|
Scalloway Museum
Scalloway ( non, Skálavágr, "bay with the large house(s)") is the largest settlement on the west coast of the Mainland, the largest island of the Shetland Islands, Scotland. The village had a population of roughly 900, at the 2011 census. Now a fishing port, until 1708 it was the capital of the Shetland Islands (now Lerwick, on the east coast of the Shetland Mainland). It contains one of the two castles built in Shetland; this one was constructed in 1600. Scalloway is the location of the North Atlantic Fisheries College (part of the University of the Highlands and Islands), which offers courses and supports research programmes in fisheries sciences, aquaculture, marine engineering and coastal management. It is also home to the Centre for Nordic Studies. NAFC Marine Centre at Ness of Westshore offers courses in "nautical studies, marine science and technology, and seafood quality". Nearby are the Scalloway Islands, which derive their name from the village. The village has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
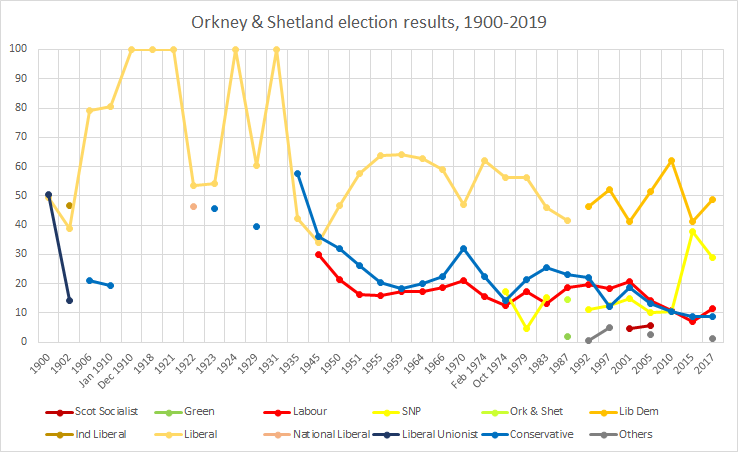
Orkney And Shetland (UK Parliament Constituency)
Orkney and Shetland is a constituency of the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It elects one Member of Parliament (MP) by the first past the post system of election. In the Scottish Parliament, Orkney and Shetland are separate constituencies. The constituency was historically known as Orkney and Zetland (an alternative name for Shetland). In the 2014 Scottish independence referendum, 65.4% of the constituency's electors voted for Scotland to stay part of the United Kingdom. Creation The British parliamentary constituency was created in 1708 following the Acts of Union, 1707 and replaced the former Parliament of Scotland shire constituency of Orkney & Zetland. Boundaries The constituency is made up of the two northernmost island groups of Scotland, Orkney and Shetland. A constituency of this name has existed continuously since 1708. However, before 1918 the town of Kirkwall (the capital of Orkney) formed part of the Northern Burghs constituency. It i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
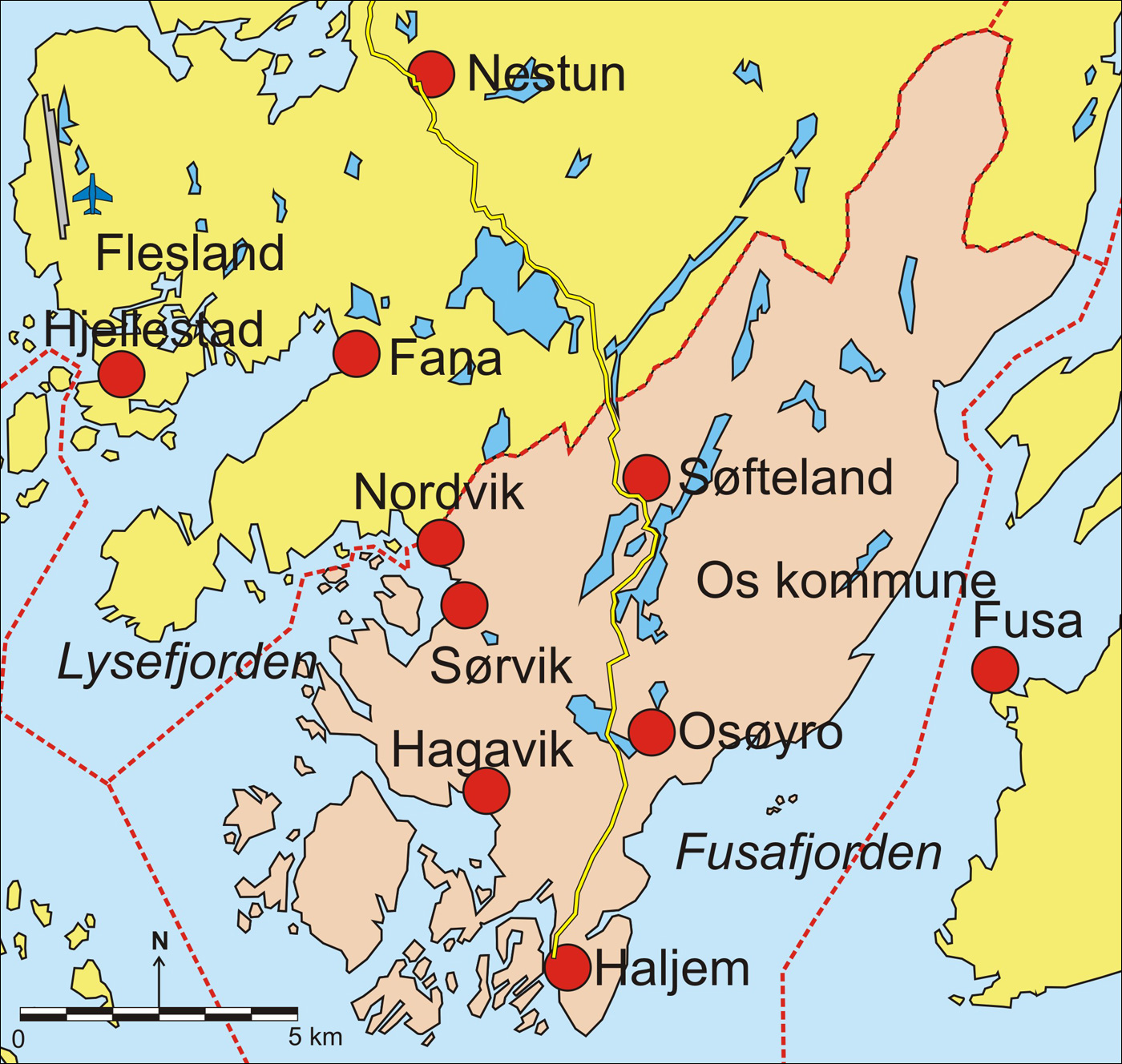
Os, Hordaland
Os is a former municipality in the old Hordaland county, Norway. It was located in the Midhordland region, just south of Norway's second-largest city, Bergen. Due to its proximity to Bergen, Os experienced strong population growth. The administrative centre (and commercial centre) of Os was the village of Osøyro. It is the largest settlement in the municipality, with over 60% of the municipal residents living here. Other large villages in Os included Hagavik, Halhjem, Søfteland, Søre Øyane, and Søvik. On 1 January 2020, the municipality became part of Bjørnafjorden Municipality in Vestland county. Prior to its dissolution in 2020, the municipality is the 360th largest by area out of the 422 municipalities in Norway. Os is the 57th most populous municipality in Norway with a population of 20,152. The municipality's population density is and its population has increased by 29.2% over the last decade. History The parish of Os was established as a formannskapsdistrikt, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Armine Howarth
David Armine Howarth (28 July 1912 – 2 July 1991) was a British naval officer, boatbuilder, historian and author. Biography After graduating from the University of Cambridge, he became a war correspondent for BBC radio at the start of World War II. Howarth joined the Navy after the fall of France. He served in the Special Operations Executive (SOE) and helped set up the Shetland Bus, an SOE operation manned by Norwegians running a clandestine route between Shetland and Norway. He was second in command at the Naval base in Shetland. For his contributions to espionage operations against the German occupation of Norway, he received King Haakon VII's Cross of Liberty.Simenstad, Arne: ''Norwegian War Decorations Awarded to Members of the British Armed Forces 1940–1945'', London: The London Stamp Exchange, 1990, p. 41. The King also made Howarth a Chevalier First Class of the Order of St Olav. After the war, he wrote numerous books on naval and military history, including a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalloway Museum
Scalloway ( non, Skálavágr, "bay with the large house(s)") is the largest settlement on the west coast of the Mainland, the largest island of the Shetland Islands, Scotland. The village had a population of roughly 900, at the 2011 census. Now a fishing port, until 1708 it was the capital of the Shetland Islands (now Lerwick, on the east coast of the Shetland Mainland). It contains one of the two castles built in Shetland; this one was constructed in 1600. Scalloway is the location of the North Atlantic Fisheries College (part of the University of the Highlands and Islands), which offers courses and supports research programmes in fisheries sciences, aquaculture, marine engineering and coastal management. It is also home to the Centre for Nordic Studies. NAFC Marine Centre at Ness of Westshore offers courses in "nautical studies, marine science and technology, and seafood quality". Nearby are the Scalloway Islands, which derive their name from the village. The village has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
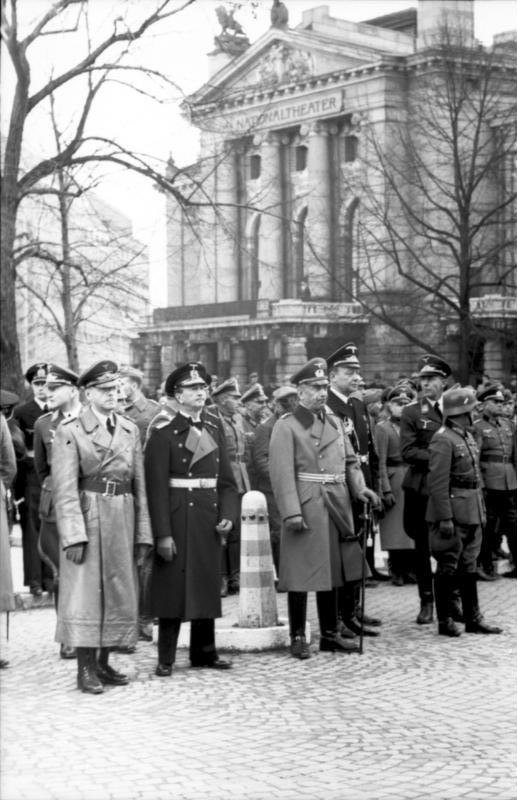
Occupation Of Norway By Nazi Germany
The occupation of Norway by Nazi Germany during the Second World War began on 9 April 1940 after Operation Weserübung. Conventional armed resistance to the German invasion ended on 10 June 1940, and Nazi Germany controlled Norway until the capitulation of German forces in Europe on 8 May 1945. Throughout this period, a pro-German government named Den nasjonale regjering (English: the National Government) ruled Norway, while the Norwegian king Haakon VII and the prewar government escaped to London, where they formed a government in exile. Civil rule was effectively assumed by the ''Reichskommissariat Norwegen'' (Reich Commissariat of Norway), which acted in collaboration with the pro-German puppet government. This period of military occupation is, in Norway, referred to as the "war years", "occupation period" or simply "the war". Background Having maintained its neutrality during the First World War (1914–1918), Norwegian foreign and military policy since 1933 was largely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
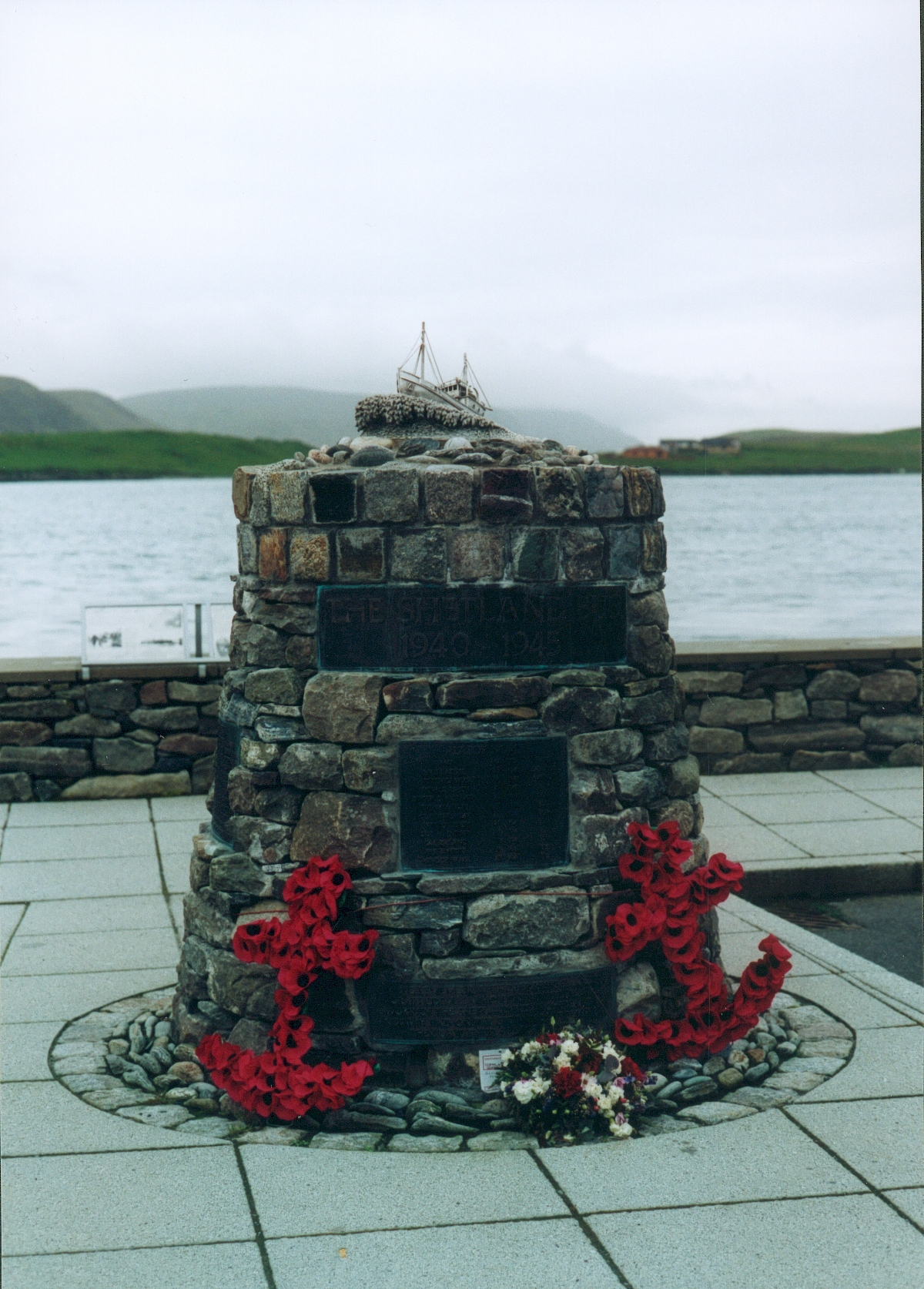
Shetland Bus
The Shetland Bus (Norwegian Bokmål: ''Shetlandsbussene'', def. pl.) was the nickname of a clandestine special operations group that made a permanent link between Mainland Shetland in Scotland and German-occupied Norway from 1941 until the surrender of Nazi Germany on 8 May 1945. From mid-1942, the group's official name was the Norwegian Naval Independent Unit (NNIU). In October 1943, it became an official part of the Royal Norwegian Navy and was renamed the Royal Norwegian Naval Special Unit (RNNSU). The unit was operated initially by a large number of small fishing boats and later augmented by three fast and well-armed submarine chasers – , and . Crossings were mostly made during the winter under the cover of darkness. This meant the crews and passengers had to endure very heavy North Sea conditions, with no lights and constant risk of discovery by German aircraft or patrol boats. There was also the possibility of being captured whilst carrying out the mission on the Norw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallow Hill
Gallow Hill is one of the hills of the Sidlaw range in South East Perthshire, Scotland. At . Gallow Hill is located near Newbigging and is smaller than Craigowl Hill Craigowl Hill is a summit towards the eastern end of the Sidlaw Hills in Angus, Scotland. Northeast of Kirkton of Auchterhouse and approximately eight kilometres north of Dundee, Craigowl Hill represents the highest point in the range. It also .... References Mountains and hills of Angus, Scotland {{Angus-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hillswick
Hillswick is a small village in Northmavine, on the shore of the Atlantic Ocean and lies to the north-north west of Mainland, Shetland, the most northerly group of islands in the United Kingdom. It is situated from Lerwick. There is a community shop, a blacksmith, a public hall, a health centre, and a Church of Scotland kirk that is now mainly used for funerals, weddings and christenings. There is a wildlife sanctuary, situated at the historic former Hanseatic trading booth on the seafront, a small private art gallery with occasional public exhibitions, and the St Magnus Bay Hotel which offers accommodation, bar and restaurant services. A large dairy and sheep farm takes up the spectacular peninsula called Hillswick Ness, but there is public access and a signed walking route. There is a modern primary school at nearby Urafirth. A small automatic lighthouse is located 1.5 miles south of Hillswick, at the tip of the Ness. See also * List of lighthouses in Scotland * List of Norther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s), Hamburgian(s) , timezone1 = Central (CET) , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = Central (CEST) , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = Postal code(s) , postal_code = 20001–21149, 22001–22769 , area_code_type = Area code(s) , area_code = 040 , registration_plate = , blank_name_sec1 = GRP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €123 billion (2019) , blank1_name_sec1 = GRP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 = €67,000 (2019) , blank1_name_sec2 = HDI (2018) , blank1_info_sec2 = 0.976 · 1st of 16 , iso_code = DE-HH , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 = DE6 , website = , footnotes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
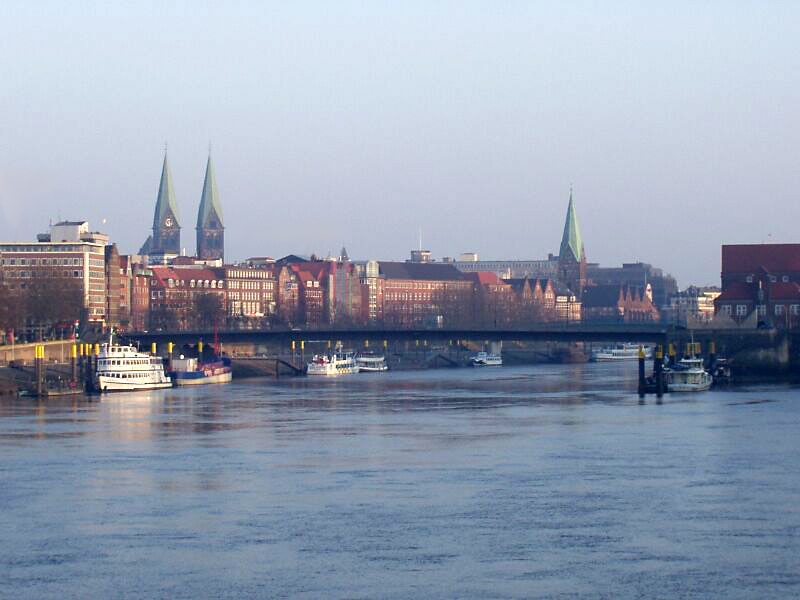
Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consisting of the cities of Bremen and Bremerhaven. With about 570,000 inhabitants, the Hanseatic city is the 11th largest city of Germany and the second largest city in Northern Germany after Hamburg. Bremen is the largest city on the River Weser, the longest river flowing entirely in Germany, lying some upstream from its mouth into the North Sea, and is surrounded by the state of Lower Saxony. A commercial and industrial city, Bremen is, together with Oldenburg and Bremerhaven, part of the Bremen/Oldenburg Metropolitan Region, with 2.5 million people. Bremen is contiguous with the Lower Saxon towns of Delmenhorst, Stuhr, Achim, Weyhe, Schwanewede and Lilienthal. There is an exclave of Bremen in Bremerhaven, the "Citybremian Overseas Port ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German towns in the late 12th century, the League ultimately encompassed nearly 200 settlements across seven modern-day countries; at its height between the 13th and 15th centuries, it stretched from the Netherlands in the west to Russia in the east, and from Estonia in the north to Kraków, Poland in the south. The League originated from various loose associations of German traders and towns formed to advance mutual commercial interests, such as protection against piracy and banditry. These arrangements gradually coalesced into the Hanseatic League, whose traders enjoyed duty-free treatment, protection, and diplomatic privileges in affiliated communities and their trade routes. Hanseatic Cities gradually developed a common legal system governing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |