|
Saʿumu
Saʿumu was a king (Lugal) of the second Mariote kingdom who reigned c. 2416–2400 BC. Some scholars, such as Joseph Martin Pagan, interpreted the king's name as derived from the root "ś-y-m", a cognate of the Akkadian word "šâmu-m", meaning "to buy". In a letter written by the later Mariote king Enna-Dagan, Saʿumu is attested launching a major attack on the Eblaites. The king's campaigns recorded in the letter were concentrated in the middle Euphrates valley east of Emar ) , image = View_from_the_Byzantine_Tower_at_Meskene,_ancient_Barbalissos.jpg , alt = , caption = View from the Byzantine Tower at Meskene, ancient Barbalissos , map_type = Syria , map_alt = , map_size = 200 ..., where he defeated the cities of Tibalat and Ilwani, leaving ruins in the mountainous area of Angai. Saʿumu continued his war defeating the cities of Ra'ak, Nirum, Ashaldu and Badul, leaving ruins in the borders of Nahal's region. See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Išhtup-Išar
Ishtup-Ishar (Ištup-Išar) was a king (Lugal) of the second Mariote kingdom who reigned c. 2400 BC. The king's name was traditionally read as Išhtup-šar, with šar being a common divine element in personal names attested in the region. However, the king's name is read as Ishtup-Ishar by Alfonso Archi, Ishar being an important justice deity worshiped in Mari and Ebla. In a letter written by the later Mariote king Enna-Dagan, Ishar is attested conquering and destroying the Eblaite cities of Lalanium and Emar ) , image = View_from_the_Byzantine_Tower_at_Meskene,_ancient_Barbalissos.jpg , alt = , caption = View from the Byzantine Tower at Meskene, ancient Barbalissos , map_type = Syria , map_alt = , map_size = 200 .... See also * Eblaite-Mariote war Citations 24th-century BC rulers Kings of Mari 24th-century BC people {{MEast-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ansud
Ansud (also read as Ianupu, Yanup, Anubu, Gansud, Anusu and Hanusum), was an early king (Lugal) of the second Mari, Syria#The second kingdom, Mariote kingdom who reigned c. 2423-2416 BC. Ansud is known for warring against the Eblaites from a letter written by the later Mariote king Enna-Dagan. Reign Identity It has been proposed that a bead (reference M. 4439) discovered at Mari, was sent as a gift by Mesannepada of Ur to king "Hanusum" (Gansud) of Mari. This has now been corrected with new translations only giving Mesannepada as son of Meskalamdug:Description with photograph: It is unclear how this bead came to be in Mari, but this points to some kind of relation between Ur and Mari at that time. The bead was discovered in a jar containing other objects from Ur or Kish. The letter of Enna-Dagan is extremely difficult to read, and the word "Sa'umu" appeared in three passages of it. In the second and third passages, the word referred to Ansud's successor Sa'umu. However, in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
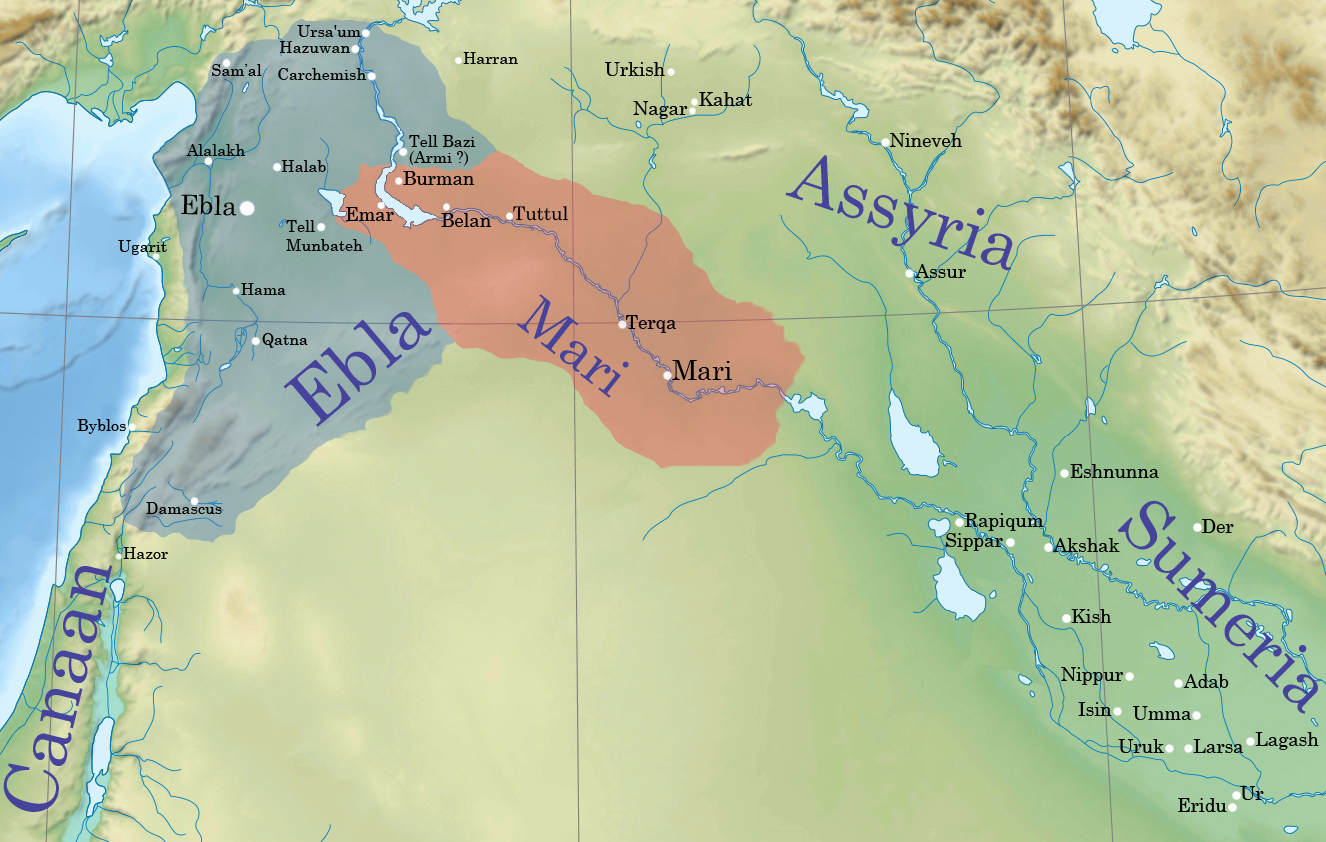
Mari, Syria
Mari (Cuneiform: , ''ma-riki'', modern Tell Hariri; ar, تل حريري) was an ancient Semitic city-state in modern-day Syria. Its remains form a tell 11 kilometers north-west of Abu Kamal on the Euphrates River western bank, some 120 kilometers southeast of Deir ez-Zor. It flourished as a trade center and hegemonic state between 2900 BC and 1759 BC. The city was purposely built in the middle of the Euphrates trade routes between Sumer in the south and the Eblaite kingdom and the Levant in the west. Mari was first abandoned in the middle of the 26th century BC but was rebuilt and became the capital of a hegemonic East Semitic state before 2500 BC. This second Mari engaged in a long war with its rival Ebla and is known for its strong affinity with Sumerian culture. It was destroyed in the 23rd century BC by the Akkadians, who allowed the city to be rebuilt and appointed a military governor (''Shakkanakku''). The governors became independent with the disint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebla
Ebla ( Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', ar, إبلا, modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center throughout the and in the first half of the Its discovery proved the Levant was a center of ancient, centralized civilization equal to Egypt and Mesopotamia and ruled out the view that the latter two were the only important centers in the Near East during the Early Bronze Age. The first Eblaite kingdom has been described as the first recorded world power. Starting as a small settlement in the Early Bronze Age ( ), Ebla developed into a trading empire and later into an expansionist power that imposed its hegemony over much of northern and eastern Syria. Ebla was destroyed during the It was then rebuilt and was mentioned in the records of the Third Dynasty of Ur. The second Ebla was a continuation of the first, ruled by a new royal d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Chronology
The chronology of the ancient Near East is a framework of dates for various events, rulers and dynasties. Historical inscriptions and texts customarily record events in terms of a succession of officials or rulers: "in the year X of king Y". Comparing many records pieces together a relative chronology relating dates in cities over a wide area. For the 3rd and 2nd millennia BC, this correlation is less certain but the following periods can be distinguished: *Early Bronze Age: Following the rise of cuneiform writing in the preceding Uruk period and Jemdet Nasr periods came a series of rulers and dynasties whose existence is based mostly on scant contemporary sources (e.g. En-me-barage-si), combined with archaeological cultures, some of which are considered problematic (e.g. Early Dynastic II). The lack of dendrochronology, astronomical correlations, and sparsity of modern, well-stratified sequences of radiocarbon dates from Southern Mesopotamia makes it difficult to assign abso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
25th-century BC Rulers
The 5th century is the time period from 401 ( CDI) through 500 ( D) ''Anno Domini'' (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar. The 5th century is noted for being a period of migration and political instability throughout Eurasia. It saw the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, which came to an end in 476 AD. This empire had been ruled by a succession of weak emperors, with the real political might being increasingly concentrated among military leaders. Internal instability allowed a Visigoth army to reach and ransack Rome in 410. Some recovery took place during the following decades, but the Western Empire received another serious blow when a second foreign group, the Vandals, occupied Carthage, capital of an extremely important province in Africa. Attempts to retake the province were interrupted by the invasion of the Huns under Attila. After Attila's defeat, both Eastern and Western empires joined forces for a final assault on Vandal North Africa, but this campaign was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweyhat
Tell es-Sweyhat is the name of a large archaeological site on the Euphrates River in northern Syria. It is located in Raqqa Governorate roughly 95 km northeast of Aleppo and 60 km south of Carchemish. Also, a Uruk site of Jebel Aruda and a Bronze Age site Tell Hadidi (Azu) are located just across the river. History Sweyhat dates from 3100–1900 BC, or the Early Bronze Age and the very beginning of the Middle Bronze Age. The site covers approximately 45 hectares and consists of a central, high mound standing 15 meters above the surrounding plain and an extensive low mound surrounded by the remains of an earthen rampart. The site is located within Mesopotamia in a very marginal environment for agriculture, yet in antiquity it was a prosperous city. The site was also occupied during the Hellenistic Period. Archaeology Sweyhat is best known for its intact fortifications of the mid-to-late 3rd millennium BC and its late-3rd-millennium temple located at the summit of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |