|
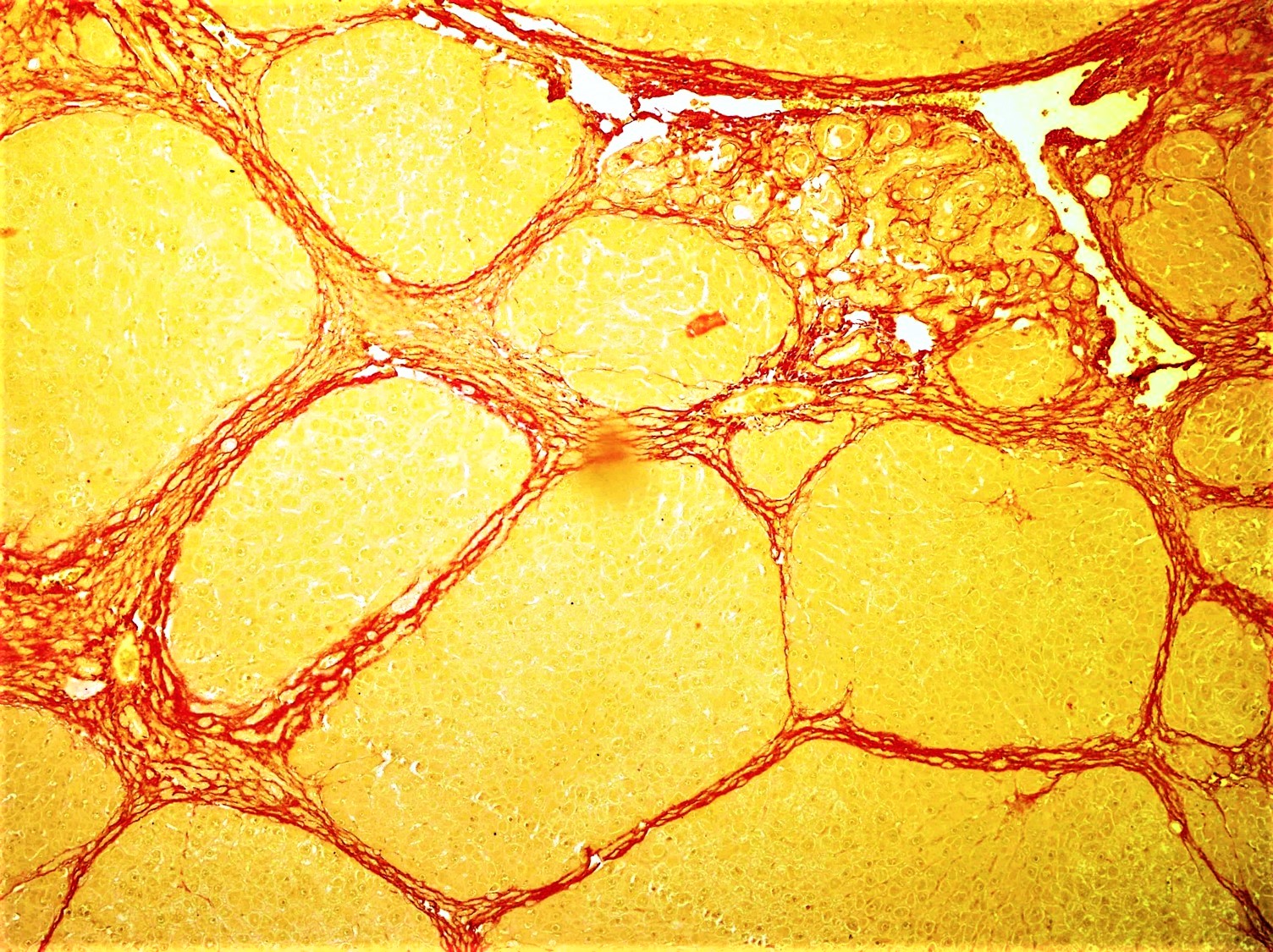
Scleromyositis
Scleromyositis, is an autoimmune disease (a disease in which the immune system attacks the body). People with scleromyositis have symptoms of both systemic scleroderma and either polymyositis or dermatomyositis, and is therefore considered an overlap syndrome. Although it is a rare disease, it is one of the more common overlap syndromes seen in scleroderma patients, together with MCTD and Antisynthetase syndrome. Autoantibodies often found in these patients are the anti-PM/Scl (anti- exosome) antibodies. The symptoms that are seen most often are typical symptoms of the individual autoimmune diseases and include Raynaud's phenomenon, arthritis, myositis and scleroderma. Treatment of these patients is therefore strongly dependent on the exact symptoms with which a patient reports to a physician and is similar to treatment for the individual autoimmune disease, often involving either immunosuppressive or immunomodulating drugs. Signs and symptoms Symptoms vary but they mostl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exosome Complex
The exosome complex (or PM/Scl complex, often just called the exosome) is a multi-protein intracellular complex capable of degrading various types of RNA (ribonucleic acid) molecules. Exosome complexes are found in both eukaryotic cells and archaea, while in bacteria a simpler complex called the degradosome carries out similar functions. The core of the exosome contains a six-membered ring structure to which other proteins are attached. In eukaryotic cells, the exosome complex is present in the cytoplasm, nucleus, and especially the nucleolus, although different proteins interact with the exosome complex in these compartments regulating the RNA degradation activity of the complex to substrates specific to these cell compartments. Substrates of the exosome include messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and many species of small RNAs. The exosome has an exoribonucleolytic function, meaning it degrades RNA starting at one end (the 3′ end in this case), and in eukaryotes also an endori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoimmune Disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly any body part can be involved. Common symptoms can be diverse and transient, ranging from mild to severe, and generally include low grade fever and feeling tired. The cause is unknown. Some autoimmune diseases such as lupus run in families, and certain cases may be triggered by infections or other environmental factors. Some common diseases that are generally considered autoimmune include celiac disease, diabetes mellitus type 1, graves' disease, inflammatory bowel disease, multiple sclerosis, alopecia areata, addison’s disease, pernicious anemia, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. The diagnosis can be difficult to determine. Treatment depends on the type and severity of the condition. Nonsteroidal ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myositis
Myositis is a rare disease that involves inflammation of the muscles. This can present with a variety of symptoms such as skin involvement (i.e., rashes), muscle weakness, and other organ involvement. Systemic symptoms such as weight loss, fatigue, and low fever can also present. Causes Injury, medicines, infection, or an autoimmune disorder can lead to myositis. It can also be idiopathic. * Injury - A mild form of myositis can occur with hard exercise. A more severe form of muscle injury, called rhabdomyolysis, is also associated with myositis. This is a condition where injury to your muscles causes them to quickly break down. * Medicines - A variety of different medicines can cause myositis. One of the most common drug types that can cause myositis is statins. Statins are drugs that are used to help lower high cholesterol. One of the most common side effects of statin therapy is muscle pain. Rarely, statin therapy can lead to myositis. * Infection - The most common infectious c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rituximab
