|
Satellite Glial Cell
Satellite glial cells, formerly called amphicytes, are glial cells that cover the surface of neuron Soma (biology), cell bodies in Ganglion, ganglia of the peripheral nervous system. Thus, they are found in Dorsal root ganglion, sensory, Sympathetic ganglion, sympathetic, and Parasympathetic ganglion, parasympathetic ganglia. Both satellite glial cells (SGCs) and Schwann cells (the cells that ensheathe some axon, nerve fibers in the PNS) are derived from the neural crest of the embryo during development. SGCs have been found to play a variety of roles, including control over the microenvironment of sympathetic ganglia. They are thought to have a similar role to astrocytes in the central nervous system (CNS). They supply nutrients to the surrounding neurons and also have some structural function. Satellite cells also act as protective, cushioning cells. Additionally, they express a variety of receptors that allow for a range of interactions with neuroactive chemicals. Many of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit. A typical neuron consists of a cell body (soma), dendrites, and a single axon. The soma is a compact structure, and the axon and dend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
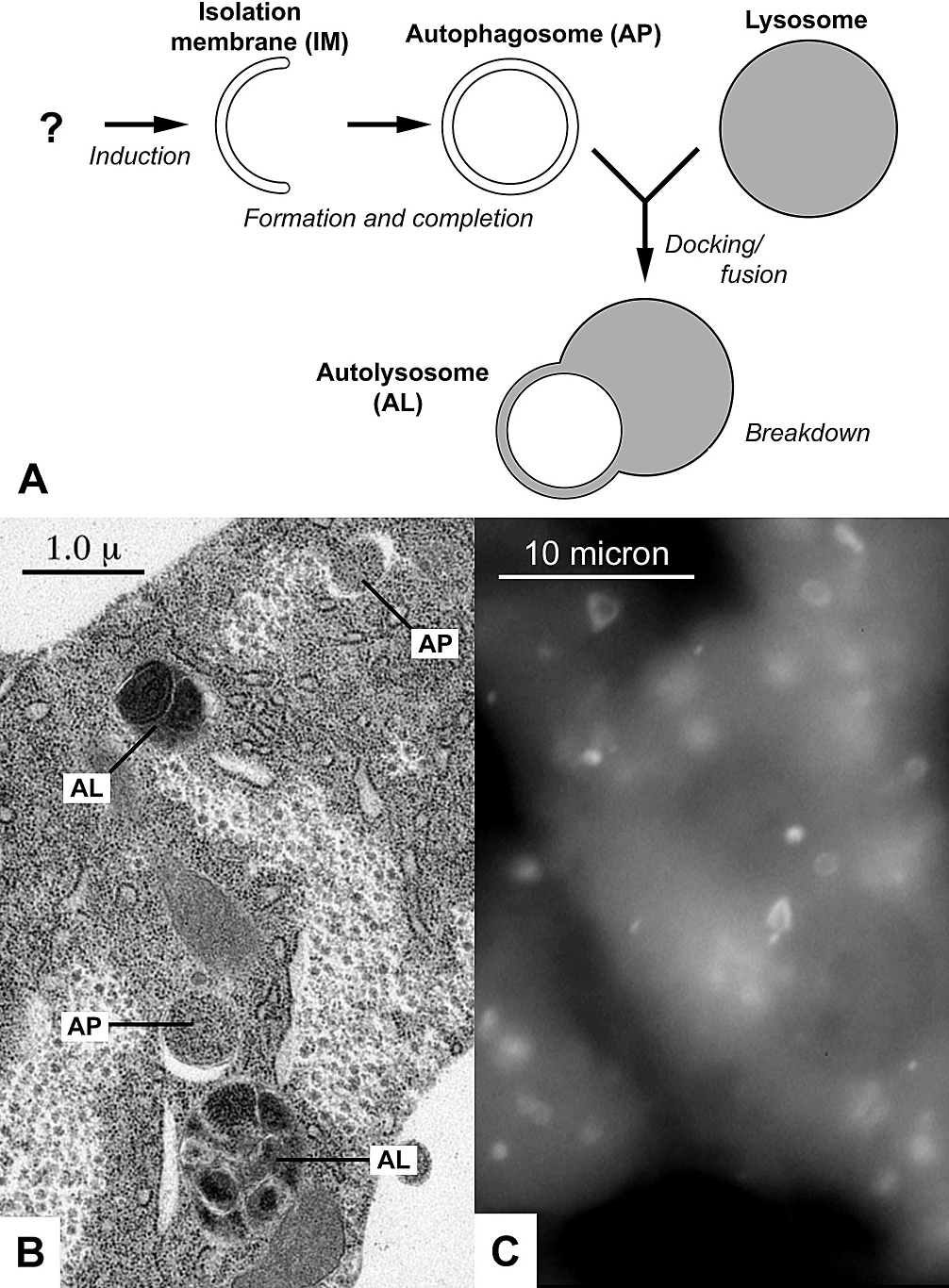
Autophagy
Autophagy (or autophagocytosis; from the Ancient Greek , , meaning "self-devouring" and , , meaning "hollow") is the natural, conserved degradation of the cell that removes unnecessary or dysfunctional components through a lysosome-dependent regulated mechanism. It allows the orderly degradation and recycling of cellular components. Although initially characterized as a primordial degradation pathway induced to protect against starvation, it has become increasingly clear that autophagy also plays a major role in the homeostasis of non-starved cells. Defects in autophagy have been linked to various human diseases, including neurodegeneration and cancer, and interest in modulating autophagy as a potential treatment for these diseases has grown rapidly. Four forms of autophagy have been identified: macroautophagy, microautophagy, chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), and crinophagy. In macroautophagy (the most thoroughly researched form of autophagy), cytoplasmic components (like mit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitochondrion
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used throughout the cell as a source of chemical energy. They were discovered by Albert von Kölliker in 1857 in the voluntary muscles of insects. The term ''mitochondrion'' was coined by Carl Benda in 1898. The mitochondrion is popularly nicknamed the "powerhouse of the cell", a phrase coined by Philip Siekevitz in a 1957 article of the same name. Some cells in some multicellular organisms lack mitochondria (for example, mature mammalian red blood cells). A large number of unicellular organisms, such as microsporidia, parabasalids and diplomonads, have reduced or transformed their mitochondria into other structures. One eukaryote, ''Monocercomonoides'', is known to have completely lost its mitochondria, and one multicellular organism, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centriole
In cell biology a centriole is a cylindrical organelle composed mainly of a protein called tubulin. Centrioles are found in most eukaryotic cells, but are not present in conifers (Pinophyta), flowering plants (angiosperms) and most fungi, and are only present in the male gametes of charophytes, bryophytes, seedless vascular plants, cycads, and ''Ginkgo''. A bound pair of centrioles, surrounded by a highly ordered mass of dense material, called the pericentriolar material (PCM), makes up a structure called a centrosome. Centrioles are typically made up of nine sets of short microtubule triplets, arranged in a cylinder. Deviations from this structure include crabs and ''Drosophila melanogaster'' embryos, with nine doublets, and '' Caenorhabditis elegans'' sperm cells and early embryos, with nine singlets. Additional proteins include centrin, cenexin and tektin. The main function of centrioles is to produce cilia during interphase and the aster and the spindle during cell divis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles inside the cell before the vesicles are sent to their destination. It resides at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. It is of particular importance in processing proteins for secretion, containing a set of glycosylation enzymes that attach various sugar monomers to proteins as the proteins move through the apparatus. It was identified in 1897 by the Italian scientist Camillo Golgi and was named after him in 1898. Discovery Owing to its large size and distinctive structure, the Golgi apparatus was one of the first organelles to be discovered and observed in detail. It was discovered in 1898 by Italian physician Camillo Golgi during an investigation of the nervous system. After first observing it under his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa. The two types of ER share many of the same proteins and engage in certain common activities such as the synthesis of certain lipids and cholesterol. Different types of cells contain different ratios of the two types of ER depending on the activities of the cell. RER is found mainly toward the nucleus of cell and SER towards the cell membrane or plasma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ions across the cell membrane, controlling the flow of ions across secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell volume. Ion channels are present in the membranes of all cells. Ion channels are one of the two classes of ionophoric proteins, the other being ion transporters. The study of ion channels often involves biophysics, electrophysiology, and pharmacology, while using techniques including voltage clamp, patch clamp, immunohistochemistry, X-ray crystallography, fluoroscopy, and RT-PCR. Their classification as molecules is referred to as channelomics. Basic features There are two distinctive features of ion channels that differentiate them from other types of ion transporter proteins: #The rate of ion transport through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell. Neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft where they are able to interact with neurotransmitter receptors on the target cell. The neurotransmitter's effect on the target cell is determined by the receptor it binds. Many neurotransmitters are synthesized from simple and plentiful precursors such as amino acids, which are readily available and often require a small number of biosynthetic steps for conversion. Neurotransmitters are essential to the function of complex neural systems. The exact number of unique neurotransmitters in humans is unknown, but more than 100 have been identified. Common neurotransmitters include glutamate, GABA, acetylcholine, glycine and norepinephrine. Mechanism and cycle Synthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (the extracellular space). The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols (a lipid component) interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles, being selectively permeable to ions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance or cytoplasmic matrix which remains after exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, the plant plastids, lipid droplets, and vacuoles. Most cellular activities take place within the cytoplasm, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long stands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the cell by regulating gene expres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |