|
Second-degree Relative
A second-degree relative (SDR) is someone who shares 25% of a person's genes. It includes uncles, aunts, nephews, nieces, grandparents, grandchildren, half-siblings, and double cousins. See also *Family *First-degree relative *Third-degree relative Third-degree relatives are a segment of the extended family and includes first cousins, great grandparents and great grandchildren. Third-degree relatives are generally defined by the expected amount of genetic overlap that exists between two peop ... References Genetics Family {{socio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First-degree Relative
A first-degree relative (FDR) is a person's parent (father or mother), full sibling (brother or sister) or child. It constitutes a category of family members that largely overlaps with the term nuclear family, but without spouses. If the persons are related by blood, the first degree relatives share approximately 50% of their genes. First-degree relatives are a common measure used to diagnose risks for common diseases by analyzing family history. See also *Second-degree relatives * Third-degree relatives *Family Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its ... * Next of kin References Family {{society-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
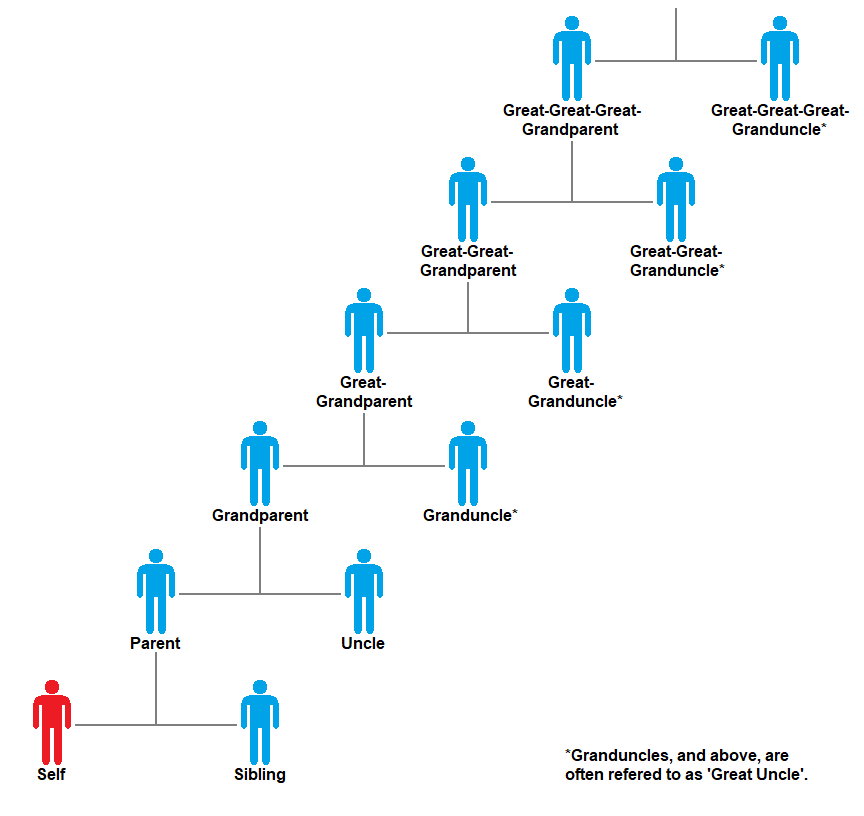
Uncle
An uncle is usually defined as a male relative who is a sibling of a parent or married to a sibling of a parent. Uncles who are related by birth are second-degree relatives. The female counterpart of an uncle is an aunt, and the reciprocal relationship is that of a nephew or niece. The word comes from la, avunculus, the diminutive of ''avus'' (grandfather), and is a family relationship within an extended or immediate family. In some cultures and families, children may refer to the cousins of their parents as uncle (or aunt). It is also used as a title of respect for older relatives, neighbours, acquaintances, family friends, and even total strangers in some cultures, for example Aboriginal Australian elders. Using the term in this way is a form of fictive kinship. Any social institution where a special relationship exists between a man and his sisters' children is known as an avunculate (or avunculism or avuncularism). This relationship can be formal or informal, dependi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aunt
An aunt is a woman who is a sibling of a parent or married to a sibling of a parent. Aunts who are related by birth are second-degree relatives. Known alternate terms include auntie or aunty. Children in other cultures and families may refer to the cousins of their parents as aunt or uncle due to the age and generation gap. The word comes from la, amita via Old French ''ante'' and is a family relationship within an extended or immediate family. The male counterpart of an aunt is an uncle, and the reciprocal relationship is that of a nephew or niece. Additional terms * A half-aunt is a half-sister of a parent. * An aunt-in-law is the aunt of one's spouse and is the wife of the uncle of somebody. . * A great-aunt/grandaunt (sometimes written grand-aunt) is the sister of one's grandparent. Despite the popular usage of great-aunt, genealogists consider it more correct to use grandaunt for a grandparent's sister to avoid confusion with earlier generations. Similarly, the fem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephew
In the lineal kinship system used in the English-speaking world, a niece or nephew is a child of the subject's sibling or sibling-in-law. The converse relationship, the relationship from the niece or nephew's perspective, is that of an aunt or uncle. A niece is female and a nephew is male. The term nibling has been used in place of the common, gender-specific terms in some specialist literature. As aunt/uncle and niece/nephew are separated by one generation, they are an example of a second-degree relationship. They are 25% related by blood. Lexicology The word nephew is derived from the French word ''neveu'' which is derived from the Latin ''nepos''. The term ''nepotism'', meaning familial loyalty, is derived from this Latin term. ''Niece'' entered Middle English from the Old French word ''nece'', which also derives from Latin ''nepotem''. The word ''nibling'' is a neologism suggested by Samuel Martin (linguist), Samuel Martin in 1951 as a cover term for "nephew o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niece
In the lineal kinship system used in the English-speaking world, a niece or nephew is a child of the subject's sibling or sibling-in-law. The converse relationship, the relationship from the niece or nephew's perspective, is that of an aunt or uncle. A niece is female and a nephew is male. The term nibling has been used in place of the common, gender-specific terms in some specialist literature. As aunt/uncle and niece/nephew are separated by one generation, they are an example of a second-degree relationship. They are 25% related by blood. Lexicology The word nephew is derived from the French word ''neveu'' which is derived from the Latin ''nepos''. The term ''nepotism'', meaning familial loyalty, is derived from this Latin term. ''Niece'' entered Middle English from the Old French word ''nece'', which also derives from Latin ''nepotem''. The word ''nibling'' is a neologism suggested by Samuel Martin (linguist), Samuel Martin in 1951 as a cover term for "nephew o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grandparent
Grandparents, individually known as grandmother and grandfather, are the parents of a person's father or mother – paternal or maternal. Every sexually-reproducing living organism who is not a genetic chimera has a maximum of four genetic grandparents, eight genetic great-grandparents, sixteen genetic great-great-grandparents, thirty-two genetic great-great-great-grandparents, sixty-four genetic great-great-great-great grandparents, etc. In the history of modern humanity, around 30,000 years ago, the number of modern humans who lived to be a grandparent increased. It is not known for certain what spurred this increase in longevity but largely results in the improved medical technology and living standard, but it is generally believed that a key consequence of three generations being alive together was the preservation of information which could otherwise have been lost; an example of this important information might have been where to find water in times of drought. In cases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grandchild
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as members mature and learn to participate in the community. Historically, most human societies use family as the primary locus of attachment, nurturance, and socialization. Anthropologists classify most family organizations as matrifocal (a mother and her children), patrifocal (a father and his children), conjugal (a wife, her husband, and children, also called the nuclear family), avuncular (a man, his sister, and her children), or extended (in addition to parents and children, may include grandparents, aunts, uncles, or cousins). The field of genealogy aims to trace family lineages through history. The family is also an important economic unit studied in family economics. The w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half-sibling
A sibling is a relative that shares at least one parent with the subject. A male sibling is a brother and a female sibling is a sister. A person with no siblings is an only child. While some circumstances can cause siblings to be raised separately (such as foster care), most societies have siblings grow up together. This causes the development of strong emotional bonds, with siblinghood considered a unique type of relationship unto itself. The emotional bond between siblings is often complicated and is influenced by factors such as parental treatment, birth order, personality, and personal experiences outside the family. Medically, a full sibling is a first-degree relative and a half sibling is a second-degree relative as they are related by 50% and 25% respectively. Definitions The word ''sibling'' was reintroduced in 1903 in an article in '' Biometrika'', as a translation for the German ''Geschwister'', having not been used since 1425. Siblings or full siblings ( 'full'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Cousin
Most generally, in the lineal kinship system used in the English-speaking world, a cousin is a type of familial relationship in which two relatives are two or more familial generations away from their most recent common ancestor. Commonly, "cousin" refers to a first cousin – a relative of the same generation whose most recent common ancestor with the subject is a grandparent. Degrees and removals are separate measures used to more precisely describe the relationship between cousins. ''Degree'' measures the separation, in generations, from the most recent common ancestor(s) to a parent of one of the cousins (whichever is closest), while ''removal'' measures the difference in generations between the cousins themselves, relative to their most recent common ancestor(s). To illustrate usage, a second cousin is a cousin with a ''degree'' of two; there are three (not two) generations from the common ancestor(s). When the degree is not specified, first cousin is assumed. A cousin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family
Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideally, families offer predictability, structure, and safety as members mature and learn to participate in the community. Historically, most human societies use family as the primary locus of Attachment theory, attachment, nurturance, and socialization. Anthropologists classify most family organizations as Matrifocal family, matrifocal (a mother and her children), patrifocal (a father and his children), wikt:conjugal, conjugal (a wife, her husband, and children, also called the nuclear family), avuncular (a man, his sister, and her children), or Extended family, extended (in addition to parents and children, may include grandparents, aunts, uncles, or cousins). The field of genealogy aims to trace family lineages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third-degree Relative
Third-degree relatives are a segment of the extended family and includes first cousins, great grandparents and great grandchildren. Third-degree relatives are generally defined by the expected amount of genetic overlap that exists between two people, with the third-degree relatives of an individual sharing approximately 12.5% of their genes. The category includes great-grandparents, great-grandchildren, grand-uncles, grand-aunts, first cousins, half-uncles, half-aunts, half-nieces and half-nephews. See also *Family * First-degree relative *Second-degree relative A second-degree relative (SDR) is someone who shares 25% of a person's genes. It includes uncles, aunts, nephews, nieces, grandparents, grandchildren, half-siblings, and double cousins. See also *Family Family (from la, familia) is a ... References Family {{society-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar working in the 19th century in Brno, was the first to study genetics scientifically. Mendel studied "trait inheritance", patterns in the way traits are handed down from parents to offspring over time. He observed that organisms (pea plants) inherit traits by way of discrete "units of inheritance". This term, still used today, is a somewhat ambiguous definition of what is referred to as a gene. Trait inheritance and molecular inheritance mechanisms of genes are still primary principles of genetics in the 21st century, but modern genetics has expanded to study the function and behavior of genes. Gene structure and function, variation, and distribution are studied within the context of the cell, the organism (e.g. dominance), and within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)




_und_ihre_Kinder.jpg)