|
Science And Technology In Kyrgyzstan
Science and technology in Kyrgyzstan examines government efforts to develop a national innovation system and the impact of these policies. Socio-economic context Most of the Central Asian economies have emerged relatively unscathed from the global financial crisis of 2008–2009. Kyrgyzstan's performance has been more erratic, but this trend was visible well before 2008. The Kyrgyz economy was shaken by a series of shocks between 2010 and 2012. In April 2010, President Kurmanbek Bakiyev was deposed by a popular uprising, with former minister of foreign affairs Roza Otunbayeva assuring the interim presidency until the election of Almazbek Atambayev in November 2011. Food prices rose two years in a row and, in 2012, production at the major Kumtor gold mine fell by 60% after the site was perturbed by geological movements. According to the World Bank, 33.7% of the population was living in absolute poverty in 2010 and 36.8% a year later. In 2012, Kyrgyzstan's external debt (89%) wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the east. Its capital and largest city is Bishkek. Ethnic Kyrgyz make up the majority of the country's seven million people, followed by significant minorities of Uzbeks and Russians. The Kyrgyz language is closely related to other Turkic languages. Kyrgyzstan's history spans a variety of cultures and empires. Although geographically isolated by its highly mountainous terrain, Kyrgyzstan has been at the crossroads of several great civilizations as part of the Silk Road along with other commercial routes. Inhabited by a succession of tribes and clans, Kyrgyzstan has periodically fallen under larger domination. Turkic nomads, who trace their ancestry to many Turkic states. It was first established as the Yenisei Kyrgyz Khaganate later in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organization For Security And Co-operation In Europe
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is the world's largest regional security-oriented intergovernmental organization with observer status at the United Nations. Its mandate includes issues such as arms control, promotion of human rights, freedom of the press, and free and fair elections. It employs around 3,460 people, mostly in its field operations but also in its secretariat in Vienna, Austria, and its institutions. It has its origins in the mid-1975 Conference on Security and Co-operation in Europe (CSCE) held in Helsinki, Finland. The OSCE is concerned with early warning, conflict prevention, crisis management, and post-conflict rehabilitation. Most of its 57 participating countries are in Europe, but there are a few members present in Asia and North America. The participating states cover much of the land area of the Northern Hemisphere. It was created during the Cold War era as a forum for discussion between the Western Bloc and Eastern Bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
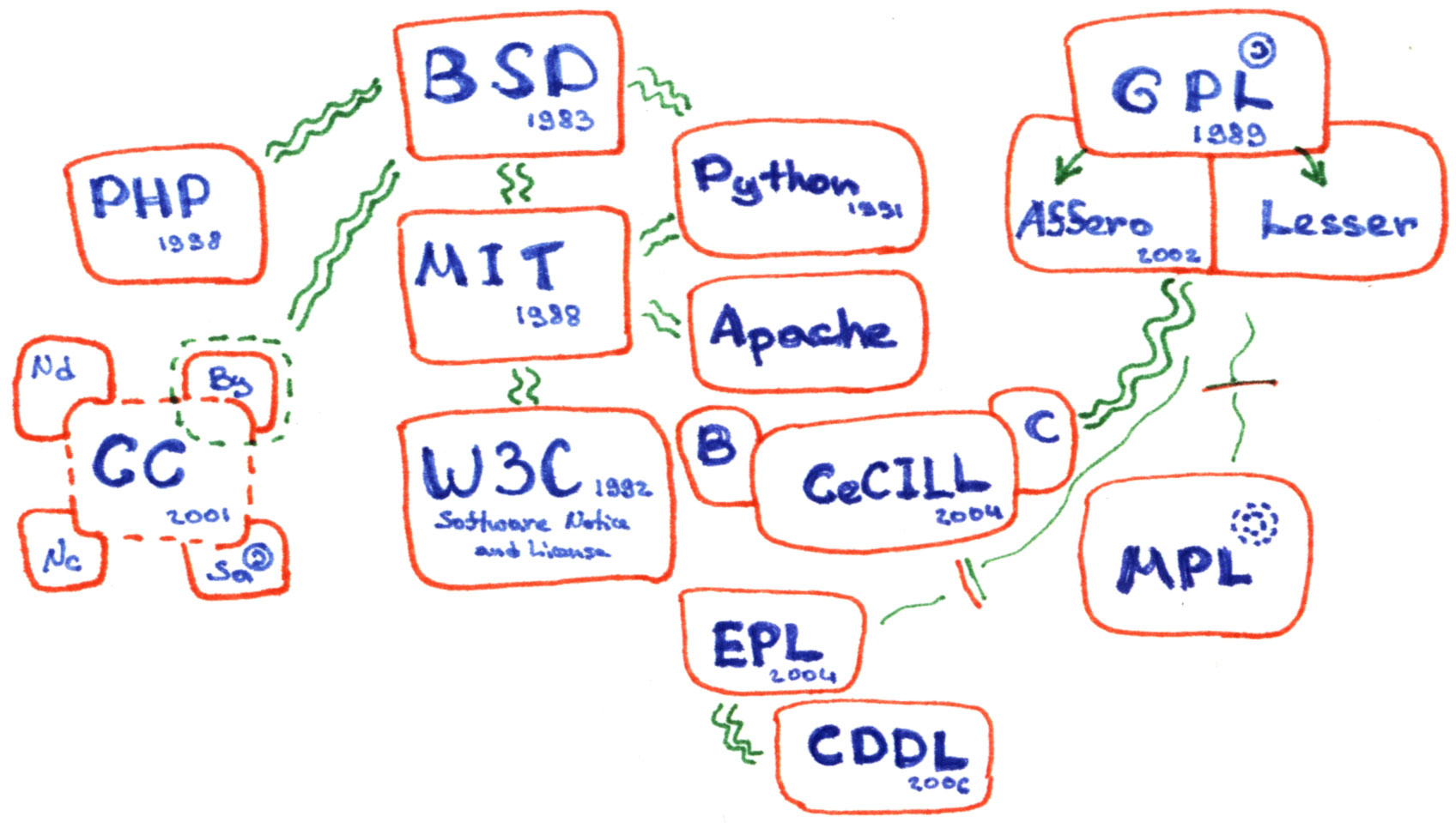
Adding Open License Text To Wikipedia
Addition (usually signified by the plus symbol ) is one of the four basic operations of arithmetic, the other three being subtraction, multiplication and division. The addition of two whole numbers results in the total amount or '' sum'' of those values combined. The example in the adjacent image shows a combination of three apples and two apples, making a total of five apples. This observation is equivalent to the mathematical expression (that is, "3 ''plus'' 2 is equal to 5"). Besides counting items, addition can also be defined and executed without referring to concrete objects, using abstractions called numbers instead, such as integers, real numbers and complex numbers. Addition belongs to arithmetic, a branch of mathematics. In algebra, another area of mathematics, addition can also be performed on abstract objects such as vectors, matrices, subspaces and subgroups. Addition has several important properties. It is commutative, meaning that the order of the operands d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free License
A free license or open license is a license which allows others to reuse another creator’s work as they wish. Without a special license, these uses are normally prohibited by copyright, patent or commercial license. Most free licenses are worldwide, royalty-free, non-exclusive, and perpetual (see copyright durations). Free licenses are often the basis of crowdsourcing and crowdfunding projects. The invention of the term "free license" and the focus on the rights of users were connected to the sharing traditions of the hacker culture of the 1970s public domain software ecosystem, the social and political free software movement (since 1980) and the open source movement (since the 1990s). These rights were codified by different groups and organizations for different domains in Free Software Definition, Open Source Definition, Debian Free Software Guidelines, Definition of Free Cultural Works and The Open Definition. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and enforce the rules that govern international trade. It officially commenced operations on 1 January 1995, pursuant to the 1994 Marrakesh Agreement, thus replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) that had been established in 1948. The WTO is the world's largest international economic organization, with 164 member states representing over 98% of global trade and global GDP. The WTO facilitates trade in goods, services and intellectual property among participating countries by providing a framework for negotiating trade agreements, which usually aim to reduce or eliminate tariffs, quotas, and other restrictions; these agreements are signed by representatives of member governmentsUnderstanding the WTO' Handbook at WTO officia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Science And Technology Center
The International Science and Technology Center (ISTC) is an intergovernmental nonproliferation organization connecting scientists with their peers and research organizations in other countries. The ISTC Headquarters is currently in Nur Sultan, Kazakhstan. Member governments have included Armenia, the European Union, Georgia, Japan, Kazakhstan, the Republic of Korea, Kyrgyzstan, Norway, Tajikistan, and the United States. Scientists from nearly 60 countries have participated in ISTC activities. ISTC facilitates international science projects and assists the global scientific and business community to source and engage scientists and institutes that develop or possess an excellence of scientific know-how. History The ISTC was established in 1992. Its headquarters were originally in Moscow. In 2015, the ISTC moved to Astana Astana, previously known as Akmolinsk, Tselinograd, Akmola, and most recently Nur-Sultan, is the capital city of Kazakhstan. The city lies on the banks of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizon 2020
The Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development, also called Framework Programmes or abbreviated FP1 to FP9, are funding programmes created by the European Union/European Commission to support and foster research in the European Research Area (ERA). Starting in 2014, the funding programmes were named Horizon. The funding programmes began in 1984 and continue to the present day. The most recent programme, Horizon Europe, has a budget of 95.5 billion Euros to be distributed over 7 years. The specific objectives and actions vary between funding periods. In FP6 and FP7, focus was on technological research. In Horizon 2020, the focus was on innovation, delivering economic growth faster, and delivering solutions to end users that are often governmental agencies. Background Conducting European research policies and implementing European research programmes is an obligation under the Amsterdam Treaty, which includes a chapter on research and technological development. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union's Scientific Cooperation Beyond The Bloc
The European Union's scientific collaboration beyond the bloc describes the European Union's frameworks for bilateral cooperation and specific projects in science and technology with countries and regional blocs situated beyond the European Union. Types of association Since 1994, the European Union (EU) has signed international agreements for scientific and technological cooperation with 20 non-EU countries: Algeria, Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, China, Egypt, India, Japan, Jordan, Rep. Korea, Mexico, Morocco, New Zealand, Russian Federation, South Africa, Tunisia, Ukraine and the USA. For the European Parliament, ‘the science diplomacy aspect of this cooperation is emphasized at EU level to facilitate interactions with third countries, as well as to increase the EU's soft power’. The EU invites countries beyond the bloc to participate in its seven-year framework programmes for research and innovation, including developing countries. Horizon Europe, the Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science And Technology In Armenia
Science and technology in Armenia describes trends and developments in science, technology and innovation policy and governance in Armenia. Recent history Armenia experienced recession in 2009 during the global financial crisis, before returning to modest economic growth. Over the period 2008-2013, Armenia's economy grew by 1.7% per year, on average. Building an efficient research system was a state strategic objective for the Armenian authorities in 2014. Armenia has a number of assets, including a strong science base, a large Armenian diaspora and traditional national values that emphasize education and skills. Nonetheless, according to UNESCO in 2015, there were still hurdles to overcome in building the national innovation system. The biggest among these were the poor linkages between universities, research institutions and the business sector. This was partly a legacy of the country's Soviet past, when the policy focus was on developing linkages across the Soviet economy rather ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian Economic Union
The Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU or EEU)EAEU is the acronym used on thorganisation's website However, many media outlets use the acronym EEU. is an economic union of some post-Soviet states located in Eurasia. The Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union was signed on 29 May 2014 by the leaders of Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Russia, and came into force on 1 January 2015. Treaties aiming for Armenia's and Kyrgyzstan's accession to the Eurasian Economic Union were signed on 9 October and 23 December 2014, respectively. Armenia's accession treaty came into force on 2 January 2015. Kyrgyzstan's accession treaty came into effect on 6 August 2015. Kyrgyzstan participated in the EAEU from the day of its establishment as an acceding state. The Eurasian Economic Union has an integrated single market of 184 million people and a gross domestic product of over $1.9 trillion. The EAEU encourages the free movement of goods and services, and provides for common policies in the macroeconomic spher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Most Prolific Countries In Central Asia – Kazakhstan And Uzbekistan – Specialize In Physics And Chemistry
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)