Rituximab, sold under the brand name Rituxan among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat certain autoimmune diseases and types of cancer. It is used for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (in non-geriatric patients), rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, pemphigus vulgaris, myasthenia gravis and Epstein–Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcers. It is given by slow injection into a vein. Biosimilars of Rituxan include Blitzima, Riabni, Ritemvia, Rituenza (F.K.A. Tuxella), Rixathon, Ruxience, and Truxima. Common side effects which often occur within two hours of the medication being given include rash, itchiness, low blood pressure, and shortness of breath. Infections are also common. Severe side effects include reactivation of hepatitis B in those previously infected, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and death. It is unclear if use during pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which connective tissue replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of permanent scar tissue. Repeated injuries, chronic inflammation and repair are susceptible to fibrosis where an accidental excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components, such as the collagen is produced by fibroblasts, leading to the formation of a permanent fibrotic scar. In response to injury, this is called scarring, and if fibrosis arises from a single cell line, this is called a fibroma. Physiologically, fibrosis acts to deposit connective tissue, which can interfere with or totally inhibit the normal architecture and function of the underlying organ or tissue. Fibrosis can be used to describe the pathological state of excess deposition of fibrous tissue, as well as the process of connective tissue deposition in healing. Define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatomyositis
Dermatomyositis (DM) is a long-term inflammatory disorder which affects skin and the muscles. Its symptoms are generally a skin rash and worsening muscle weakness over time. These may occur suddenly or develop over months. Other symptoms may include weight loss, fever, lung inflammation, or light sensitivity. Complications may include calcium deposits in muscles or skin. The cause is unknown. Theories include that it is an autoimmune disease or a result of a viral infection. Dermatomyositis may develop as a paraneoplastic syndrome associated with several forms of malignancy. It is a type of inflammatory myopathy. Diagnosis is typically based on some combination of symptoms, blood tests, electromyography, and muscle biopsies. While no cure for the condition is known, treatments generally improve symptoms. Treatments may include medication, physical therapy, exercise, heat therapy, orthotics and assistive devices, and rest. Medications in the corticosteroids family are typic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymyositis
Polymyositis (PM) is a type of chronic inflammation of the muscles (inflammatory myopathy) related to dermatomyositis and inclusion body myositis. Its name means "inflammation of many muscles" ('' poly-'' + '' myos-'' + ''-itis''). The inflammation of polymyositis is mainly found in the endomysial layer of skeletal muscle, whereas dermatomyositis is characterized primarily by inflammation of the perimysial layer of skeletal muscles. Signs and symptoms The hallmark of polymyositis is weakness and/or loss of muscle mass in the proximal musculature, as well as flexion of the neck and torso. These symptoms can be associated with marked pain in these areas as well. The hip extensors are often severely affected, leading to particular difficulty in climbing stairs and rising from a seated position. The skin involvement of dermatomyositis is absent in polymyositis. Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) or other problems with esophageal motility occur in as many as 1/3 of patients. Low grad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scleroderma
Scleroderma is a group of autoimmune diseases that may result in changes to the skin, blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs. The disease can be either localized to the skin or involve other organs, as well. Symptoms may include areas of thickened skin, stiffness, feeling tired, and poor blood flow to the fingers or toes with cold exposure. One form of the condition, known as CREST syndrome, classically results in calcium deposits, Raynaud's syndrome, esophageal problems, thickening of the skin of the fingers and toes, and areas of small, dilated blood vessels. The cause is unknown, but it may be due to an abnormal immune response. Risk factors include family history, certain genetic factors, and exposure to silica. The underlying mechanism involves the abnormal growth of connective tissue, which is believed to be the result of the immune system attacking healthy tissues. Diagnosis is based on symptoms, supported by a skin biopsy or blood tests. While no cure is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunosuppressive Drug
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent activity of the immune system. Classification Immunosuppressive drugs can be classified into five groups: * glucocorticoids * cytostatics * antibodies * drugs acting on immunophilins * other drugs Glucocorticoids In pharmacologic (supraphysiologic) doses, glucocorticoids, such as prednisone, dexamethasone, and hydrocortisone are used to suppress various allergic, inflammatory, and autoimmune disorders. They are also administered as posttransplantory immunosuppressants to prevent the acute transplant rejection and graft-versus-host disease. Nevertheless, they do not prevent an infection and also inhibit later reparative processes. Immunosuppressive mechanism Glucocorticoids suppress cell-mediated immunity. They act by inhibiting genes that code for the cytokines Interleukin 1 (IL-1), IL-2, IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scleroderma
Scleroderma is a group of autoimmune diseases that may result in changes to the skin, blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs. The disease can be either localized to the skin or involve other organs, as well. Symptoms may include areas of thickened skin, stiffness, feeling tired, and poor blood flow to the fingers or toes with cold exposure. One form of the condition, known as CREST syndrome, classically results in calcium deposits, Raynaud's syndrome, esophageal problems, thickening of the skin of the fingers and toes, and areas of small, dilated blood vessels. The cause is unknown, but it may be due to an abnormal immune response. Risk factors include family history, certain genetic factors, and exposure to silica. The underlying mechanism involves the abnormal growth of connective tissue, which is believed to be the result of the immune system attacking healthy tissues. Diagnosis is based on symptoms, supported by a skin biopsy or blood tests. While no cure is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raynaud's Phenomenon
Raynaud syndrome, also known as Raynaud's phenomenon, eponymously named after the physician Auguste Gabriel Maurice Raynaud, who first described it in his doctoral thesis in 1862, is a medical condition in which the spasm of small arteries causes episodes of reduced blood flow to end arterioles. Typically, the fingers, and less commonly, the toes, are involved. Rarely, the nose, ears, or lips are affected. The episodes classically result in the affected part turning white and then blue. Often, numbness or pain occurs. As blood flow returns, the area turns red and burns. The episodes typically last minutes but can last several hours. Episodes are typically triggered by cold or emotional stress. Primary Raynaud's, also known as idiopathic, means that it is spontaneous, of unknown cause, and unrelated to another disease. Secondary Raynaud's occurs as a result of another condition and has an older age at onset; episodes are intensely painful and can be asymmetric and associated wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthritis
Arthritis is a term often used to mean any disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In some types of arthritis, other organs are also affected. Onset can be gradual or sudden. There are over 100 types of arthritis. The most common forms are osteoarthritis (degenerative joint disease) and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis usually occurs with age and affects the fingers, knees, and hips. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that often affects the hands and feet. Other types include gout, lupus, fibromyalgia, and septic arthritis. They are all types of rheumatic disease. Treatment may include resting the joint and alternating between applying ice and heat. Weight loss and exercise may also be useful. Recommended medications may depend on the form of arthritis. These may include pain medications such as ibuprofen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |