|
Scania K IA
The Scania K series is a series of chassis in Scania's city bus and coach range with longitudinally, straight-up mounted engine at the rear, replacing the K- ( K94, K114, K124) and L-type ( L94) chassis of the 4 series. The K series was first presented on Busworld 2005 in Kortrijk, Belgium, and models were available from 2006. Type designation breakdown ;Plant at which the vehicle was assembled (integral buses only) * C: former Kapena plant, Slupsk, Poland (K UB, K UA) * L: Lahden Autokori plant, Lahti, Finland – Interlink and OmniExpress (K UB, K IB, K EB) * T: Higer plant, China – A30 and A808 Touring coaches (K EB chassis only) ;Engine location * K: chassis with centrally mounted longitudinal engine behind rearmost axle ;Power code Approximation of the power rating in hp to the nearest ten. The power code has spaces on both sides. ;Type of transport * E: coach, long distance, high comfort * I: intercity, short to long distance, normal comfort * U: urban, short dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australia Wide Coaches
Australia Wide Coaches is an Australian coach company operating charter services, an express service between Orange and Sydney and services in Central West New South Wales under contract to NSW TrainLink. History Australia Wide Coaches was founded by Richard Dawes and Phil Langley in 1993 in Dubbo."Australia Wide Coaches" ''Fleetline'' October 1993 page 218 In October 2009, the coach operations of Selwoods Coaches, Orange were purchased. Selwoods had been operating a service from Orange to Sydney since April 1989. Since June 1990, Selwoods had been operating services under contract to CountryLink from Lithgow to Orange, Grenfell and Parkes.Australia Wide Coaches Australian Bus Fleet Lists Both of these remain in operation today. In November 2013, Australia Wide Coaches commenced operating < ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZF Ecomat
The ZF Ecomat automotive transmission was specifically designed by ZF Friedrichshafen AG primarily for city-buses and motorcoaches. It has several generations – all of the automatic transmission type, and many variants. The latest variants use a lock-up torque converter along with a retarder. Some variants are listed below. Gear ratios Ecomat I (1980–1985) Gear ratios Ecomat I/II/IV (1985–2016) 1st generation — Ecomat (1980–2002) All generations of the Ecomat series are no longer in production. *4HP500 / 5HP500 / 6HP500 — four-, five- or six-speed; maximum input torque of 1100 Nm *4HP590 / 5HP590 / 6HP590 — four-, five- or six-speed; maximum input torque of 1250 Nm *4HP600 / 5HP600 / 6HP600 — four-, five- or six-speed; maximum input torque of 1400 Nm 2nd generation — Ecomat 2 (1997–2007) All generations of the Ecomat series are no longer in production. *4HP502/C / 5HP502/C / 6HP502/C — four-, five- or six-speed; maximum input torque of *4HP592/C / ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
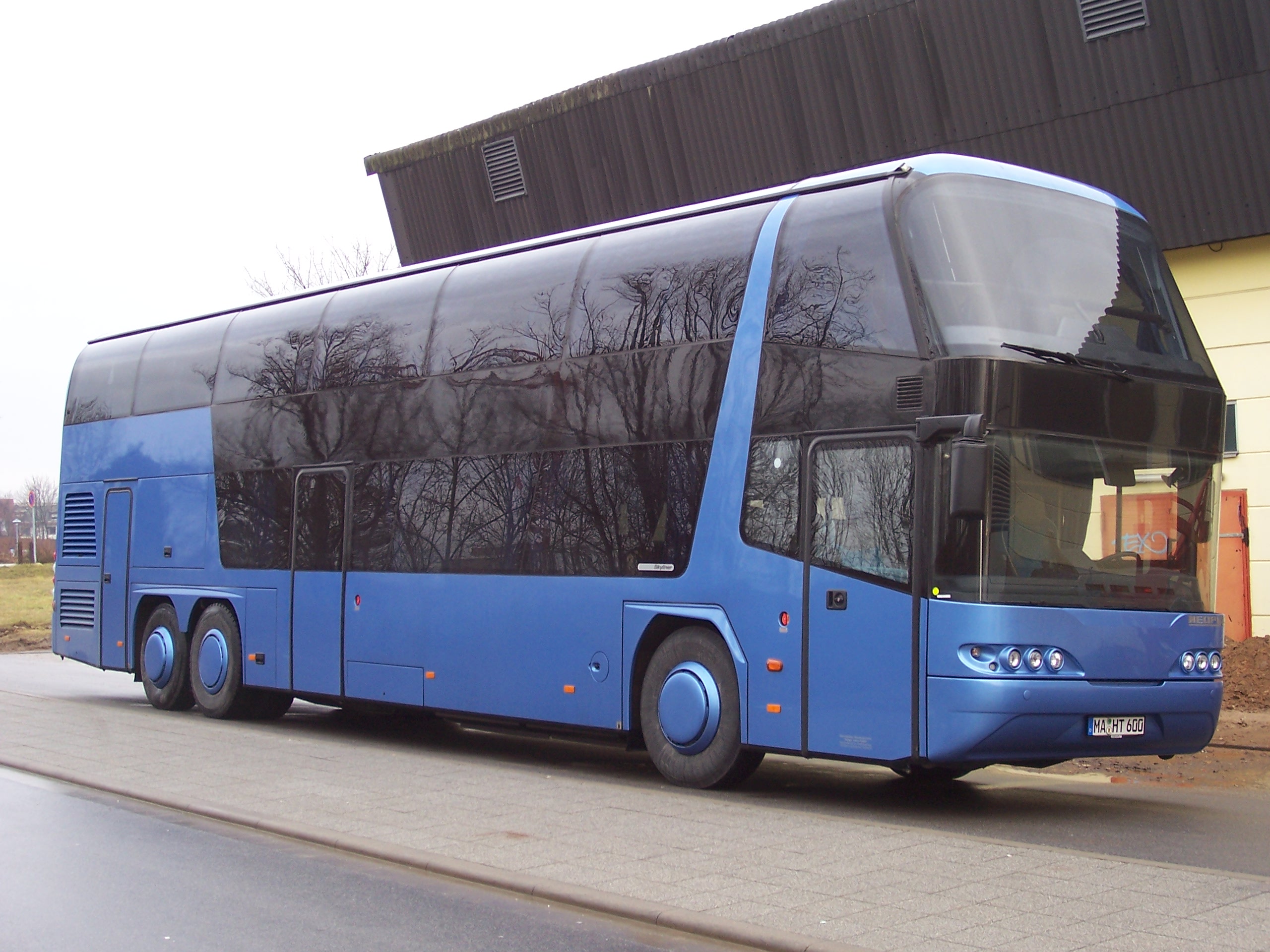
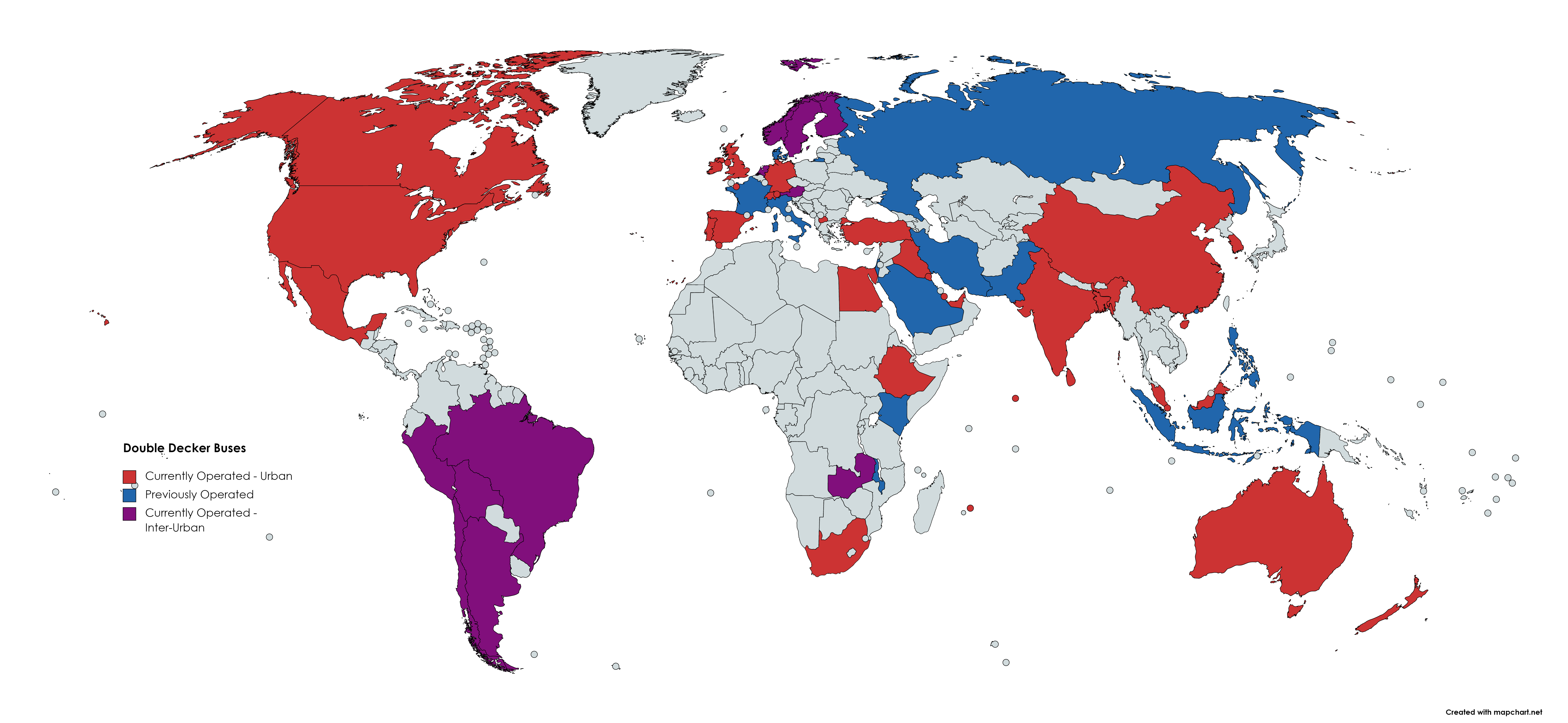
Double-decker Bus
A double-decker bus or double-deck bus is a bus that has two storeys or decks. They are used for mass transport in the United Kingdom, the United States, New Zealand, Europe, Asia and also in cities such as Sydney; the best-known example is the red London bus, namely the AEC Routemaster. Early double-deckers put the driver in a separate cab. Passenger access was via an open platform at the rear and a bus conductor collected fares. Modern double-deckers have a main entrance door at the front and the driver takes fares, thus halving the number of workers aboard, but slowing the boarding process. The rear open platform, popular with passengers, was abandoned for safety reasons, as there was a risk of passengers falling when running and jumping onto the bus. Double-deckers are primarily for commuter transport, but open-top models are used as sight-seeing buses for tourists. William Gladstone, speaking of London's double-deck horse-drawn omnibuses, once observed that "...the best w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin America
Latin America or * french: Amérique Latine, link=no * ht, Amerik Latin, link=no * pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived from Latin — are predominantly spoken. The term was coined in the nineteenth century, to refer to regions in the Americas that were ruled by the Spanish, Portuguese and French empires. The term does not have a precise definition, but it is "commonly used to describe South America, Central America, Mexico, and the islands of the Caribbean." In a narrow sense, it refers to Spanish America plus Brazil (Portuguese America). The term "Latin America" is broader than categories such as ''Hispanic America'', which specifically refers to Spanish-speaking countries; and ''Ibero-America'', which specifically refers to both Spanish and Portuguese-speaking countries while leaving French and British excolonies aside. The term ''Latin America'' was f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quad-axle Bus
A multi-axle bus is a bus or coach that has more than the conventional two axles (known as a twin-axle bus), usually three (known as a tri-axle bus), or more rarely, four (known as a quad-axle bus). Extra axles are usually added for legal weight restriction reasons, or to accommodate different vehicle designs such as articulation, or rarely, to implement trailer buses. History An early example of a multi-axle bus was a one-off three-axle Crossley Condor, showhere built for the 1932 Scottish Bus Show. Reasons for multiple axles Usually vehicle licensing authorities of different countries will set legal limits on the amount of weight that can be put on each axle. In the UK, a recent extension to the legal limit on the length of rigid buses and coaches has led to the increased use of three axles to accommodate the heavier chassis and passenger load. Certain countries apply exceptions to vehicle rules for specific operations. Extra axles may also be provided on shorter buses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kortrijk Xpo
Kortrijk Xpo is one of the biggest multi-purpose indoor arenas and convention centres in the BENELUX, covering some (2009).Nieuwbladarticle/ref> The complex is situated in the city of Kortrijk, Belgium and is home to some internationally renowned fairs, like the Kortrijk design fair ''Interieur'' and ''Busworld''. History The City of Kortrijk initiated the construction of the first exposition halls in 1966 in Kortrijk-South (Kortrijk-Zuid), close to the highway exit of the plannen E3, the current E17. The 'Kortrijk Halls' were officially inaugurated in April 1967. As a result of the more international approach of the exhibition centre, on 2 December 1999, the name was transformed into Kortrijk Xpo. Whereas the complex covered some of exposition space and of meeting space at the beginning, the complex was later enlarged to , to in 2005, and covers . This makes the complex one of the biggest fair centres in the BENELUX and even Europe. A new multipurpose hall, 'XXL', the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scania L94
The Scania 4-series low floor city bus and coach range was introduced by Scania in 1997 as a successor to the 3-series bus range. The 4-series bus range was first presented in September 1996, when the integral low-floor city bus OmniCity was revealed. Production of the chassis range started in second half of 1997, and by the end of 1998 all worldwide production facilities had changed from 3-series to 4-series. Unlike the 3-series, which was a range of 45 different chassis models, the 4-series is one basic chassis with different modular configurations depending on usage and customer needs. At launch there were a total of seven major configurations, presumably the F HB, K EB, K IB, L IB, L UB, N UA and N UB. These were later followed by the F HA, K UB, L IA, L UA and N UD. The first letter describing the position of the engine, and the last two letters describing areas of use. In marketing of the 4-series, Scania have g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scania K124
The Scania 4-series low floor city bus and coach range was introduced by Scania in 1997 as a successor to the 3-series bus range. The 4-series bus range was first presented in September 1996, when the integral low-floor city bus OmniCity was revealed. Production of the chassis range started in second half of 1997, and by the end of 1998 all worldwide production facilities had changed from 3-series to 4-series. Unlike the 3-series, which was a range of 45 different chassis models, the 4-series is one basic chassis with different modular configurations depending on usage and customer needs. At launch there were a total of seven major configurations, presumably the F HB, K EB, K IB, L IB, L UB, N UA and N UB. These were later followed by the F HA, K UB, L IA, L UA and N UD. The first letter describing the position of the engine, and the last two letters describing areas of use. In marketing of the 4-series, Scania have g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scania K114
The Scania 4-series Low-floor bus, low floor city bus and coach (bus), coach range was introduced by Scania AB, Scania in 1997 as a successor to the Scania 3-series (bus), 3-series bus range. The 4-series bus range was first presented in September 1996, when the integral Low-floor bus, low-floor city bus Scania OmniCity, OmniCity was revealed. Production of the chassis range started in second half of 1997, and by the end of 1998 all worldwide production facilities had changed from 3-series to 4-series. Unlike the 3-series, which was a range of 45 different chassis models, the 4-series is one basic chassis with different modular configurations depending on usage and customer needs. At launch there were a total of seven major configurations, presumably the F HB, K EB, K IB, L IB, L UB, N UA and N UB. These were later followed by the F HA, K UB, L IA, L UA and N UD. The first letter describing the position of the engine, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scania K94
The Scania 4-series low floor city bus and coach range was introduced by Scania in 1997 as a successor to the 3-series bus range. The 4-series bus range was first presented in September 1996, when the integral low-floor city bus OmniCity was revealed. Production of the chassis range started in second half of 1997, and by the end of 1998 all worldwide production facilities had changed from 3-series to 4-series. Unlike the 3-series, which was a range of 45 different chassis models, the 4-series is one basic chassis with different modular configurations depending on usage and customer needs. At launch there were a total of seven major configurations, presumably the F HB, K EB, K IB, L IB, L UB, N UA and N UB. These were later followed by the F HA, K UB, L IA, L UA and N UD. The first letter describing the position of the engine, and the last two letters describing areas of use. In marketing of the 4-series, Scania have g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longitudinal Engine
In automotive engineering, a longitudinal engine is an internal combustion engine in which the crankshaft is oriented along the long axis of the vehicle, front to back. Use This type of motor is usually used for rear-wheel drive cars, except for some Audi and SAAB models equipped with longitudinal engines in front wheel drive. In front-wheel drive cars a transverse engine is usually used. Trucks often have longitudinal engines with rear-wheel drive. For motorcycles, the use of a particular type depends on the drive: in case of a chain or belt drive a transverse engine is usually used, and with shaft drives a longitudinal engine. Longitudinal engines in motorcycles do have one disadvantage: the "tipping point" of the crankshaft tilts along the entire motorcycle to a greater or lesser degree when accelerating. This is partly resolved by having other components, such as the generator and the gearbox, rotate in the opposite direction to the crankshaft. Most larger, "premium" ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coach (bus)
A coach (or coach bus/motorcoach) is a type of bus built for longer-distance service, in contrast to transit buses that are typically used within a single metropolitan region. Often used for touring, intercity, and international bus service, coaches are also used for private charter for various purposes. Coaches are also related and fall under a specific category/type of RVs. Deriving the name from horse-drawn carriages and stagecoaches that carried passengers, luggage, and mail, modern motor coaches are almost always high-floor buses, with separate luggage hold mounted below the passenger compartment. In contrast to transit buses, motor coaches typically feature forward-facing seating, with no provision for standing. Other accommodations may include onboard restrooms, televisions, and overhead luggage space. History Background Horse-drawn chariots and carriages ("coaches") were used by the wealthy and powerful where the roads were of a high enough standard from p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
