to have a presence here. A non-profit group operates the fort and grounds as a state park and preserves it in part as a museum and site for historical re-enactments. It is also a venue for special events related to the region's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of York
The Battle of York was a War of 1812 battle fought in York, Upper Canada (today's Toronto, Ontario, Canada) on April 27, 1813. An American force supported by a naval flotilla landed on the lakeshore to the west and advanced against the town, which was defended by an outnumbered force of regulars, militia and Ojibwe natives under the overall command of Major General Roger Hale Sheaffe, the Lieutenant Governor of Upper Canada. Sheaffe's forces were defeated and Sheaffe retreated with his surviving regulars to Kingston, abandoning the militia and civilians. The Americans captured the fort, town, and dockyard. They themselves suffered heavy casualties, including force leader Brigadier General Zebulon Pike and others killed when the retreating British blew up the fort's magazine. The American forces subsequently carried out several acts of arson and looting in the town before they withdrew several days later. Although the Americans won a clear victory, the battle did not have decis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
York, Upper Canada
York was a town and second capital of the colony of Upper Canada. It is the predecessor to the Old Toronto, old city of Toronto (1834–1998). It was established in 1793 by Lieutenant-Governor John Graves Simcoe as a "temporary" location for the capital of Upper Canada, while he made plans to build a capital near today's London, Ontario. Simcoe renamed the location York after Prince Frederick, Duke of York and Albany, George III of the United Kingdom, George III's second son. Simcoe gave up his plan to build a capital at London, and York became the permanent capital of Upper Canada on February 1, 1796. That year Simcoe returned to Britain and was temporarily replaced by Peter Russell (politician), Peter Russell. The original townsite was a compact ten blocks near the mouth of the Don River (Ontario), Don River and a Fort York, garrison was built at the channel to Toronto Harbour. Government buildings and a law court were established. Yonge Street was built, connecting York to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada (french: link=no, province du Haut-Canada) was a part of British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North America, formerly part of the Province of Quebec since 1763. Upper Canada included all of modern-day Southern Ontario and all those areas of Northern Ontario in the which had formed part of New France, essentially the watersheds of the Ottawa River or Lakes Huron and Superior, excluding any lands within the watershed of Hudson Bay. The "upper" prefix in the name reflects its geographic position along the Great Lakes, mostly above the headwaters of the Saint Lawrence River, contrasted with Lower Canada (present-day Quebec) to the northeast. Upper Canada was the primary destination of Loyalist refugees and settlers from the United States after the American Revolution, who often were granted land to settle in Upper Canada. Already populated by Indigenous peoples, land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Dearborn
Henry Dearborn (February 23, 1751 – June 6, 1829) was an American military officer and politician. In the Revolutionary War, he served under Benedict Arnold in his expedition to Quebec, of which his journal provides an important record. After being captured and exchanged, he served in George Washington's Continental Army. He was present at the British surrender at Yorktown. Dearborn served on General George Washington's staff in Virginia. He served as Secretary of War under President Thomas Jefferson, from 1801 to 1809, and served as a commanding general in the War of 1812. In later life, his criticism of General Israel Putnam's performance at the Battle of Bunker Hill caused a major controversy. Fort Dearborn in Illinois, Dearborn County in Indiana, and the city of Dearborn, Michigan, were named in his honor. U.S. Army Center of Military History U.S. Biographical Directory Background Henry Dearborn was born February 23, 1751, to Simon Dearborn and Sarah Marston in N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingston, Ontario
Kingston is a city in Ontario, Canada. It is located on the north-eastern end of Lake Ontario, at the beginning of the St. Lawrence River and at the mouth of the Cataraqui River (south end of the Rideau Canal). The city is midway between Toronto, Ontario and Montreal, Quebec. Kingston is also located nearby the Thousand Islands, a tourist region to the east, and the Prince Edward County tourist region to the west. Kingston is nicknamed the "Limestone City" because of the many heritage buildings constructed using local limestone. Growing European exploration in the 17th century, and the desire for the Europeans to establish a presence close to local Native occupants to control trade, led to the founding of a French trading post and military fort at a site known as "Cataraqui" (generally pronounced /kætə'ɹɑkweɪ/, "kah-tah-ROCK-way") in 1673. This outpost, called Fort Cataraqui, and later Fort Frontenac, became a focus for settlement. Since 1760, the site of Kingston, Ont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paine
Paine may refer to: Geography *Paine, Chile *Paine College, a defunct Historically Black college in Augusta, Georgia *Paine Field, an airport in Everett, Washington, United States *Paine Lake, a lake in Minnesota *Paine River, a waterstream located in the Magallanes Region of Chile *Torres del Paine, a mountain group in Chilean Patagonia *Cordillera del Paine, a mountain group in Chilean Patagonia Other *Paine (surname) * Paine (''Final Fantasy''), a fictional female character in the video game Final Fantasy X-2 *John Alsop Paine, botanist whose standard author abbreviation is "Paine" *John Knowles Paine, an American-born composer *Thomas Paine, (1737-1809) activist-philosopher *Hurricane Paine, name of several storms in the Eastern Pacific Ocean See also * * Payne (other) *Pain (other) Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging stimuli. Pain may also refer to: Arts * "Pain", a season one episode of ''Stargate Universe'' * "Pain", an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)



