|
Scheunenviertel
(''German'': "Barn Quarter") is a neighborhood of Mitte in the centre of Berlin. It is situated to the north of the medieval Altberlin area, east of the ''Rosenthaler Straße'' and '' Hackescher Markt''. Until the Second World War it was regarded as a slum district and had a substantial Jewish population with a high proportion of migrants from Eastern Europe. History The name derives from several barns erected here outside the city walls in 1672 by order of Elector Frederick William of Brandenburg. The barns were used to store hay for use at a large cattle market at nearby Alexanderplatz. In 1737 King Frederick William I of Prussia required Berlin Jews to settle here. Prior to World War I, the Berlin City Council (''Magistrat'') redeveloped parts of the area. Since then the core of the neighborhood is the triangular Rosa-Luxemburg-Platz, former ''Bülowplatz'', where on 9 August 1931 the Communist and later Stasi Executive Erich Mielke shot two police officers. Mielke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spandauer Vorstadt
Spandauer Vorstadt ("Spandauer suburb", formerly also called Spandauer Quarter or Spandauer Viertel) is a historic district in what is now the Mitte district of Berlin. Geography The Spandauer neighborhood is bordered in the south by the Spree and the Stadtbahn viaduct, in the east by Karl Liebknecht St. and the adjacent neighborhoods of Königsstadt to the north, Torstrasse and Rosenthaler and Oranienburger to the east and Friedrichstrasse and Friedrich Wilhelm City to the south. Spandauer is connected to Dorotheenstadt via the Weidendammer Bridge, the Ebert Bridge and the Monbijou Bridge. History Namesake The neighborhood takes its name from the adjacent Spandauer Gate (Spandauer Tor) a relic from Berlin's history as a historic walled city. The eastern part of Spandauer along Rosenthaler St. is also known as the Scheunenviertel; a name that is often erroneously extended to streets to the west of it because of the shtetl located there around 1900, especially Oranie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Synagogue (Berlin)
The New Synagogue (german: Neue Synagoge) on Oranienburger Straße in Berlin is a mid-19th century synagogue built as the main place of worship for Berlin's Jewish community, succeeding the Old Synagogue which the community outgrew. Because of its eastern Moorish style and resemblance to the Alhambra, the New Synagogue is an important architectural monument in Germany. The building was designed by Eduard Knoblauch. Following Knoblauch's death in 1865, Friedrich August Stüler took responsibility for the majority of its construction as well as for its interior arrangement and design. It was inaugurated in the presence of Count Otto von Bismarck, then Minister President of Prussia, in 1866. One of the few synagogues to survive Kristallnacht, it was badly damaged prior to and during World War II and subsequently much was demolished; the present building on the site is a reconstruction of the ruined street frontage with its entrance, dome and towers, and only a few rooms behi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexanderplatz
() ( en, Alexander Square) is a large public square and transport hub in the central Mitte district of Berlin. The square is named after the Russian Tsar Alexander I, which also denotes the larger neighbourhood stretching from in the north-east to and the in the south-west. is reputedly the most visited area of Berlin, beating Friedrichstrasse and City West. It is a popular starting point for tourists, with many attractions including the (TV tower), the Nikolai Quarter and the ('Red City Hall') situated nearby. is still one of Berlin's major commercial areas, housing various shopping malls, department stores and other large retail locations. History Early history to the 18th century A hospital stood at the location of present-day since the 13th century. Named (St. George), the hospital gave its name to the nearby (George Gate) of the Berlin city wall. Outside the city walls, this area was largely undeveloped until around 1400, when the first settlers be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
