|
Saul Sternberg
Saul Sternberg is a Professor Emeritus of Psychology and former Paul C. Williams Term Professor (1993–1998) at the University of Pennsylvania. He is a pioneer in the field of cognitive psychology in the development of experimental techniques to study human information processing. Sternberg received a B.A. in mathematics in 1954 from Swarthmore College and a PhD in social psychology from Harvard University in 1959. He completed a postdoctoral fellowship in mathematical statistics at the University of Cambridge in 1960, and he subsequently worked as a research scientist in the linguistics and artificial intelligence research department at Bell Laboratories, where he continued to work as a member of the technical staff for over twenty years. Sternberg's first academic position was at the University of Pennsylvania, where he was employed from 1961–1964, and where he has remained since 1985. He has also served as a visiting professor at University College, London, the Univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Professor Emeritus
''Emeritus'' (; female: ''emerita'') is an adjective used to designate a retired chair, professor, pastor, bishop, pope, director, president, prime minister, rabbi, emperor, or other person who has been "permitted to retain as an honorary title the rank of the last office held". In some cases, the term is conferred automatically upon all persons who retire at a given rank, but in others, it remains a mark of distinguished service awarded selectively on retirement. It is also used when a person of distinction in a profession retires or hands over the position, enabling their former rank to be retained in their title, e.g., "professor emeritus". The term ''emeritus'' does not necessarily signify that a person has relinquished all the duties of their former position, and they may continue to exercise some of them. In the description of deceased professors emeritus listed at U.S. universities, the title ''emeritus'' is replaced by indicating the years of their appointmentsThe Proto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University College, London
, mottoeng = Let all come who by merit deserve the most reward , established = , type = Public research university , endowment = £143 million (2020) , budget = £1.544 billion (2019/20) , chancellor = Anne, Princess Royal(as Chancellor of the University of London) , provost = Michael Spence , head_label = Chair of the council , head = Victor L. L. Chu , free_label = Visitor , free = Sir Geoffrey Vos , academic_staff = 9,100 (2020/21) , administrative_staff = 5,855 (2020/21) , students = () , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , coordinates = , campus = Urban , city = London, England , affiliations = , colours = Purple and blue celeste , nickname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Missing (living People)
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calenda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
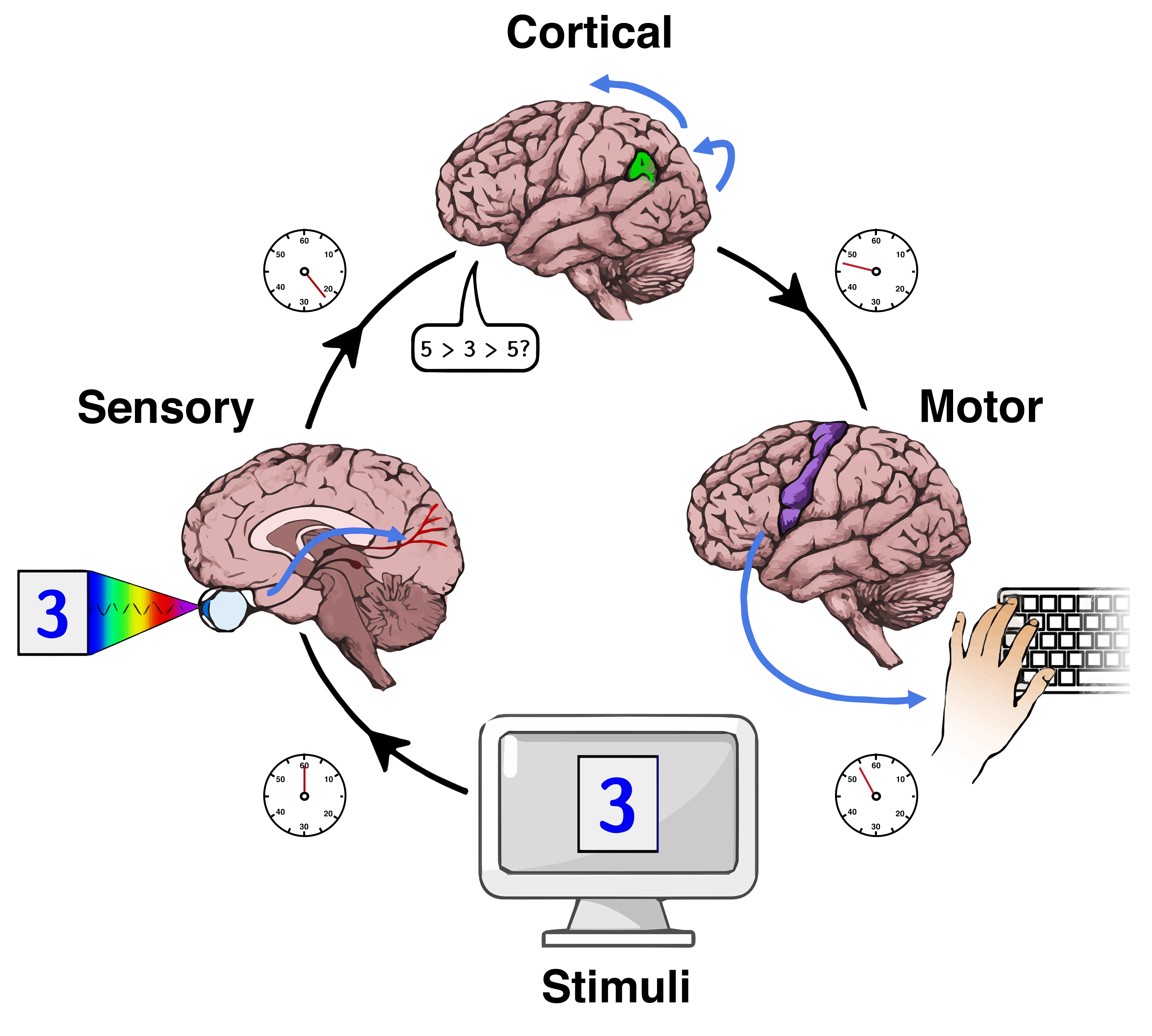
Serial Memory Processing
Serial memory processing is the act of attending to and processing one item at a time. This is usually contrasted against parallel memory processing, which is the act of attending to and processing all items simultaneously. In short-term memory tasks, participants are given a set of items (e.g. letters, digits) one at a time and then, after varying periods of delay, are asked for recall of the items. As well, participants could be asked whether a specific target item was present in their original set. The serial order of items and the relationships between them can have varying effects on the item's speed and accuracy of recall.Townsend, J. & Fific, M. (2004). Parallel versus serial processing and individual differences in high-speed search in human memory. ''Perception & Psychophysics, 66''(6). Overview Serial memory processing uses internal representations of the memory set in order to compare them to a target stimulus or item that is being presented. These internal representation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Model
A cognitive model is an approximation of one or more cognitive processes in humans or other animals for the purposes of comprehension and prediction. There are many types of cognitive models, and they can range from box-and-arrow diagrams to a set of equations to software programs that interact with the same tools that humans use to complete tasks (e.g., computer mouse and keyboard). Relationship to cognitive architectures Cognitive models can be developed within or without a cognitive architecture, though the two are not always easily distinguishable. In contrast to cognitive architectures, cognitive models tend to be focused on a single cognitive phenomenon or process (e.g., list learning), how two or more processes interact (e.g., visual search bsc1780 decision making), or making behavioral predictions for a specific task or tool (e.g., how instituting a new software package will affect productivity). Cognitive architectures tend to be focused on the structural properties of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Time
Mental chronometry is the scientific study of processing speed or reaction time on cognitive tasks to infer the content, duration, and temporal sequencing of mental operations. Reaction time (RT; sometimes referred to as "response time") is measured by the elapsed time between stimulus onset and an individual's response on elementary cognitive tasks (ETCs), which are relatively simple perceptual-motor tasks typically administered in a laboratory setting. Mental chronometry is one of the core methodological paradigms of human experimental, cognitive, and differential psychology, but is also commonly analyzed in psychophysiology, cognitive neuroscience, and behavioral neuroscience to help elucidate the biological mechanisms underlying perception, attention, and decision-making in humans and other species. Mental chronometry uses measurements of elapsed time between sensory stimulus onsets and subsequent behavioral responses to study the time course of information processing in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Additive Factor Method
Additive may refer to: Mathematics * Additive function, a function in number theory * Additive map, a function that preserves the addition operation * Additive set-functionn see Sigma additivity * Additive category, a preadditive category with finite biproducts * Additive inverse, an arithmetic concept Science * Additive color, as opposed to subtractive color * Additive model, a statistical regression model * Additive synthesis, an audio synthesis technique * Additive genetic effects * Additive quantity, a physical quantity that is additive for subsystems; see Intensive and extensive properties Engineering * Feed additive * Gasoline additive, a substance used to improve the performance of a fuel, lower emissions or clean the engine * Oil additive, a substance used to improve the performance of a lubricant * Weakly additive, the quality of preferences in some logistics problems * Polymer additive * Pit additive, a material aiming to reduce fecal sludge build-up and control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States National Academy Of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the National Academy of Medicine (NAM). As a national academy, new members of the organization are elected annually by current members, based on their distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. Election to the National Academy is one of the highest honors in the scientific field. Members of the National Academy of Sciences serve '' pro bono'' as "advisers to the nation" on science, engineering, and medicine. The group holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Founded in 1863 as a result of an Act of Congress that was approved by Abraham Lincoln, the NAS is charged with "providing independent, objective advice to the nation on matters related to science and technology. ... to provide sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Association For The Advancement Of Science
The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) is an American international non-profit organization with the stated goals of promoting cooperation among scientists, defending scientific freedom, encouraging scientific responsibility, and supporting scientific education and science outreach for the betterment of all humanity. It is the world's largest general scientific society, with over 120,000 members, and is the publisher of the well-known scientific journal ''Science''. History Creation The American Association for the Advancement of Science was created on September 20, 1848, at the Academy of Natural Sciences in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was a reformation of the Association of American Geologists and Naturalists. The society chose William Charles Redfield as their first president because he had proposed the most comprehensive plans for the organization. According to the first constitution which was agreed to at the September 20 meeting, the goal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Of Experimental Psychologists
The Society of Experimental Psychologists (SEP), originally called the Society of Experimentalists, is an academic society for experimental psychologists An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a .... It was founded by Edward Bradford Titchener in 1904 to be an ongoing workshop in which members could visit labs, study apparatus, and hear and comment on reports of ongoing research. Upon Titchener’s death in 1927 the club was reorganized and renamed the Society of Experimental Psychologists. The object of the society is “To advance psychology by arranging informal conferences on experimental psychology.” The SEP meets annually to conduct plenary sessions in which members can present papers. It holds meetings every spring, scheduled by a member at the host university who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Association For Psychological Science
The Association for Psychological Science (APS), previously the American Psychological Society, is an international non-profit organization whose mission is to promote, protect, and advance the interests of scientifically oriented psychology in research, application, teaching, and the improvement of human welfare. APS publishes several journals, holds an annual meeting, disseminates psychological science research findings to the general public, and works with policymakers to strengthen support for scientific psychology. History APS was founded in 1988 by a group of researchers and scientifically-oriented practitioners who were interested in advancing scientific psychology and its representation at the national and international level. This group felt that the American Psychological Association (APA) was not adequately supporting scientific research because it focused on the practitioner/clinician side of psychology, and had effectively "become a guild". Tensions between the scien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |