|
Sayf Al-Din Salar
Sayf al-Dīn Salār al-Manṣūrī (–September or October 1310) was the viceroy of the Mamluk sultan al-Nasir Muhammad during the latter's second reign (1299–1310). As a boy he was taken captive at the Battle of Elbistan in 1277 and became a mamluk (slave soldier) of the emir al-Salih Ali and eleven years later by the latter's father Sultan Qalawun. Salar distinguished himself in his training as a skilled horseman among other mamluks of the Mansuriyya faction (mamluks of Qalawun). He was promoted to the rank of ''ustadar'' (majordomo) by his friend, Sultan Lajin in 1299. After participating in Lajin's assassination later that year he effectively became the strongman of the sultanate alongside Baybars al-Jashnakir. Despite tensions and incidents between their respective factions, Salar and Baybars avoided direct conflict throughout their power-sharing arrangement. Salar continued as viceroy when Baybars acceded as sultan in 1309 after al-Nasir Muhammad stepped down and exiled him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Nasir Muhammad
Al-Malik an-Nasir Nasir ad-Din Muhammad ibn Qalawun ( ar, الملك الناصر ناصر الدين محمد بن قلاوون), commonly known as an-Nasir Muhammad ( ar, الناصر محمد), or by his kunya: Abu al-Ma'ali () or as Ibn Qalawun (1285–1341) was the ninth Bahri Mamluk sultan of Egypt who ruled between 1293–1294, 1299–1309, and 1310 until his death in 1341. During his first reign he was dominated by Kitbugha and al-Shuja‘i, while during his second reign he was dominated by Baibars and Salar. Not wanting to be dominated or deprived of his full rights as a sultan by his third reign, an-Nasir executed Baibars and accepted the resignation of Salar as vice Sultan. An-Nasir was known to appoint non-Mamluks loyal to himself to senior military positions and remove capable officers of their duty whose loyalty he doubted. Although, he did annul taxes and surcharges that were imposed on commoners for the benefit of the emirs and officials. Also, he employ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats in Western Mongolia as well as the Buryats and Kalmyks of Russia are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The ancestors of the modern-day Mongols are referred to as Proto-Mongols. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyk people and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Baarins, Chahars, Eastern Dorbets, Gorlos Mongols, Jalaids, Jaruud, Kharchins, Khishig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asyut
AsyutAlso spelled ''Assiout'' or ''Assiut'' ( ar, أسيوط ' , from ' ) is the capital of the modern Asyut Governorate in Egypt. It was built close to the ancient city of the same name, which is situated nearby. The modern city is located at , while the ancient city is located at . The city is home to one of the largest Coptic Catholic churches in the country. History Names and etymology The name of the city is derived from early Egyptian Zawty (''Z3JW.TJ'') (late Egyptian, Səyáwt) adopted into the Coptic as Syowt , which means "''Guardian''" of the northern approach of Upper Egypt. In Graeco-Roman Egypt, it was called Lycopolis or Lykopolis ( el, Λυκόπολις, ""), ('wolf city') Lycon, or Lyco. Ancient Asyut Ancient Asyut was the capital of the Thirteenth Nome of Upper Egypt (''Lycopolites Nome'') around 3100 BC. It was located on the western bank of the Nile. The two most prominent gods of ancient Egyptian Asyut were Anubis and Wepwawet, both funerary deit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanjar Al-Jawli
Sanjar ibn Abdullah Alam al-Din Abu Sa'id al-Jawli (also spelled Sangar al-Gawli, Sanjar al-Jawali or Sinjar al-Jawili, 1255–14 January 1345) was a powerful Mamluk ''emir'' and the Governor of Gaza and much of Palestine between 1311–20 during the sultanate of an-Nasir Muhammad and then again for a brief time in 1342 during the reign of the latter's son as-Salih Ismail. Prior to his first term as governor, al-Jawli briefly served as the Emir of Shawbak in Transjordan and before his second term as Gaza's governor, he was appointed Governor of Hama for three months. During his rule he engaged in several construction projects throughout Palestine, particularly in Gaza. The latter was transformed from a small and politically insignificant town to a major and prosperous city under his leadership. Following his appointment as Superintendent of the Maristan in Cairo in 1344, al-Jawli successfully quashed a rebellion by Ismail's brother an-Nasir Ahmad in Karak. Afterward, he focused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burji Dynasty
The Burji or Circassian Mamluk ( ar, المماليك الشركس) dynasty of Circassian origin, ruled Egypt from 1382 until 1517, during the Mamluk Sultanate. The Circassian community in Cairo especially flourished during this time. Political power-plays often became important in designating a new sultan. During this time Mamluks fought Timur and conquered Cyprus. Constant bickering may have contributed to the ability of the Ottomans to challenge them. Their name means 'of the tower', referring to them ruling from the Citadel east of Cairo. History From 1250, Egypt had been ruled by the first Mamluk dynasty, the mostly Cuman- Kipchak Turkic Bahri dynasty. In 1377 a revolt broke out in Syria which spread to Egypt, and the government was taken over by the Circassians Barakah and Barquq; Barquq was proclaimed ''sultan'' in 1382, ending the Bahri dynasty. He was expelled in 1389 but recaptured Cairo in 1390. Early on, the Zahiri Revolt threatened to overthrow Barquq though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia in the North Caucasus. As a consequence of the Circassian genocide, which was perpetrated by the Russian Empire in the 19th century during the Russo-Circassian War, most Circassians were exiled from their homeland in Circassia to modern-day Turkey and the rest of the Middle East, where the majority of them are concentrated today. The Unrepresented Nations and Peoples Organization estimated in the early 1990s that there are as many as 3.7 million Circassians in diaspora in over 50 countries. The Circassian language is the ancestral language of the Circassian people, and Islam has been the dominant religion among them since the 17th century. Circassia has been subject to repeated invasions since ancient times; its isolated terrain coupled wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salihiyya
Salihiyya ( so, Saalixiya; Urwayniya, ar, الصالحية) is a ''tariqa'' (order) of Sufi Islam prevalent in Somalia and the adjacent Somali region of Ethiopia. It was founded in the Sudan by Sayyid Muhammad Salih (1854-1919). The order is characterized by a puritanism typical of other revivalist movements. History The order ultimately traces its origins back to the Sufi scholar of Moroccan origin Ahmad ibn Idris al-Fasi (1760-1837). His followers and students spread al-Fasi's teachings across the globe. Among his students was Ibrahim ibn Salih ibn ‘Abd al-Rahman al-Duwayhi (1813-1874), known as al-Rashid. In his native Sudan, al-Rashid popularized the teachings of al-Fasi, eventually establishing his own ''tariqa'', the Rashidiyya. Having been at al-Fasi's side when he died, al-Rashid was recognized as the successor to his teacher, and the Rashidiyya found many followers in Mecca. His nephew, Sayyid Muhammad Salih, was one of them; he spread the Rashidiyya to the Sud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Maqrizi
Al-Maqrīzī or Maḳrīzī (Arabic: ), whose full name was Taqī al-Dīn Abū al-'Abbās Aḥmad ibn 'Alī ibn 'Abd al-Qādir ibn Muḥammad al-Maqrīzī (Arabic: ) (1364–1442) was a medieval Egyptian Arab historian during the Mamluk era, known for his interest in the Fatimid dynasty and its role in Egyptian history. Life A direct student of Ibn Khaldun, Al-Maqrīzī was born in Cairo and spent most of his life in Egypt. When he presents himself in his books he usually stops at the 10th forefather although he confessed to some of his close friends that he can trace his ancestry to Al-Mu‘izz li-Dīn Allāh – first Fatimid caliph in Egypt and the founder of al-Qahirah – and even to Ali ibn Abi Talib. He was trained in the Hanafite school of law. Later, he switched to the Shafi'ite school and finally to the Zahirite school. Maqrizi studied theology under one of the primary masterminds behind the Zahiri Revolt, and his vocal support and sympathy with that revolt against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
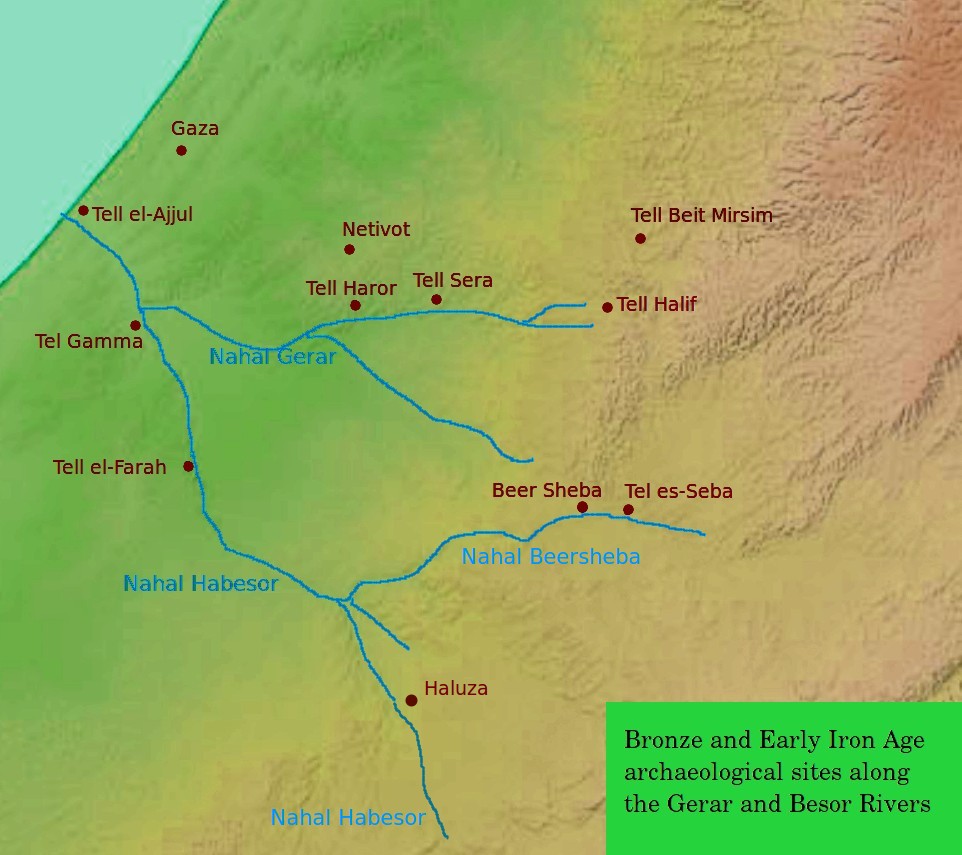
Gaza City
Gaza (;''The New Oxford Dictionary of English'' (1998), , p. 761 "Gaza Strip /'gɑːzə/ a strip of territory in Palestine, on the SE Mediterranean coast including the town of Gaza...". ar, غَزَّة ', ), also referred to as Gaza City, is a Palestinian city in the Gaza Strip, with a population of 590,481 (in 2017), making it the largest city in the State of Palestine. Inhabited since at least the 15th century BCE, Gaza has been dominated by several different peoples and empires throughout its history. The Philistines made it a part of their pentapolis after the Ancient Egyptians had ruled it for nearly 350 years. Under the Roman Empire Gaza experienced relative peace and its port flourished. In 635 CE, it became the first city in Palestine to be conquered by the Muslim Rashidun army and quickly developed into a center of Islamic law. However, by the time the Crusaders invaded the country starting in 1099, Gaza was in ruins. In later centuries, Gaza experienced several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Al-Ajjul
Tall al-Ajjul or Tell el-'Ajul is an archaeological mound or '' tell'' in the Gaza Strip. The fortified city excavated at the site dates as far back as ca. 2000-1800 BCE and was inhabited during the Bronze Age. It is located at the mouth of Wadi Ghazzah just south of the town of Gaza. History Bronze Age Archaeologists have excavated remains dated mainly to the Middle and Late Bronze Age. Middle Bronze In the MBII, Tell el-Ajjul was an important city in the Southern Levant. In the MBIIB, Tell el-Ajjul had the largest number of Egyptian Second Intermediate Period imports. Late Bronze Large quantities of pumice were deposited during the Late Bronze Age, which may have been caused by the Thera (Santorini) volcanic eruption. If proven correct, this would offer a good correlation and dating tool. Treaty of Tell Ajul (1229) The Sixth Crusade came to an end with the so-called Treaty of Jaffa and Tell Ajul. These were in fact two different treaties, the first being the one signe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitbugha
Kitbuqa Noyan (died 1260), also spelled Kitbogha, Kitboga, or Ketbugha, was an Eastern Christian of the Naimans, a group that was subservient to the Mongol Empire. He was a lieutenant and confidant of the Mongol Ilkhan Hulagu, assisting him in his conquests in the Middle East and massive destruction of Baghdad and massacre of innocent citizens. When Hulagu took the bulk of his forces back with him to attend a ceremony in Mongolia, Kitbuqa was left in control of Syria, and was responsible for further Mongol raids southwards towards the Mamluk Sultanate based in Cairo. He was killed at the Battle of Ain Jalut in 1260. Biography In 1252, Möngke Khan ordered Kitbuqa to lead the advance guard of Hulagu Khan's army against the fortresses of the Nizari Ismailis. He advanced with Hulagu into western Persia, mounting a series of sieges, and commanded one of the flanks that sacked Baghdad in 1258 before assisting in the conquest of Damascus in 1260. Historical accounts, quoting fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestine (region)
Palestine ( el, Παλαιστίνη, ; la, Palaestina; ar, فلسطين, , , ; he, פלשתינה, ) is a geographic region in Western Asia. It is usually considered to include Israel and the State of Palestine (i.e. West Bank and Gaza Strip), though some definitions also include part of northwestern Jordan. The first written records to attest the name of the region were those of the Twentieth dynasty of Egypt, which used the term "Peleset" in reference to the neighboring people or land. In the 8th century, Assyrian inscriptions refer to the region of "Palashtu" or "Pilistu". In the Hellenistic period, these names were carried over into Greek, appearing in the Histories of Herodotus in the more recognizable form of "Palaistine". The Roman Empire initially used other terms for the region, such as Judaea, but renamed the region Syria Palaestina after the Bar Kokhba revolt. During the Byzantine period, the region was split into the provinces of Palaestina Prima, Palaestin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_DSCF2920.jpg)





.jpeg)