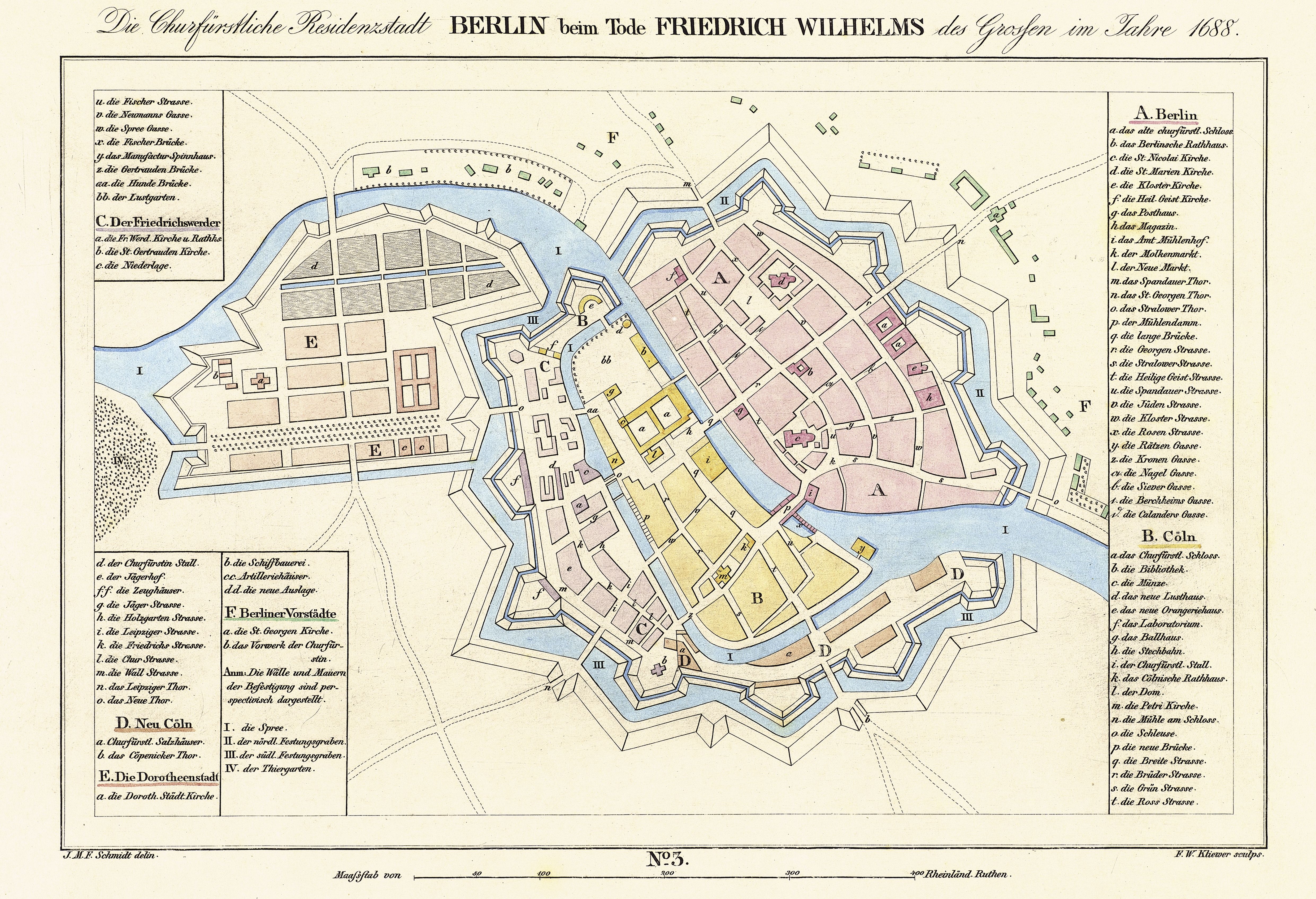
Altberlin
Alt-Berlin ("Old Berlin"), also spelled ''Altberlin'', is a neighborhood (''Stadtviertel''), situated in the Berliner locality (''Ortsteil'') of Mitte, part of the homonymous borough. In the 13th century it was the sister town of the old Cölln, located on the northern Spree Island in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. It counts in its territory the zone of Nikolaiviertel. History First mentioned in 1244, 7 years after Cölln, it represents the original core of the modern Berlin. The first stone fortification was built, to defend both cities, in 1250 and in 1251 it gained city rights. In 1280 Berlin, gained the right to mint currency. In that period it appeared on a coat of arms for the first time, close to the symbol of the imperial eagle, two stylized bears, antecedents of the bear currently serving as the symbol of the city. On 20 March 1307 the town was united with Cölln (maintaining its name, Berlin) forming a trading union on political and security matters, and parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volksbühne
The Volksbühne ("People's Theatre") is a theater in Berlin. Located in Berlin's city center Mitte on Rosa-Luxemburg-Platz (Rosa Luxemburg Square) in what was the GDR's capital. It has been called Berlin's most iconic theatre. About The Volksbühne was built during the years 1913 to 1914 and was designed by Oskar Kaufmann, with integrated sculpture by Franz Metzner. It opened on December 30, 1914 and has its origin in an organization known as the "Freie Volksbühne" ("Free People's Theater") founded in 1890 by Bruno Wille and Wilhelm Bölsche, which sketched out the vision for a theater "of the people" in 1892. The goal of the organization was to promote the naturalist plays of the day at prices accessible to the common worker. The original slogan inscribed on the edifice was "Die Kunst dem Volke" ("Art to the people"). During World War II, the theatre was heavily damaged like much of the rest of Berlin. From 1950 to 1954, it was rebuilt according to the design of archite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oskar Kaufmann
Oskar Kaufmann (2 February 1873 – 8 September 1956) was a Hungarian architect. He was an expert in construction and design and was active in Berlin beginning in 1900. Among his best-known works are the Krolloper, the Hebbel Theater and the , all in Berlin, the in Vienna, and the Habima Theater in Tel Aviv. Youth and Education Kaufmann was born in Újszentanna/Neu Sankt Anna (today Sântana), near Arad, Romania), the son of a wealthy and prestigious Jewish family in Hungary. After completing the Abitur, he began to study architecture at a university in Budapest. This created tension with his parents, who wished him to become a pianist. The tension was so great that Kaufmann's parents refused to support him financially, so that he had to leave Hungary and continue his education in Germany, at the ''Großherzogliche Technische Hochschule'' (English: Grand Ducal Technical College) in Karlsruhe. Ironically, he supported himself by working as a pianist. This placed him in conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Metzner
Franz Metzner (18 November 1870, Wscherau, near Plzeň – 24 March 1919, Berlin) was an influential German sculptor, particularly his sculptural figures integrated into the architecture of Central European public buildings in the Art Nouveau / Jugendstil / Vienna Secession period. His style is difficult to classify. Biography Metzer learned the craft of stone-cutting in Breslau with Christian Behrens and did apprenticeships in Saxony through 1894. He founded his own studio in Berlin in 1896 and worked predominantly for the royal porcelain factory until 1903, and became a professor at the Vienna college of arts and sciences. Metzner achieved fame by winning a gold medal at the Paris Exposition Universelle (1900). Among his important works are the sculptures for Josef Hoffmann's 1904–1911 landmark Vienna Secession Palais Stoclet in Brussels, including the eccentric four green male nudes at the summit of the building. The Palais Stoclet is an example of "Gesamtkunstwerk", t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl-Liebknecht-Haus
The Karl-Liebknecht-Haus or ''Karl Liebknecht House'' is the headquarters of the party '' The Left'' in Germany. It is located between the Alexanderplatz and Rosa-Luxemburg-Platz in Berlin-Mitte. Constructed in 1912 as a factory, the building was purchased by the Communist Party of Germany (''Kommunistische Partei Deutschlands'', KPD) in 1926. It became the seat of its Central Committee and was named in honor of Karl Liebknecht, the KPD leader who was murdered by a paramilitary unit in January 1919. After Adolf Hitler was appointed as German chancellor, the Berlin police raided the headquarters, and by March 1, the Nazi swastika flag was flying over the building. Renamed the Horst Wessel House, the building at first served as a district police station and detention center in which Jews and political opponents were tortured. In 1935, the finance department of the state of Prussia moved into the building. Severely damaged during World War II, the building was repaired in 1948, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communist Party Of Germany
The Communist Party of Germany (german: Kommunistische Partei Deutschlands, , KPD ) was a major political party in the Weimar Republic between 1918 and 1933, an underground resistance movement in Nazi Germany, and a minor party in West Germany in the postwar period until it was banned by the Federal Constitutional Court in 1956. Founded in the aftermath of the First World War by socialists who had opposed the war, the party joined the Spartacist uprising of January 1919, which sought to establish a soviet republic in Germany. After the defeat of the uprising, and the murder of KPD leaders Rosa Luxemburg, Karl Liebknecht and Leo Jogiches, the party temporarily steered a more moderate, parliamentarian course under the leadership of Paul Levi. During the Weimar Republic period, the KPD usually polled between 10 and 15 percent of the vote and was represented in the national and in state parliaments. Under the leadership of Ernst Thälmann from 1925 the party became thorou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Poelzig
Hans Poelzig (30 April 1869 – 14 June 1936) was a German architect, painter and set designer. Life Poelzig was born in Berlin in 1869 to Countess Clara Henrietta Maria Poelzig while she was married to George Acland Ames, an Englishman. Uncertain of his paternity, Ames refused to acknowledge Hans as his son and consequently he was brought up by a local choirmaster and his wife. In 1899 he married Maria Voss with whom he had four children.Dawson, p.96 His mother was the daughter of Alexander von Hanstein, Count of Pölzig and Beiersdorf who married Princess Louise of Saxe-Gotha-Altenburg in 1826. Because of this, Clara was the step-sister to Albert, Prince Consort making Hans a step-cousin to Albert's children. Education In 1903 he became a teacher and director at the Breslau Academy of Art and Design (german: Kunst- und Gewerbeschule Breslau; today in Wrocław, Poland). From 1920–1935 he taught at the Technical University of Berlin (). Career After finishing his architect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |