|
Schander
Carl Fredrik Christoffer Schander (21 May 1960 – 21 February 2012) was a professor in marine biology at the University of Bergen, Norway. He was also a thematic leader at the Centre of Excellence in Geobiology. His doctoral thesis (1997, University of Gothenburg, Sweden) explored the evolutionary relationships of the parasitic marine gastropod family Pyramidellidae. He worked on marine invertebrates, mainly molluscs, and published more than 90 scientific papers in peer-reviewed journals, 76 are indexed in the Web of Knowledge, and fourteen of them have been cited ten or more times. According to his web page, he considered the goal of his research to be understanding the roles that evolutionary forces and phylogeny have played in creating organismal diversity. To help develop this understanding, he used phylogenetic analyses that integrated morphological, ultrastructural and molecular data. His research focused on molluscs and more specifically on the ectoparasitic pyramidelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramidellidae
Pyramidellidae, common name the pyram family, or pyramid shells, is a voluminous taxonomic family of mostly small and minute ectoparasitic sea snails, marine heterobranch gastropod molluscs. The great majority of species of pyrams are micromolluscs. The pyram family is distributed worldwide with more than 6,000 named species in more than 350 nominal genera and subgenera. This family of micromollusks has been little studied and the phylogenetic relationships within the family are not well worked out. There is an absence of a general consensus regarding which species belong to a specific genus or subgenus, contributing to much confusion. Schander (1999) names more than 300 supraspecific names. As there has been no serious generic revision of the genera worldwide, generic polyphyly can be expected to be rampant throughout the family. However, the family itself is deemed monophyletic. However a study in 2011 seems to indicate that this family is deeply nested within the Pulmonata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molluscs
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine biology, marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater mollusc, freshwater and Terrestrial molluscs, terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic class (biology), classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurobiology, neurologically advanced of all inve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aplacophora
Aplacophora is a presumably paraphyletic taxon. This is a class of small, deep-water, exclusively benthic, marine molluscs found in all oceans of the world. MolluscaBase eds. (2021). MolluscaBase. Aplacophora. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=411 on 2021-04-13 All known modern forms are shell-less: only some extinct primitive forms possessed valves. The group comprises the two clades Solenogastres (Neomeniomorpha) and Caudofoveata (Chaetodermomorpha), which between them contain 28 families and about 320 species. The aplacophorans are traditionally considered ancestral to the other mollusc classes. However, the relationship between the two aplacophoran groups and to the other molluscan classes and to each other is as yet unclear. Aplacophorans are cylindrical and worm-like in form, and most very small, being no longer than ; some species, however, can reach a length of . Habitat Caudofoveates generall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borås
Borås ( , , ) is a city (officially, a locality) and the seat of Borås Municipality, Västra Götaland County, Sweden. It had 66,273 inhabitants in 2010. Geography Borås is located at the point of two crossing railways, among them the railway between Gothenburg and Kalmar, and is often considered the Swedish city gaining the most from the nationwide railway system laid between 1870 and 1910. History The city of Borås received its privileges in 1621 by King Gustav II Adolf. The reason was to give local pedlars a legal place for vending their merchandise (and for the government the ability to collect taxes on this trade). The city developed soon after it was founded. After a century it had increased to over 2,000 inhabitants. Borås has been ravaged by fires four times: in 1681, 1727, 1822 and 1827. The Caroli church is the oldest of Borås's buildings, and has withstood all fires. In its 2017 report, Police in Sweden placed the Norrby, Hässleholmen and Hulta dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
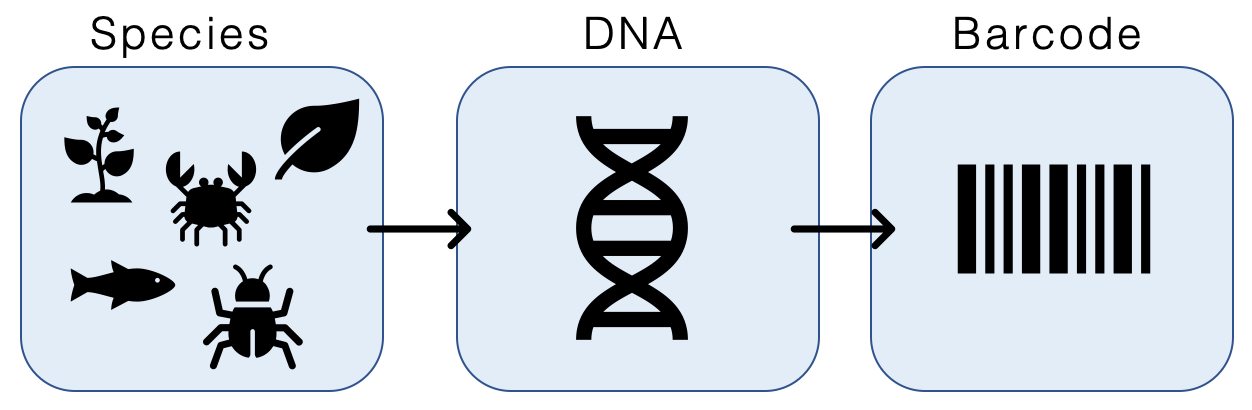
DNA Barcoding
DNA barcoding is a method of species identification using a short section of DNA from a specific gene or genes. The premise of DNA barcoding is that by comparison with a reference library of such DNA sections (also called "sequences"), an individual sequence can be used to uniquely identify an organism to species, just as a supermarket scanner uses the familiar black stripes of the UPC barcode to identify an item in its stock against its reference database. These "barcodes" are sometimes used in an effort to identify unknown species or parts of an organism, simply to catalog as many taxa as possible, or to compare with traditional taxonomy in an effort to determine species boundaries. Different gene regions are used to identify the different organismal groups using barcoding. The most commonly used barcode region for animals and some protists is a portion of the cytochrome ''c'' oxidase I (COI or COX1) gene, found in mitochondrial DNA. Other genes suitable for DNA barcoding ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Fiction Fandom
Science fiction fandom or SF fandom is a community or fandom of people interested in science fiction in contact with one another based upon that interest. SF fandom has a life of its own, but not much in the way of formal organization (although formal clubs such as the Futurians (1937–1945) and the Los Angeles Science Fantasy Society (1934–present) are recognized examples of organized fandom). Most often called simply "fandom" within the community, it can be viewed as a distinct subculture, with its own literature and jargon; marriages and other relationships among fans are common, as are multi-generational fan families. Origins and history Science fiction fandom started through the letter column of Hugo Gernsback's fiction magazines. Not only did fans write comments about the stories—they sent their addresses, and Gernsback published them. Soon, fans were writing letters directly to each other, and meeting in person when they lived close together, or when one of them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Fiction Fanzines
A science-fiction fanzine is an amateur or semi-professional magazine published by members of science-fiction fandom, from the 1930s to the present day. They were one of the earliest forms of fanzine, within one of which the term "''fanzine''" was coined, and at one time constituted the primary type of science-fictional fannish activity ("fanac"). Origins and history The first science-fiction fanzine, ''The Comet'', was published in 1930 by the Science Correspondence Club in Chicago. The term "fanzine" was coined by Russ Chauvenet in the October 1940 issue of his fanzine ''Detours''. in "Science Fiction Citations" for the Oxford English Dictionary "Fanzines" were distinguished from "prozines", that is, all professional s. Prior to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amateur Press Association
An amateur press association (APA) is a group of people who produce individual pages or zines that are sent to a Central Mailer for collation and distribution to all members of the group. History The first APAs were formed by groups of amateur printers. The earliest to become more than a small informal group of friends was the National Amateur Press Association (NAPA) founded February 19, 1876, by Evan Reed Riale and nine other members in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It is still running as of 2018. The first British APA was the British Amateur Press Association founded in 1890. This is a different organisation from that launched by comics fans in 1978 (see below). The second United States APA was the United Amateur Press Association (UAPA) founded in 1895 by a group of teenagers including William H. Greenfield (aged 14) and Charles W. Heins (aged 17). This became a confederation of small amateur publishers which split into two organisations known interchangeably as UAP and UAAPA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Fiction Conventions
Science fiction conventions are gatherings of fans of the speculative fiction genre, science fiction. Historically, science fiction conventions had focused primarily on literature, but the purview of many extends to such other avenues of expression as films, television, comics, animation, and games. The format can vary but will tend to have a few similar features such as a guest of honour, discussion panels, readings and large special events such as opening/closing ceremonies and some form of party or entertainment. Science fiction conventions started off primarily in the UK and US but have now spread further and several countries have their own individual conventions as well as playing host to rotating international conventions. History The precise time and place of the first science fiction convention is a matter of some dispute. The idea and form was clearly anticipated in Robert Bloch's short story about a large convention of writers, "The Ultimate Ultimatum" (''Fanta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Biology
Marine biology is the scientific study of the biology of marine life, organisms in the sea. Given that in biology many phyla, families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy. A large proportion of all life on Earth lives in the ocean. The exact size of this ''large proportion'' is unknown, since many ocean species are still to be discovered. The ocean is a complex three-dimensional world covering approximately 71% of the Earth's surface. The habitats studied in marine biology include everything from the tiny layers of surface water in which organisms and abiotic items may be trapped in surface tension between the ocean and atmosphere, to the depths of the oceanic trenches, sometimes 10,000 meters or more beneath the surface of the ocean. Specific habitats include estuaries, coral reefs, kelp forests, seagrass meadows, the surrounds of seamounts and therm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxon (journal)
''Taxon'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering plant taxonomy. It is published by Wiley on behalf of the International Association for Plant Taxonomy, of which it is the official journal. It was established in 1952 and is the only place where nomenclature proposals and motions to amend the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (except for the rules concerning fungi) can be published. The editor-in-chief is Dirk C. Albach (University of Oldenburg). Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 2.817. References External links *{{Official website, https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |