|
Schleicher ASG 32
The ASG 32 is a Two Seater Class glider manufactured by Alexander Schleicher. The prototype had its maiden flight in Poppenhausen on 31 May 2014. Deliveries began in 2015. Design and development The ASG 32 is a two-seat mid-wing sailplane of composite construction, it has a retractable landing wheel and a horizontal tail mounted atop the vertical fin (T-tail). The aircraft was announced in April 2013, with the intention that it would fill the gap between the ASK 21 trainer and the larger Schleicher ASH 30 Open Class two seater. The ASG 32 meets the requirements of the FAI 20 metre Two-Seater Class. Pure sailplane, motorized self-launching and sustainer engine versions were announced. Construction of the prototype started in 2013, during which the fuselage and tailplane were displayed. The maiden flight was on 31 May 2014, piloted by the designer Michael Greiner and the Schleicher CEO, Peter Kremer. The electrically powered variant of the ASG 32 will be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austro Engine AE50R
The Austro Engine EA50R is an Austrian aircraft engine, produced by Austro Engine of Wiener Neustadt for use in motorgliders and UAVs.Bayerl, Robby; Martin Berkemeier; et al: ''World Directory of Leisure Aviation 2011-12'', pages 238-239. WDLA UK, Lancaster UK, 2011. ISSN 1368-485X Design and development The AE50R is based on the MidWest AE50. Diamond Aircraft Industries purchased the design from Mid-West Engines Limited on 10 March 2003 and took over as the type certificate holder. Diamond formed its subsidiary, Austro Engine, to produce the engine. The engine is a single rotor four-stroke, air and liquid-cooled, gasoline Wankel engine design, with a mechanical gearbox reduction drive employing a helical gear set with a reduction ratio of 3.225:1. Cooling is predominantly liquid, with forced air cooling for the rotor core. A starter and generator are standard equipment. It employs dual capacitor discharge ignition with variable ignition timing and produces at 7750 rpm. The en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-wing Aircraft
A monoplane is a fixed-wing aircraft configuration with a single mainplane, in contrast to a biplane or other types of multiplanes, which have multiple planes. A monoplane has inherently the highest efficiency and lowest drag of any wing configuration and is the simplest to build. However, during the early years of flight, these advantages were offset by its greater weight and lower manoeuvrability, making it relatively rare until the 1930s. Since then, the monoplane has been the most common form for a fixed-wing aircraft. Characteristics Support and weight The inherent efficiency of the monoplane is best achieved in the cantilever wing, which carries all structural forces internally. However, to fly at practical speeds the wing must be made thin, which requires a heavy structure to make it strong and stiff enough. External bracing can be used to improve structural efficiency, reducing weight and cost. For a wing of a given size, the weight reduction allows it to fly slower a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
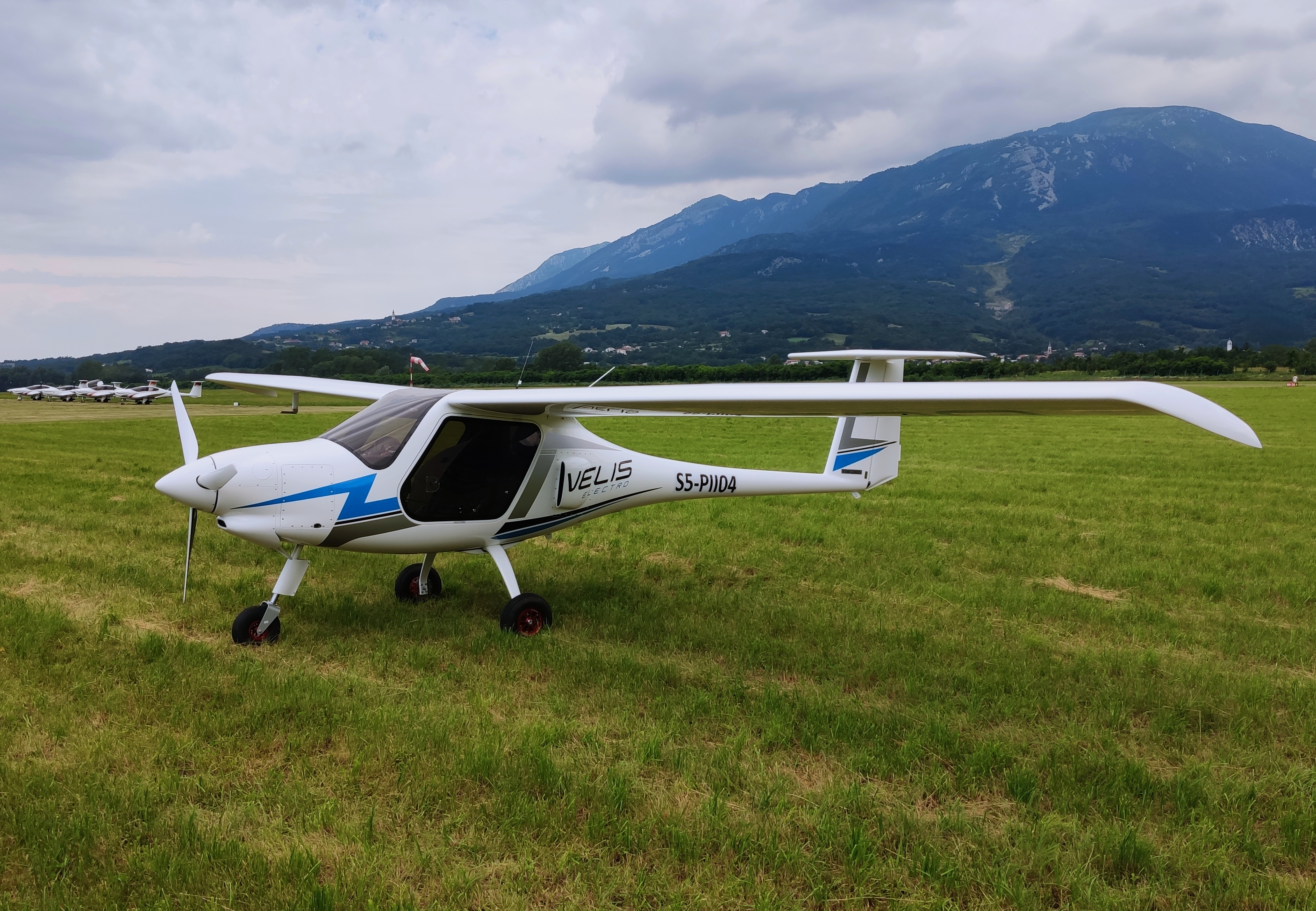
Electric Aircraft
An electric aircraft is an aircraft powered by electricity. Electric aircraft are seen as a way to reduce the environmental effects of aviation, providing zero emissions and quieter flights. Electricity may be supplied by a variety of methods, the most common being batteries. Most have electric motors driving propellers or turbines. Crewed flights in an electrically powered airship go back to the 19th century, and to 1917 for a tethered helicopter. Electrically powered model aircraft have been flown at least since the 1970s, preceding the small unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) or drones used today. Small UAS could be used for parcel deliveries, and larger ones for long-endurance applications: aerial imagery, surveillance, telecommunications. The first crewed free flight by an electrically powered aeroplane, the MB-E1, was made in 1973, and most crewed electric aircraft today are still only experimental prototypes. Between 2015 and 2016, Solar Impulse 2 completed a circ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Gliders
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy. Available energy sources include potential energy (e.g. energy of the Earth's gravitational field as exploited in hydroelectric power generation), heat energy (e.g. geothermal), chemical energy, electric potential and nuclear energy (from nuclear fission or nuclear fusion). Many of these processes generate heat as an intermediate energy form, so heat engines have special importance. Some natural processes, such as atmospheric convection cells convert environmental heat into motion (e.g. in the form of rising air currents). Mechanical energy is of particular importance in transportation, but also plays a role in many industrial processes such as cutting, grinding, crushing, and mixing. Mechanical heat engines convert heat into work via various thermodynamic processes. The internal combustion engine is perhaps the most common example of a mechanical heat engine, in which he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schleicher Aircraft
Schleicher may refer to: *Schleicher (surname), a German surname *Schleicher County, Texas, a county in Texas, United States *Schleicher (Hammond) Schleicher is a small neighborhood in the southern portion of Hammond, IN. It is south of I-80/94, with US Route 41 (Indianapolis BLVD) bordering it to the east, Columbia AVE to the west, and the Little Calumet River to the south, separating Hammo ..., a neighborhood of Hammond, Indiana, United States See also * Alexander Schleicher GmbH & Co, a sailplane manufacturer {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2010s German Sailplanes
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schempp-Hirth Arcus
The Schempp-Hirth Arcus is a flapped Two Seater Class glider in production by Schempp-Hirth. It first flew 7 April 2009. It is offered in addition to the Duo Discus which is an unflapped 20 metre two-seater, whose fuselage it shares. The wings have flaperons integrated along the whole span. It is available as a pure glider, a turbo using the Solo 2350-engine, and as a self-launching glider using the Solo 2625-02i. An electric power unit based on Antares 20E equipment was produced until end 2016 when cooperation with Lange stopped.Arcus Description' Variants ;Arcus :Production variant with a 20 m wingspan. ;Arcus T :Production variant with self-sustaining capabilities, using the Solo 2350 engine. ;Arcus M :Production variant with self-launching capabilities, using the Solo 2625-02i The Solo 2625 is a series of German aircraft engines, designed and produced by Solo Vertriebs- und Entwicklungs GmbH of Fellbach for use in ultralight aircraft, self-launching sailplanes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Gliders
This is a list of gliders/sailplanes of the world, (this reference lists all gliders with references, where available) Note: Any aircraft can glide for a short time, but gliders are designed to glide for longer. By nationality *List of American gliders *List of Argentine gliders * List of Australian gliders *List of Austrian gliders *List of Belgian gliders *List of Brazilian gliders *List of British gliders * List of Bulgarian gliders *List of Canadian gliders *List of Chinese gliders *List of Czechoslovak gliders *List of Danish gliders *List of Dutch gliders * List of Estonian gliders *List of Finnish gliders *List of French gliders *List of German gliders *List of Greek gliders *List of Hungarian gliders *List of Indian gliders *List of Iranian gliders *List of Irish gliders *List of Italian gliders *List of Japanese gliders *List of Latvian gliders *List of Lithuanian gliders *List of New Zealand gliders *List of Philippines gliders *List of Polish gliders *List of Portugu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
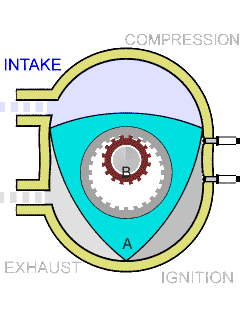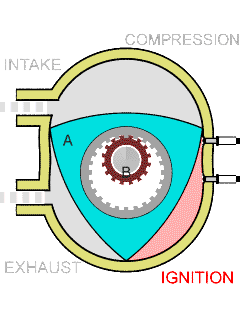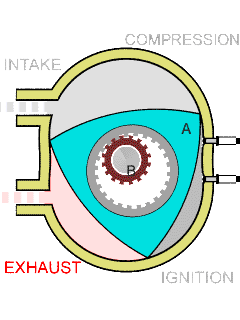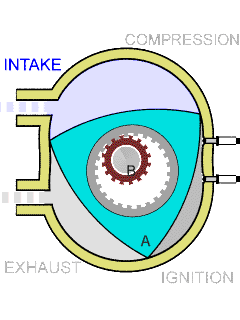
Wankel Engine
The Wankel engine (, ) is a type of internal combustion engine using an Eccentric (mechanism), eccentric rotary combustion engine, rotary design to convert pressure into rotating motion. It was invented by German engineer Felix Wankel, and designed by German engineer Hanns-Dieter Paschke. The Wankel engine's rotor, which creates the turning motion, is similar in shape to a Reuleaux triangle, with the sides having less curvature. The rotor rotates inside an oval-like epitrochoidal housing, around a central output shaft. The rotor spins in a hula-hoop fashion around the central output shaft, spinning the shaft via toothed gearing. Due to its inherent poor thermodynamics, the Wankel engine has a significantly worse thermal efficiency and worse exhaust gas behaviour when compared against the Otto engine or the Diesel engine, which is why the Wankel engine has seen limited use since its introduction in the 1960s. However, its advantages of compact design, smoothness, lower weight and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austro Engine
Austro Engine is an Austrian manufacturer of aircraft engines based at Wiener Neustadt in Lower Austria. History The production site and headquarters was built in 2007 with an investment of EUR 13 Million. The company was founded by Diamond Aircraft Industries and partners. The products are reciprocating engines and Wankel engines. The Wankel aero-engines are developed from the MidWest AE series engines developed at Staverton by MidWest, a UK firm that was bought by Diamond. Products Austro Engine E4 (AE 300) Reciprocating four-cylinder, four-stroke diesel aircraft engine, marketed as the AE 300, it produces 170 hp (127 kW). Certified through the European Aviation Safety Agency EASA on January 28, 2009 and through the FAA on July 29, 2009. The E4 is installed on various types of Diamond Aircraft Industries aircraft. Austro Engine AE 330 Derived from the AE300, the AE 330 produces an increased 180hp (132kW) of power. Two AE330s are used to power the Diamond DA62. AE50R Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft/page Content
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)