|
Schmidt Net
The Schmidt net is a manual drafting method for the Lambert azimuthal equal-area projection using graph paper. It results in one lateral hemisphere of the Earth with the grid of parallels and meridians. The method is common in geoscience. Construction In the figure, the area-preserving property of the projection can be seen by comparing a grid sector near the center of the net with one at the far right of the net. The two sectors have the same area on the sphere and the same area on the disk. The angle-distorting property can be seen by examining the grid lines; most of them do not intersect at right angles on the Schmidt net. A single Schmidt net can only represent one hemisphere of the earth; typically a pair of Schmidt nets is used to represent both sides of the globe. It is relatively simple to re-plot a gridded map of the world onto a Schmidt net if the azimuth is chosen to be the junction of the equator with any particular meridian from the world-map's grid. Each grid square ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lambert Azimuthal Equal-area Projection
The Lambert azimuthal equal-area projection is a particular mapping from a sphere to a disk. It accurately represents area in all regions of the sphere, but it does not accurately represent angles. It is named for the Swiss mathematician Johann Heinrich Lambert, who announced it in 1772. "Zenithal" being synonymous with "azimuthal", the projection is also known as the Lambert zenithal equal-area projection. The Lambert azimuthal projection is used as a map projection in cartography. For example, the National Atlas of the US uses a Lambert azimuthal equal-area projection to display information in the online Map Maker application, and the European Environment Agency recommends its usage for European mapping for statistical analysis and display. It is also used in scientific disciplines such as geology for plotting the orientations of lines in three-dimensional space. This plotting is aided by a special kind of graph paper called a Schmidt net.Ramsay (1967) Definition To define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle Of Latitude
A circle of latitude or line of latitude on Earth is an abstract east–west small circle connecting all locations around Earth (ignoring elevation) at a given latitude coordinate line. Circles of latitude are often called parallels because they are Parallel (geometry), parallel to each other; that is, planes that contain any of these circles never Intersection, intersect each other. A location's position along a circle of latitude is given by its longitude. Circles of latitude are unlike circles of longitude, which are all great circles with the centre of Earth in the middle, as the circles of latitude get smaller as the distance from the Equator increases. Their length can be calculated by a common sine or cosine function. The 60th parallel north or 60th parallel south, south is half as long as the Equator (disregarding Earth's minor flattening by 0.335%). On the Mercator projection or on the Gall-Peters projection, a circle of latitude is perpendicular to all meridian (geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meridian (geography)
In geography and geodesy, a meridian is the locus connecting points of equal longitude, which is the angle (in degrees or other units) east or west of a given prime meridian (currently, the IERS Reference Meridian). In other words, it is a line of longitude. The position of a point along the meridian is given by that longitude and its latitude, measured in angular degrees north or south of the Equator. On a Mercator projection or on a Gall-Peters projection, each meridian is perpendicular to all circles of latitude. A meridian is half of a great circle on Earth's surface. The length of a meridian on a modern ellipsoid model of Earth (WGS 84) has been estimated as . Pre-Greenwich The first prime meridian was set by Eratosthenes in 200 BCE. This prime meridian was used to provide measurement of the earth, but had many problems because of the lack of latitude measurement. Many years later around the 19th century there were still concerns of the prime meridian. Multiple loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Science
Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to the planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical, chemical, and biological complex constitutions and synergistic linkages of Earth's four spheres, namely biosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and geosphere. Earth science can be considered to be a branch of planetary science, but with a much older history. Earth science encompasses four main branches of study, the lithosphere, the hydrosphere, the atmosphere, and the biosphere, each of which is further broken down into more specialized fields. There are both reductionist and holistic approaches to Earth sciences. It is also the study of Earth and its neighbors in space. Some Earth scientists use their knowledge of the planet to locate and develop energy and mineral resources. Others study the impact of human activity on Earth's environment, and design methods to protect the planet. Some use their knowledge about Earth processes suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Geology
Structural geology is the study of the three-dimensional distribution of rock units with respect to their deformational histories. The primary goal of structural geology is to use measurements of present-day rock geometries to uncover information about the history of deformation (strain) in the rocks, and ultimately, to understand the stress field that resulted in the observed strain and geometries. This understanding of the dynamics of the stress field can be linked to important events in the geologic past; a common goal is to understand the structural evolution of a particular area with respect to regionally widespread patterns of rock deformation (e.g., mountain building, rifting) due to plate tectonics. Use and importance The study of geologic structures has been of prime importance in economic geology, both petroleum geology and mining geology. Folded and faulted rock strata commonly form traps that accumulate and concentrate fluids such as petroleum and natural gas. Simil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lineation (geology)
Lineations in structural geology are linear structural features within rocks. There are several types of lineations, intersection lineations, crenulation lineations, mineral lineations and stretching lineations being the most common. Lineation field measurements are recorded as map lines with a plunge angle and azimuth. Intersection lineations Intersection lineations are linear structures formed by the intersection of any two surfaces in a three-dimensional space. The trace of bedding on an intersecting foliation plane commonly appears as colour stripes generally parallel to local fold's hinges. Intersection lineations can also be due to the intersection of two foliations. Intersection lineations are measured in relation to the two structures which intersect to form them. For instance, according to the measurement conventions of structural geology, original bedding, S0 intersected by a fold's axial plane foliation, forms an intersection lineation L0-1, with an azimuth and plun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foliation (geology)
Foliation in geology refers to repetitive layering in metamorphic rocks.Marshak, Stephen, ''Essentials of Geology,'' W. W. Norton 3rd Ed, 2009 Each layer can be as thin as a sheet of paper, or over a meter in thickness. The word comes from the Latin ''folium'', meaning "leaf", and refers to the sheet-like planar structure. It is caused by shearing forces (pressures pushing different sections of the rock in different directions), or differential pressure (higher pressure from one direction than in others). The layers form parallel to the direction of the shear, or perpendicular to the direction of higher pressure. Nonfoliated metamorphic rocks are typically formed in the absence of significant differential pressure or shear. Foliation is common in rocks affected by the regional metamorphic compression typical of areas of mountain belt formation (orogenic belts). More technically, foliation is any penetrative planar fabric present in metamorphic rocks. Rocks exhibiting foliat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slickenside
In geology, a slickenside is a smoothly polished surface caused by frictional movement between rocks along a fault. This surface is typically striated with linear features, called slickenlines, in the direction of movement. Geometry of slickensides A slickenside can occur as a single surface at a fault between two hard surfaces. Alternatively, the gouge between the fault surfaces may contain many anastamosing slip surfaces that host slickensides. These slip surfaces are on the order of 100 micrometers thick, and the size of the grains that constitute the surface are ultra-fine (0.01-1 micrometers in diameter).Power, William L., and Terry E. Tullis. "The relationship between slickenside surfaces in fine-grained quartz and the seismic cycle." Journal of Structural Geology 11.7 (1989): 879-893. These grains are unlike typical grains of fault rock in that they have irregular grain boundaries and few crystal lattice defects (termed dislocations). Slickensides have conspicuou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (geology)
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
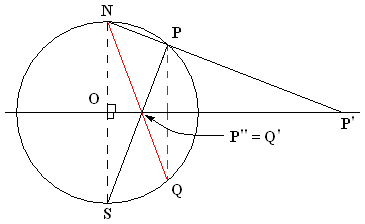
Stereographic Projection
In mathematics, a stereographic projection is a perspective projection of the sphere, through a specific point on the sphere (the ''pole'' or ''center of projection''), onto a plane (geometry), plane (the ''projection plane'') perpendicular to the diameter through the point. It is a smooth function, smooth, bijection, bijective function (mathematics), function from the entire sphere except the center of projection to the entire plane. It maps circle of a sphere, circles on the sphere to generalised circle, circles or lines on the plane, and is conformal map, conformal, meaning that it preserves angles at which curves meet and thus Local property, locally approximately preserves similarity (geometry), shapes. It is neither isometry, isometric (distance preserving) nor Equiareal map, equiareal (area preserving). The stereographic projection gives a way to representation (mathematics), represent a sphere by a plane. The metric tensor, metric induced metric, induced by the inverse s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |