|
Schloss Fantaisie
The Schloss Fantaisie is a castle, situated 3.1 miles west of the city Bayreuth in the community Eckersdorf. The roots of this castle are in the medieval, but there is not much left from this time. In the 16th century the Lords of Lüchau (Lüchauer Herren) built a plain Renaissance Castle. When Friedrich Ludwig von Lüchau died in 1757, the castle fell back to Frederick, Margrave of Brandenburg-Bayreuth. In 1761 he started to build a new castle at the same location as an additional summer residence. The building was inspired from impressions of an Italian journey of the Margrave couple Wilhelmine and Frederick, Margrave of Brandenburg-Bayreuth. In the year 1763 the Margraves only daughter Fredericka Sophie inherited the castle. She used the name Fantaisie for her castle and authorized the builder Johann Jakob Spindler to continue the building. Because of many modifications there is not much left from the original castle but you can see a replica of the "Spindler-Kabinett", a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayreuth
Bayreuth (, ; bar, Bareid) is a town in northern Bavaria, Germany, on the Red Main river in a valley between the Franconian Jura and the Fichtelgebirge Mountains. The town's roots date back to 1194. In the 21st century, it is the capital of Upper Franconia and has a population of 72,148 (2015). It hosts the annual Bayreuth Festival, at which performances of operas by the 19th-century German composer Richard Wagner are presented. History Middle Ages and Early Modern Period The town is believed to have been founded by the counts of Andechs probably around the mid-12th century,Mayer, Bernd and Rückel, Gert (2009). ''Bayreuth – Tours on Foot'', Heinrichs-Verlag, Bamberg, p.5, . but was first mentioned in 1194 as ''Baierrute'' in a document by Bishop Otto II of Bamberg. The syllable ''-rute'' may mean ''Rodung'' or "clearing", whilst ''Baier-'' indicates immigrants from the Bavarian region. Already documented earlier, were villages later merged into Bayreuth: Seulbitz (in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eckersdorf
Eckersdorf is a municipality in the district of Bayreuth in Bavaria in Germany. Geography The municipality of Eckersdorf is located on the northern edge of an area called "Little Switzerland" (German: Fränkische Schweiz), close to the world-famous festival town of Bayreuth. The highest elevation in the region of Eckersdorf is the ''Sophienberg'' with an altitude of 593 m. Districts The present-day municipality of Eckersdorf was created in the course of municipal reform in 1978. According to the information given by the local government, there are 22 official districts. Neighboring communities The neighboring communities of Eckersdorf are (starting north in clockwise order): Thurnau, Bayreuth, Mistelbach, and Mistelgau. History Eckersdorf was first mentioned in 1149 in the so-called ''Giechburgvertrag''. The Counts of Andechs-Meranien (Grafen von Andechs-Meranien) owned the current area of Eckersdorf until they died off in 1248. The lords of Berg Plassenberg (Her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas and achievements of classical antiquity. It occurred after the Crisis of the Late Middle Ages and was associated with great social change. In addition to the standard periodization, proponents of a "long Renaissance" may put its beginning in the 14th century and its end in the 17th century. The traditional view focuses more on the early modern aspects of the Renaissance and argues that it was a break from the past, but many historians today focus more on its medieval aspects and argue that it was an extension of the Middle Ages. However, the beginnings of the period – the early Renaissance of the 15th century and the Italian Proto-Renaissance from around 1250 or 1300 – overlap considerably with the Late Middle Ages, conventionally da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick, Margrave Of Brandenburg-Bayreuth
Frederick, Margrave of Brandenburg-Bayreuth (May 10, 1711 in Weferlingen – February 26, 1763 in Bayreuth), was a member of the House of Hohenzollern and Margrave of Brandenburg-Bayreuth. He was the eldest son of Georg Frederick Karl, nominal Margrave of Brandenburg-Bayreuth-Kulmbach, by his wife Dorothea of Schleswig-Holstein-Sonderburg-Beck. Life Born a minor member of the house of Brandenburg-Bayreuth, Frederick's fate changed in 1726, when his father inherited the principality of Bayreuth after a long dispute with the kingdom of Prussia over his rights of succession. The sixteen-year-old Frederick became the Hereditary Margrave of Bayreuth. In 1735, on his father's death, Frederick became the new Margrave of Brandenburg-Bayreuth. Frederick has the reputation of being an enlightened monarch. In Bayreuth, Frederick is referred to as "the Beloved." In his residence of Bayreuth, he promoted the sciences and arts and owned numerous buildings. Frederick received a good educa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelmine Of Prussia, Margravine Of Brandenburg-Bayreuth
Princess Friederike Sophie Wilhelmine of Prussia (3 July 170914 October 1758) was a princess of Prussia (the older sister of Frederick the Great) and composer. She was the eldest daughter of Frederick William I of Prussia and Sophia Dorothea of Hanover, and granddaughter of George I of Great Britain. In 1731, she married Frederick, Margrave of Brandenburg-Bayreuth. The baroque buildings and parks built during her reign shape much of the present appearance of the town of Bayreuth, Germany. Early life Born in Berlin, Wilhelmine shared the unhappy childhood of her brother, Frederick the Great, whose friend and confidante she remained all her life, with the exception of one short interval. She was fiercely beaten and abused by her governess during her childhood. Wilhelmine later wrote: "Not a day passed that she he governessdid not prove upon me the fearful power of her fists." The mistreatment continued until the prince's governess finally said to their mother, who had been obli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elisabeth Fredericka Sophie Of Brandenburg-Bayreuth
Princess Elisabeth Friederike Sophie of Brandenburg-Bayreuth (30 August 1732 – 6 April 1780), was a German princess of the House of Hohenzollern and the Duchess of Württemberg by marriage. Biography Early life She was born in Bayreuth, the daughter of Frederick, Margrave of Brandenburg-Bayreuth by his first wife, Princess Wilhelmine of Prussia, the favourite sister of King Frederick the Great. Both the Margrave and the Margravine hoped for the eventual birth of a son and heir; however, this never happened. Thus, Elisabeth Fredericka Sophie grew up as an only child at the court of her father in Bayreuth. At the time of her birth, her parents' marriage was still intact. However, during the following years the couple became estranged as Margrave Frederick turned his affections to other women. His most prominent mistress was Wilhelmine von Marwitz, one of his wife's ladies-in-waiting. Elisabeth Fredericka Sophie was considered one of the most beautiful princesses of her time. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intarsia
Intarsia is a form of wood inlaying that is similar to marquetry. The start of the practice dates from before the seventh century AD. The technique of intarsia inlays sections of wood (at times with contrasting ivory or bone, or mother-of-pearl) within the solid wood matrix of floors and walls or of tabletops and other furniture; by contrast marquetry assembles a pattern out of veneers glued upon the carcass. The word ''intarsia'' may derive from the Latin word '' interserere'' (to insert). Certosina is a variant also using pieces of ivory, bone or mother of pearl. Intarsia is mostly used of Italian, or at least European work. Similar techniques are found over much of Asia and the Middle East. History When Egypt came under Arab rule in the seventh century, indigenous arts of intarsia and wood inlay, which lent themselves to non-representational decors and tiling patterns, spread throughout the Maghreb. The technique of intarsia was already perfected in Islamic North Afric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Garden
A German garden is a type of architecture of gardens, originating in Germany, influenced by the English garden concept. With staffages and embellishments (e.g. a grotto) and weeping trees, a sense of emotional aesthetics should be developed. Typical of this kind of park design is clear structure and domestic animals, a necessary component of the garden, as seen in former times in the Luisium Palace near Dessau in Germany or still existing the historistic park of Villa Haas (Hesse) from 1892. Livestock in the park serve to enhance the idyll (nature experience). The park area therefore had to be redesigned to protect the plants (walls, hedges, watercourses, fences). The term " Ornamental Farm", which is still used today in manors with small park areas, forms a flowing border to this. Here, too, beauty always serves the useful. An own German garden style, as demanded by the leading German garden theorist Hirschfeld and his pupils, is never concretized in the literature compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castles In Bavaria
Numerous castles are found in the German state of Bavaria. These buildings, some of which have a history of over 1,000 years, were the setting for historical events, domains of famous personalities, and are still imposing structures to this day. This list encompasses castles described in German as ''Burg'' (castle), ''Festung'' (fort/fortress), ''Schloss'' (manor house) and ''Palais''/''Palast'' (palace). Many German castles after the Middle Ages were built mainly as royal or noble residences rather than as fortified buildings. Regierungsbezirk Oberbayern Altötting # Burghausen Castle ('' in German'') # Castle Tuessling ('' in German'') Bad Tölz-Wolfratshausen # Seeburg (Münsing) # Schloss Hohenburg # Hohenburg (Lenggries) (ruin) Berchtesgadener Land # Berchtesgaden Castle ('' de'') # Gruttenstein Castle ('' de'') # Burgruine Karlstein ('' de'') # Castle Laufen # Marzoll Palace ('' de'') # Raschenberg Castle ('' de'') # Staufeneck Castle ('' de'') Dac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


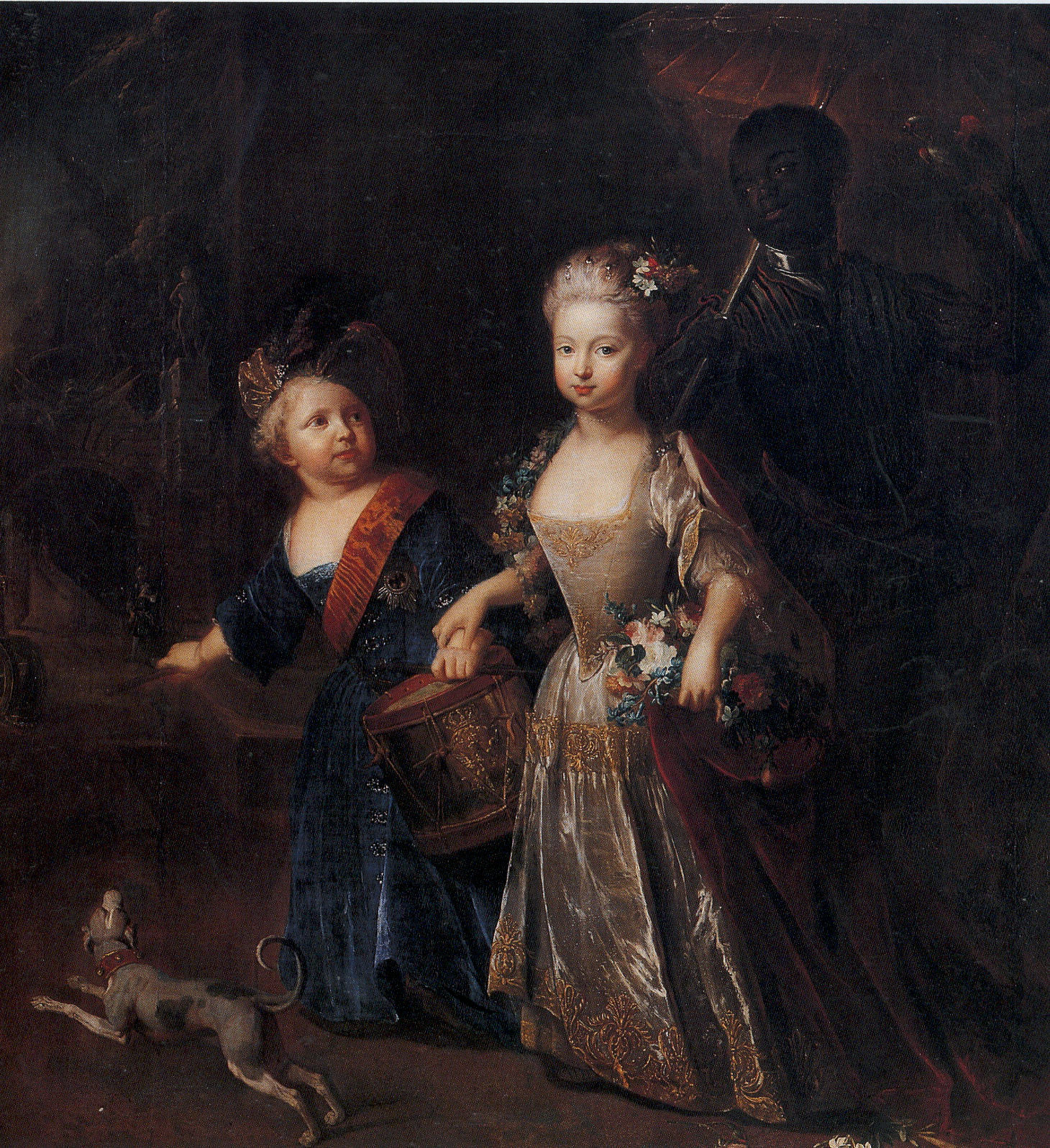
.jpg)
