|
Saturnia Cephalariae
Saturnia () is a spa town in Tuscany in north-central Italy that has been inhabited since ancient times. It is a ''frazione'' of the ''comune'' of Manciano, in the province of Grosseto. Famous for the spa which gives it its name, its population is 280. Geography It lies about from Manciano, from Grosseto, northeast of Orbetello and the coast and from Rome. Near the village, 800 L/s of sulphurous water at 37 °C gushes over a waterfall and down into a cascade of natural pools formed by the deposition of calcareous rock from evaporation of the water. History Saturnia, which until 30BC was known as ''Aurinia'', takes its name from the Roman god Saturn (or Saturnus). Legend has it that he grew tired of the constant wars of humans, and sent a thunderbolt to earth that created a magic spring of warm sulphurous water which would pacify mankind. Dionysius of Halicarnassus lists Saturnia as one of the towns first occupied by the Pelasgi and then by the Etruscan civil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
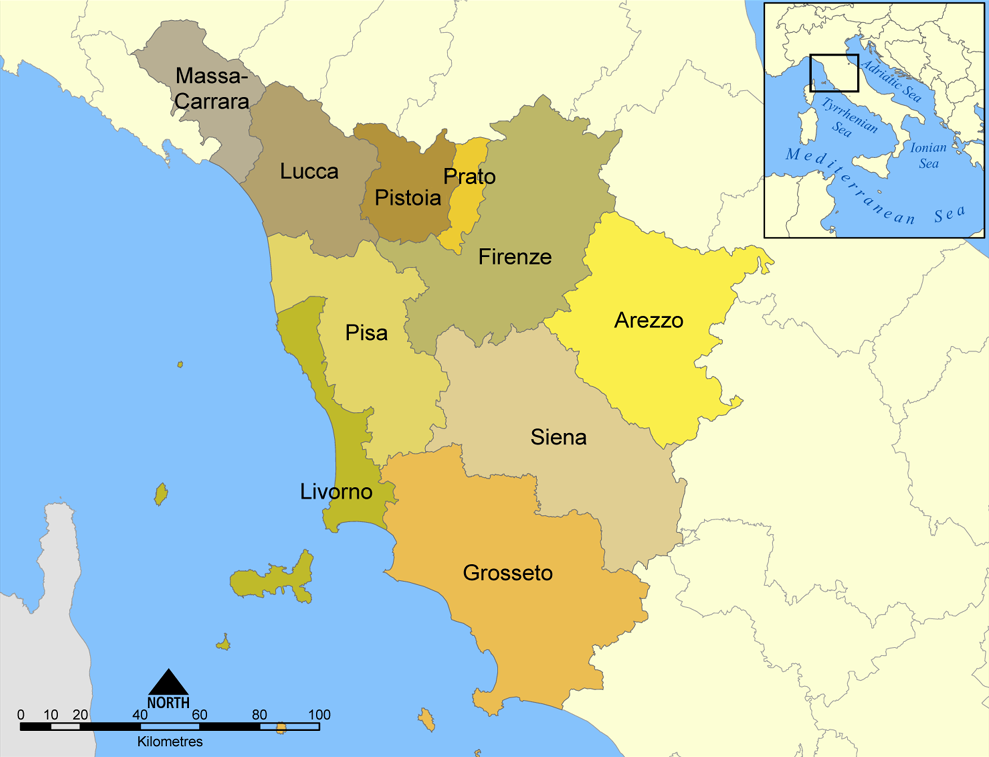
Province Of Grosseto
The province of Grosseto ( it, links=no, provincia di Grosseto) is a province in the Tuscany region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Grosseto. As of 2013 the province had a total population of 225,098 people. Geography The Province of Grosseto completely occupies the southern end of Tuscany, and with a territorial area of , it is the most extensive in the region and one of the least dense in population in Italy. The province is bordered to the northwest by the Province of Livorno, to the north by the Province of Pisa, to the northeast by the Province of Siena, and to the southeast by the Province of Viterbo in Lazio. To the south is the Tyrrhenian Sea, which includes the southern islands of the Tuscan archipelago, including Isola del Giglio and the smaller Giannutri islands and Formiche di Grosseto and Formica di Burano. The Arcipelago Toscano National Park spans both the provinces of Grosseto and Livorno, and includes the seven main islands of the Tuscan Archipelago: Elba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Wall
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates for access to the city. From ancient to modern times, they were used to enclose settlements. Generally, these are referred to as city walls or town walls, although there were also walls, such as the Great Wall of China, Walls of Benin, Hadrian's Wall, Anastasian Wall, and the Atlantic Wall, which extended far beyond the borders of a city and were used to enclose regions or mark territorial boundaries. In mountainous terrain, defensive walls such as ''letzis'' were used in combination with castles to seal valleys from potential attack. Beyond their defensive utility, many walls also had important symbolic functions representing the status and independence of the communities they embraced. Existing ancient walls are almost always masonry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poggio Capanne
Poggio Capanne is a village in Tuscany, central Italy, administratively a frazione of the comune of Manciano, province of Grosseto. At the time of the 2001 census its population amounted to 101. Geography Poggio Capanne is about 60 km from Grosseto and 18 km from Manciano, and it is situated along the Provincial Road which links Montemerano to Sovana, at the top of a small hill ("''poggio''") in the valley of Albegna. History The village, formerly known as ''Capanne di Saturnia'' and then just as ''Capanne'', was born in the 15th century as a rural hamlet of shepherds and farmers dependent on the town of Saturnia.Capanne Manciano official website. Main sights * Church of ''Visitazione di Maria'' (16th century), main parish church of the village, it was built in 1570.[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poderi Di Montemerano
Poderi di Montemerano is a village in Tuscany, central Italy, administratively a frazione of the comune of Manciano, province of Grosseto. At the time of the 2001 census its population amounted to 84. Poderi di Montemerano is about 50 km from Grosseto and 4 km from Manciano, and it is situated along the Provincial Road which links Scansano to Manciano, at the foot of the hill of Montemerano.Poderi di Montemerano Tourism in Manciano. The village was born in the late 16th century as ''Poderi di Sotto'', and it significantly developed in the 18th century.Poderi di Montemerano Manciano official ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montemerano
Montemerano is a village in Tuscany, central Italy, administratively a frazione of the comune of Manciano, province of Grosseto. At the time of the 2001 census its population amounted to 438. Geography Montemerano is about 48 km from Grosseto and 6 km from Manciano, and it is situated on a hill along the Provincial Road which links Scansano to Manciano. History The village dates back to the Middle Ages, when it was a property of the Aldobrandeschi family (13th century) and then of the Baschi from Orvieto (14th century). It was then conquered by the Republic of Siena during the 15th century. Emanuele Repetti, Montemerano», ''Dizionario Geografico Fisico Storico della Toscana'', 1833-1846. Main sights * ''San Giorgio'' (14th century), main parish church of the village, it was built by the Baschi and expanded in 1430. It was restored in 1980. The church contains a ''Madonna in trono col Bambino e santi'' by Sano di Pietro (15th century) and the curious ''Madonna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsiliana
Marsiliana, known also as Marsiliana d'Albegna, is a village in Tuscany, central Italy, administratively a frazione of the comune of Manciano, province of Grosseto. At the time of the 2001 census its population amounted to 246. Geography Marsiliana is about 40 km from Grosseto and 18 km from Manciano. It is situated in southern Maremma, along the ''Maremmana'' Regional Road halfway between Manciano and the Tyrrhenian Sea at Albinia. The old centre of Marsiliana is situated on the top of a hill overlooking the river Albegna. History The territory of Marsiliana is known for the presence of Etruscan archaeological sites: the most important one is the area of ''Banditella'', where a necropolis of more than one hundred tombs (8th-6th century BC) was discovered in 1908. The village developed at the foot of the hill after the ''Riforma fondiaria'' (land reform) in the 1950s. Buildings * ''Maria Regina del Mondo'', main parish church of the village, it was built in 1959 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldobrandeschi Family
The Aldobrandeschi were an Italian noble family from southern Tuscany. Overview Of probable Lombard origin, they appear in history as counts in the 9th century. The first known count was Hildebrand II (857). Their possession extended to what is now southern Tuscany and northern Lazio regions of Italy. In 1274, their lands were divided between the County of Santa Fiora and the County of Sovana, which thenceforth were ruled by different branches of the family. After the extinction of the Aldobrandeschi of Sovana, the county was assigned to the Orsini. The Aldobrandeschi heiress of Santa Fiora married into the Sforza family. The most famous members were: Guglielmo Aldobrandeschi, who lived in the 13th century and is cited by Dante Alighieri as the ''Gran Tosco'' ("Grand Tuscan"); Guglielmo's son is also cited in Canto XI of the ''Purgatorio'' in the '' Divine Comedy'' as an example of a sinner of pride; and Margherita, the last of the Aldobrandeschi of Sovana, who married ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
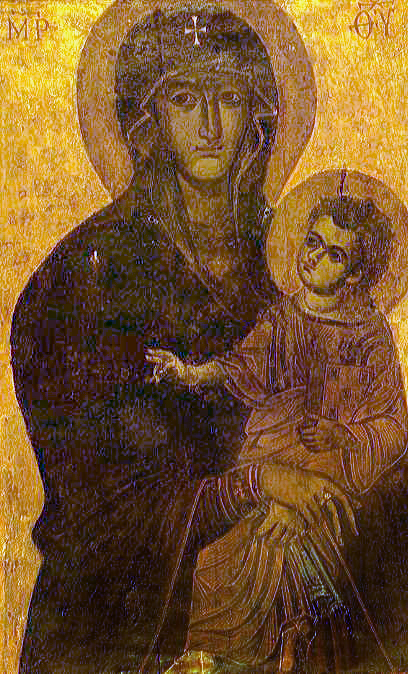
Benvenuto Di Giovanni
Benvenuto di Giovanni, also known as Benvenuto di Giovanni di Meo del Guasta (13 September 1436 – c. 1518) was an Italian painter and artist known for his choral miniatures, pavement designs, and frescoes. Working chiefly in Siena, he was first recognized to be working as an artist in 1453 and continued his work nearly until his death in approximately 1518. During his lifetime, he was influenced by many various artists and in the 1480s, Benvenuto's style changed drastically. Though Benvenuto did explore into other fields of work, painting was consistently a part of his life. His son, Girolamo di Giovanni, followed in his footsteps and also became a painter. In fact, there have often been instances in which the work of one the two has been confused for that of the other. Nevertheless, Benvenuto left behind significantly more works. Some of his works were both signed and dated, some were only signed, and some were only dated. However, regardless of debate over date or authorship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madonna And Child
In art, a Madonna () is a representation of Mary, either alone or with her child Jesus. These images are central icons for both the Catholic and Orthodox churches. The word is (archaic). The Madonna and Child type is very prevalent in Christian iconography, divided into many traditional subtypes especially in Eastern Orthodox iconography, often known after the location of a notable icon of the type, such as the ''Theotokos of Vladimir'', ''Agiosoritissa'', ''Blachernitissa'', etc., or descriptive of the depicted posture, as in ''Hodegetria'', ''Eleusa'', etc. The term ''Madonna'' in the sense of "picture or statue of the Virgin Mary" enters English usage in the 17th century, primarily in reference to works of the Italian Renaissance. In an Eastern Orthodox context, such images are typically known as '' Theotokos''. "Madonna" may be generally used of representations of Mary, with or without the infant Jesus, is the focus and central figure of the image, possibly flanke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
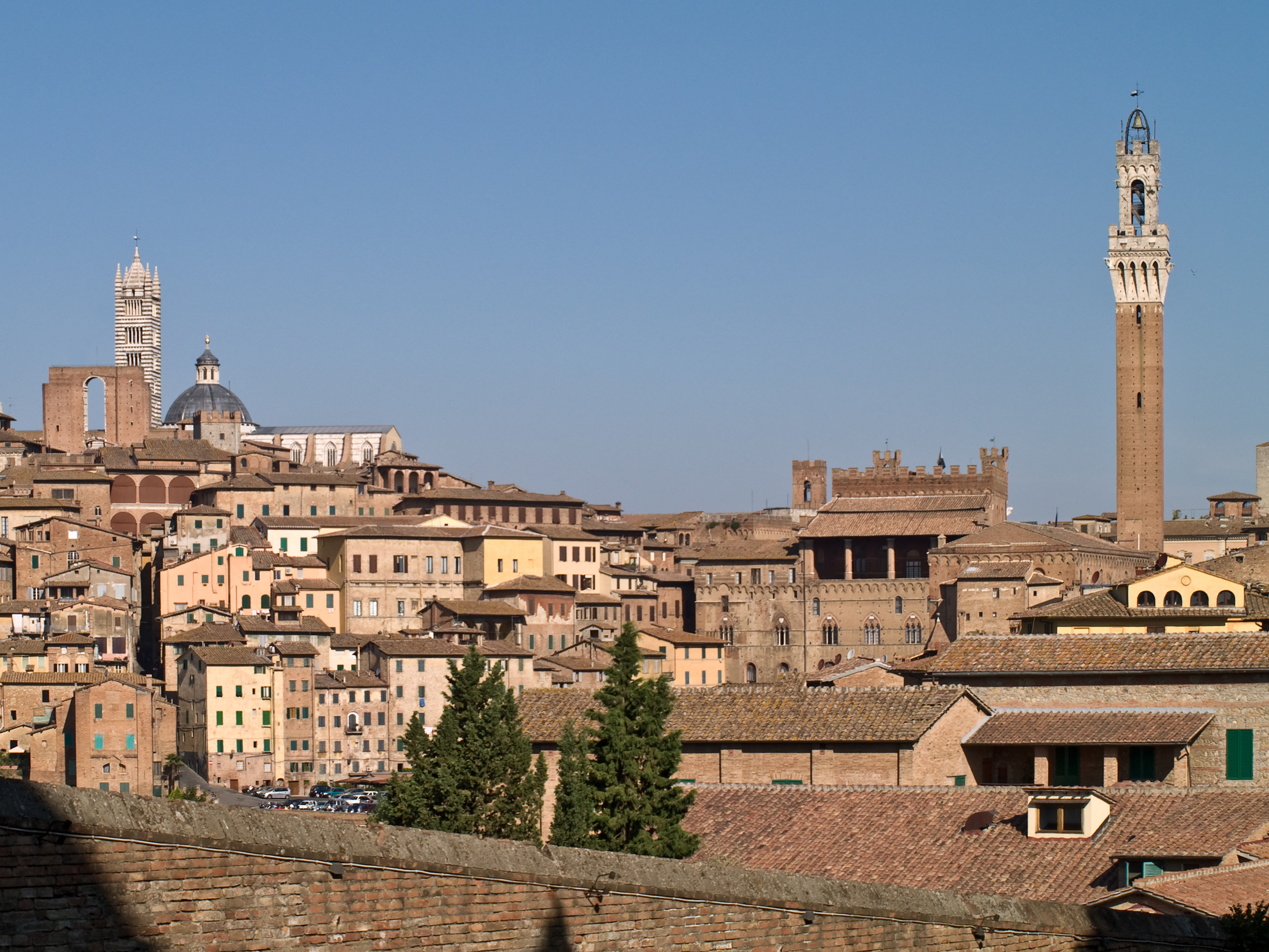
Sienese
Siena ( , ; lat, Sena Iulia) is a city in Tuscany, Italy. It is the capital of the province of Siena. The city is historically linked to commercial and banking activities, having been a major banking center until the 13th and 14th centuries. Siena is also home to the oldest bank in the world, the Monte dei Paschi bank, which has been operating continuously since 1472. Several significant Renaissance painters worked and were born in Siena, among them Duccio, Ambrogio Lorenzetti, Simone Martini and Sassetta, and influenced the course of Italian and European art. The University of Siena, originally called ''Studium Senese'', was founded in 1240, making it one of the oldest universities in continuous operation in the world. Siena was one of the most important cities in medieval Europe, and its historic centre is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. From January until the end of September of 2021 it had about 217,000 arrivals, with the largest numbers of foreign visitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalith
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea. The word was first used in 1849 by the British antiquarian Algernon Herbert in reference to Stonehenge and derives from the Ancient Greek words "mega" for great and " lithos" for stone. Most extant megaliths were erected between the Neolithic period (although earlier Mesolithic examples are known) through the Chalcolithic period and into the Bronze Age. At that time, the beliefs that developed were dynamism and animism, because Indonesia experienced the megalithic age or the great stone age in 2100 to 4000 BC. So that humans ancient tribe worship certain objects that are considered to have supernatural powers. Some relics of the megalithic era are menhirs (stone monuments) and dolmens (stone tables). Types and definitions While "megalith" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |